Rangelands
... forbs, shrubs, or trees. Common examples of invasive plants in western North America include: cheatgrass, leafy spurge, spotted knapweed, and salt cedar. Invasive plants may persist at relatively insignificant densities for a period of time until ideal conditions occur and then the plant will spread ...
... forbs, shrubs, or trees. Common examples of invasive plants in western North America include: cheatgrass, leafy spurge, spotted knapweed, and salt cedar. Invasive plants may persist at relatively insignificant densities for a period of time until ideal conditions occur and then the plant will spread ...
plants and animals on earth
... So we can see that plants and animals which are living things are dependent on other living things as well as non-living things, in order to survive. A symbiotic relationship is when two organisms of different species i.e. either a plant and an animal, or two different animal species, interact in lo ...
... So we can see that plants and animals which are living things are dependent on other living things as well as non-living things, in order to survive. A symbiotic relationship is when two organisms of different species i.e. either a plant and an animal, or two different animal species, interact in lo ...
Comparative Plant Ecology as a Tool for
... photosynthetic rate (from physiological ecology), seed production (from population ecology), and species’ richness or rates of litter decomposition (from community and ecosystem ecology) can be found intermixed in the same paper. To me, comparative plant ecology is not defined so much by what phenom ...
... photosynthetic rate (from physiological ecology), seed production (from population ecology), and species’ richness or rates of litter decomposition (from community and ecosystem ecology) can be found intermixed in the same paper. To me, comparative plant ecology is not defined so much by what phenom ...
Interactions ecology_-_part_3_-_interactions
... Symbiosis: the relationship between two organisms in which at least one benefits, but the other does not die ...
... Symbiosis: the relationship between two organisms in which at least one benefits, but the other does not die ...
Plants and Animals of the arctic
... ✔ One rag, bandana or cloth for each student, using three different colors for the class, ✔ Arctic Species cards (included) ...
... ✔ One rag, bandana or cloth for each student, using three different colors for the class, ✔ Arctic Species cards (included) ...
Plants and Animals of the arctic
... ✔ One rag, bandana or cloth for each student, using three different colors for the class, ✔ Arctic Species cards (included) ...
... ✔ One rag, bandana or cloth for each student, using three different colors for the class, ✔ Arctic Species cards (included) ...
Symbionts, mutualists, parasites? Plant
... Cyclical formation of arbuscules followed by degradation *may form vesicles ...
... Cyclical formation of arbuscules followed by degradation *may form vesicles ...
WETLAND EXPLORATION: PRAIRIES
... 2. Relate animal structures to their specific survival functions (e.g., obtaining food, escaping or hiding from enemies). 3. Classify animals according to their characteristics (e.g., body coverings and body structure). Grade Four: Diversity and Interdependence of Life 2. Relate plant structures to ...
... 2. Relate animal structures to their specific survival functions (e.g., obtaining food, escaping or hiding from enemies). 3. Classify animals according to their characteristics (e.g., body coverings and body structure). Grade Four: Diversity and Interdependence of Life 2. Relate plant structures to ...
Entire site vocabulary - Maryland Public Television Presents Bayville
... The area where a plant or animal lives, including the land, the climate, and other plants and animals The same in value or amount Upright in posture, perpendicular to the ground The wearing away of land surfaces by wind and water; a natural process in which rocks and soils are broken down by wind an ...
... The area where a plant or animal lives, including the land, the climate, and other plants and animals The same in value or amount Upright in posture, perpendicular to the ground The wearing away of land surfaces by wind and water; a natural process in which rocks and soils are broken down by wind an ...
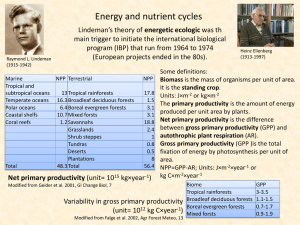
10 kcal/m 2 /year
... for useful work in the next level. Additionally some energy remains at each level. When a caterpillar eats a leaf 50% of the energy stored in the leaf passes out of the body as waste and/or heat 40% is used for the caterpillar to survive Only 10% is used to increase the size of the caterpillar ...
... for useful work in the next level. Additionally some energy remains at each level. When a caterpillar eats a leaf 50% of the energy stored in the leaf passes out of the body as waste and/or heat 40% is used for the caterpillar to survive Only 10% is used to increase the size of the caterpillar ...
Heterotrophic Nutrition
... digestion is sucking or fluid feeding. A wide variety of animals and insects are adapted to take in liquid food, either from plants or animal juices. All spiders use sucking as their digestive means. They inject digestive enzymes into the prey and allow the exoskeleton to contain the juice as intern ...
... digestion is sucking or fluid feeding. A wide variety of animals and insects are adapted to take in liquid food, either from plants or animal juices. All spiders use sucking as their digestive means. They inject digestive enzymes into the prey and allow the exoskeleton to contain the juice as intern ...
Ecology - sciencephs
... Students will be able to demonstrate how energy transfers through food webs Students will be able to define and give examples of producers and consumers ...
... Students will be able to demonstrate how energy transfers through food webs Students will be able to define and give examples of producers and consumers ...
List of key threatening processes of the Greater Blue Mountains
... Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change ...
... Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change Habitat Loss/Change ...
32 - Ecosystem Dynamics
... Dynamics of energy through ecosystems have important implications for human populations how much energy does it take to feed a human? if we are meat eaters? if we are vegetarian? What is your ecological footprint?! ...
... Dynamics of energy through ecosystems have important implications for human populations how much energy does it take to feed a human? if we are meat eaters? if we are vegetarian? What is your ecological footprint?! ...
Taiga Biomes of the Earth
... summarized in a food chain, a flow diagram with arrows pointing from the organism that is eaten to the organisms that eats it. Plants are often the first step, or link, in the chain because they make their own food and other creatures depend upon plants—directly or indirectly—for their food supplies ...
... summarized in a food chain, a flow diagram with arrows pointing from the organism that is eaten to the organisms that eats it. Plants are often the first step, or link, in the chain because they make their own food and other creatures depend upon plants—directly or indirectly—for their food supplies ...
Ecology - Fort Bend ISD
... • A keystone species is a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem. ...
... • A keystone species is a species that has an unusually large effect on its ecosystem. ...
Living and non-living things
... Nutrition (feeding) All living things need energy and nutrients (materials to build and maintain their bodies). The parrot eats seeds, fruits and other plant parts. The mango tree makes food in its leaves. You will learn more about plant and animal nutrition in the ‘Nutrition’ and ‘Plant parts and c ...
... Nutrition (feeding) All living things need energy and nutrients (materials to build and maintain their bodies). The parrot eats seeds, fruits and other plant parts. The mango tree makes food in its leaves. You will learn more about plant and animal nutrition in the ‘Nutrition’ and ‘Plant parts and c ...
More Viruses-Bacteria-Evolution Practice Question 1
... A Correct. Some bacteria are decomposers. Decomposers break down organic materials and return nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur to the soil. Plants need these nutrients in order to grow. Animals, in turn, get these nutrients by eating plants or by eating other animals. B Incorrect. Some ...
... A Correct. Some bacteria are decomposers. Decomposers break down organic materials and return nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur to the soil. Plants need these nutrients in order to grow. Animals, in turn, get these nutrients by eating plants or by eating other animals. B Incorrect. Some ...
Herbivore
_grazing_-_20050809.jpg?width=300)
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material.