Specialty 4R Performance Objectives Comparison Version
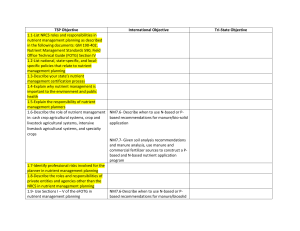
... NM7.7-Given soil analysis recommendations and manure analysis, use manure and commercial fertilizer sources to construct a Pbased and N-based nutrient application program NM7.8-Describe how the following areas are environmentally sensitive: a)surface waters, b) sinkholes, c)direct conduits to ground ...
... NM7.7-Given soil analysis recommendations and manure analysis, use manure and commercial fertilizer sources to construct a Pbased and N-based nutrient application program NM7.8-Describe how the following areas are environmentally sensitive: a)surface waters, b) sinkholes, c)direct conduits to ground ...
Characteristics of Resilient Ecosystems and Strategies for
... they are made up of many parts (trees, small mammals, birds, insects, soils, etc.) and processes (mortality, succession, disturbance cycles, nutrient cycling, species migration, etc.) that interact with one another and their environment over multiple scales of time and space; ...
... they are made up of many parts (trees, small mammals, birds, insects, soils, etc.) and processes (mortality, succession, disturbance cycles, nutrient cycling, species migration, etc.) that interact with one another and their environment over multiple scales of time and space; ...
Ch 13 lecture notes
... All living things (plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, etc.) Products of living things (wood, waste, etc.) Abiotic factors Gases (oxygen, nitrogen) soil Water/ moisture pH Minerals Sunlight Temperature Wind Ecosystem Services Important environmental benefits that ecosystems provide, such as: Clean air ...
... All living things (plants, animals, bacteria, fungi, etc.) Products of living things (wood, waste, etc.) Abiotic factors Gases (oxygen, nitrogen) soil Water/ moisture pH Minerals Sunlight Temperature Wind Ecosystem Services Important environmental benefits that ecosystems provide, such as: Clean air ...
Resource ratios determine nutrient limitation of primary productivity
... red circle in Figure 2 (a), see SI S8 and figure S9). ...
... red circle in Figure 2 (a), see SI S8 and figure S9). ...
Fertilizers & Nutrients
... • Includes granular & slow release fertilizers applied to the growing media. ...
... • Includes granular & slow release fertilizers applied to the growing media. ...
Do we live in a largely top
... large spatial (basin-wide) or temporal (seasonal) scales, higher nutrient supply from physical processes supports higher chlorophyll and meso-zooplankton (millimeter size) concentrations, as well as larger fisheries yields (bottom-up, Ware and Thomson 2005 for a spatial example). As stated in the Int ...
... large spatial (basin-wide) or temporal (seasonal) scales, higher nutrient supply from physical processes supports higher chlorophyll and meso-zooplankton (millimeter size) concentrations, as well as larger fisheries yields (bottom-up, Ware and Thomson 2005 for a spatial example). As stated in the Int ...
Essential Questions: 1) Essential Questions: How do humans have
... 11. I can explain why producers are important to the stability of an ecosystem. 12. I can label the different levels of producers and consumers on a food web. 13. I can identify which trophic level an organism is in. 14. I can explain the direction of energy flow in an energy pyramid. 15. I can expl ...
... 11. I can explain why producers are important to the stability of an ecosystem. 12. I can label the different levels of producers and consumers on a food web. 13. I can identify which trophic level an organism is in. 14. I can explain the direction of energy flow in an energy pyramid. 15. I can expl ...
Soil formation
... lichens manage to penetrate into the rock granules with their microscopic layers ...
... lichens manage to penetrate into the rock granules with their microscopic layers ...
Why is soil important to all living things?
... Background: Soil makes up the outermost layer of our planet and is formed from rocks and decaying plants and animals. Soil is the naturally occurring, loose mineral and/or organic material at the surface of the earth that is capable of supporting plant growth. Soil is synonymous to the word ‘earth’, ...
... Background: Soil makes up the outermost layer of our planet and is formed from rocks and decaying plants and animals. Soil is the naturally occurring, loose mineral and/or organic material at the surface of the earth that is capable of supporting plant growth. Soil is synonymous to the word ‘earth’, ...
Biotic components Submerged plants
... These include heterotrophic microorganisms such as bacteria fungi, which break down the organic complex food from dead producers and consumers into simple inorganic compounds made available to the producers. Pond stratification: On the basis of water depth, light penetration and types of vegetation ...
... These include heterotrophic microorganisms such as bacteria fungi, which break down the organic complex food from dead producers and consumers into simple inorganic compounds made available to the producers. Pond stratification: On the basis of water depth, light penetration and types of vegetation ...
biology i honors capacity matrix unit ix
... The objective of this indicator is to explain how populations are affected by limiting factors; therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be to construct cause-and-effect models of how each limiting factor (including density-dependent, density-independent, abiotic, and biotic factors) can af ...
... The objective of this indicator is to explain how populations are affected by limiting factors; therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be to construct cause-and-effect models of how each limiting factor (including density-dependent, density-independent, abiotic, and biotic factors) can af ...
Ocean Reflux - Horsefly River Roundtable
... journal Science provides a stark warning. The authors of the report, marine biologists Maoz Fine and Dan Tchernov, raised coral specimens in tanks of water with a pH of 7.3, roughly as acidic as the oceans are expected to become sometime in the next century. In response, the hard coral did a vanishi ...
... journal Science provides a stark warning. The authors of the report, marine biologists Maoz Fine and Dan Tchernov, raised coral specimens in tanks of water with a pH of 7.3, roughly as acidic as the oceans are expected to become sometime in the next century. In response, the hard coral did a vanishi ...
1. Write a brief paragraph (3-5 sentences) regarding Yellowstone
... Wolves are the keystone species and apex predator of Yellowstone. Elk are their prey. Wolves are necessary to keep balance in the ecosystem because they keep the elk population down, allowing plants to grow. Plants provide energy to many other organisms, sustaining vital connections in the food web ...
... Wolves are the keystone species and apex predator of Yellowstone. Elk are their prey. Wolves are necessary to keep balance in the ecosystem because they keep the elk population down, allowing plants to grow. Plants provide energy to many other organisms, sustaining vital connections in the food web ...
Small River Communities - North Carolina Wildlife Resources
... sensitive to temperature cues and recent research has shown that many species of freshwater mussels may already be living at the upper thermal tolerances of their early life stages (glochidia and juveniles) (Pandolfo et al. 2010). Extreme temperature events could be especially harmful. These systems ...
... sensitive to temperature cues and recent research has shown that many species of freshwater mussels may already be living at the upper thermal tolerances of their early life stages (glochidia and juveniles) (Pandolfo et al. 2010). Extreme temperature events could be especially harmful. These systems ...
ICS Final Exam Study Guide
... Transpiration- lost of water from a plant through its leaves Nutrients- are all chemical substances that an organism need to sustain life. Nitrogen fixation- is the process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia Denitrification- is the process where soil bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. ...
... Transpiration- lost of water from a plant through its leaves Nutrients- are all chemical substances that an organism need to sustain life. Nitrogen fixation- is the process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia Denitrification- is the process where soil bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen gas. ...
Global Biodiversity Conservation: The Critical Role of Hotspots
... oceans, and climate-driven habitat loss will disrupt ecological processes, test species’ physiological tolerances, turn forests to deserts, and drive desperate human populations toward further environmental degradation (Turner et al. 2010). Extinction is the gravest consequence of the biodiversity c ...
... oceans, and climate-driven habitat loss will disrupt ecological processes, test species’ physiological tolerances, turn forests to deserts, and drive desperate human populations toward further environmental degradation (Turner et al. 2010). Extinction is the gravest consequence of the biodiversity c ...
Organism
... increases the number of different species that can live in an ecosystem. Predators limit the size of prey populations. As a result, food and other resources are less likely to become scarce, and competition between species is reduced. ...
... increases the number of different species that can live in an ecosystem. Predators limit the size of prey populations. As a result, food and other resources are less likely to become scarce, and competition between species is reduced. ...
ABSTRACT THE INFLUENCE OF CURING TIME ON THE BEARING
... additive material that is TX-300, which is expected to improve the characteristics of the soil so the soil is worthy of a construction established. Soil samples that tested in this research is the soft clay are derived from Rawa Sragi, East Lampung. This study used soil mixed with ash content about ...
... additive material that is TX-300, which is expected to improve the characteristics of the soil so the soil is worthy of a construction established. Soil samples that tested in this research is the soft clay are derived from Rawa Sragi, East Lampung. This study used soil mixed with ash content about ...
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 50 An Introduction to
... microorganisms in nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and denitrification. Concept 55.5 Human activities now dominate most chemical cycles on Earth 27. This section looks at human impact on ecosystems. 28. How has agriculture affected nitrogen cycling? What are some negative consequences of nutrient e ...
... microorganisms in nitrogen fixation, nitrification, and denitrification. Concept 55.5 Human activities now dominate most chemical cycles on Earth 27. This section looks at human impact on ecosystems. 28. How has agriculture affected nitrogen cycling? What are some negative consequences of nutrient e ...
Preserving Biodiversity: Species, Ecosystems, or Landscapes? Jerry
... diversity can be lost if human activities eliminate essential habitat features. Conversely, management practices can be designed to retain essential habitat features and dependent species. Furthermore, far more is involved here than simply the maintenance of biological diversity for its own sake; ma ...
... diversity can be lost if human activities eliminate essential habitat features. Conversely, management practices can be designed to retain essential habitat features and dependent species. Furthermore, far more is involved here than simply the maintenance of biological diversity for its own sake; ma ...
Managing Lower Trophic Level Species in the Mid
... • Pacific sardine cutoff is 150,000 mt (or three times the overfished threshold); the control rule also contains environmental parameters to explicitly adapt harvest levels in response to ...
... • Pacific sardine cutoff is 150,000 mt (or three times the overfished threshold); the control rule also contains environmental parameters to explicitly adapt harvest levels in response to ...
Empirical and Other Stock Assessment Approaches
... No detectable evidence of biological interactions (competition, predation, prey release etc) Estimate FMSY as a proportion of M, based on Lc50 and Lm for each key species (see next slide) Set overall multi-species F as required for most vulnerable species Section 4.4, Chapter 12 ...
... No detectable evidence of biological interactions (competition, predation, prey release etc) Estimate FMSY as a proportion of M, based on Lc50 and Lm for each key species (see next slide) Set overall multi-species F as required for most vulnerable species Section 4.4, Chapter 12 ...
Name: Date: Per: ______ Study Guide for AP Biology ECOLOGY
... 9. 56.3 Describe how plants use chemical defenses against herbivores? How do monarchs take advantage of these chemical defenses? And how do nonpoisonous species of butterflies take advantage of the monarch defense system? ...
... 9. 56.3 Describe how plants use chemical defenses against herbivores? How do monarchs take advantage of these chemical defenses? And how do nonpoisonous species of butterflies take advantage of the monarch defense system? ...
Global Amphibian Declines: What Have We Done? Outline
... Introduced Species • Brown and rainbow trout – In Australia, predation on native Spotted tree frog tadpoles was higher than native fish species – Rainbow trout reduced survival of tadpoles by 50% i one week in k or less l ...
... Introduced Species • Brown and rainbow trout – In Australia, predation on native Spotted tree frog tadpoles was higher than native fish species – Rainbow trout reduced survival of tadpoles by 50% i one week in k or less l ...
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle is diverse. Agricultural and industrial nitrogen (N) inputs to the environment currently exceed inputs from natural N fixation. As a consequence of anthropogenic inputs, the global nitrogen cycle (Fig. 1) has been significantly altered over the past century. Global atmospheric nitrous oxide (N2O) mole fractions have increased from a pre-industrial value of ~270 nmol/mol to ~319 nmol/mol in 2005. Human activities account for over one-third of N2O emissions, most of which are due to the agricultural sector. This article is intended to give a brief review of the history of anthropogenic N inputs, and reported impacts of nitrogen inputs on selected terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.























