4Neuronal Migration
... to the glial processes and the timing of their appearance (revealed by detailed 3-D reconstruction studies) led to proposal that they are a substitute for primary migration of neurons in the cortical structure in which they ...
... to the glial processes and the timing of their appearance (revealed by detailed 3-D reconstruction studies) led to proposal that they are a substitute for primary migration of neurons in the cortical structure in which they ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... Mitochondria : Structure that gathers, stores, and releases energy Intracellular fluid: Fluid in which the cell’s internal structures are suspended Microtubules: Tiny tubes that transport molecules and help give the cell its shape Cell membrane: Membrane surrounding the cell ...
... Mitochondria : Structure that gathers, stores, and releases energy Intracellular fluid: Fluid in which the cell’s internal structures are suspended Microtubules: Tiny tubes that transport molecules and help give the cell its shape Cell membrane: Membrane surrounding the cell ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... Mitochondria : Structure that gathers, stores, and releases energy Intracellular fluid: Fluid in which the cell’s internal structures are suspended Microtubules: Tiny tubes that transport molecules and help give the cell its shape Cell membrane: Membrane surrounding the cell ...
... Mitochondria : Structure that gathers, stores, and releases energy Intracellular fluid: Fluid in which the cell’s internal structures are suspended Microtubules: Tiny tubes that transport molecules and help give the cell its shape Cell membrane: Membrane surrounding the cell ...
Copy Notes
... parietal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields temporal l ...
... parietal lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; receives sensory input for touch and body position occipital lobes: portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; includes areas that receive information from the visual fields temporal l ...
RAPID REVIEW The nervous system is made up of a complex
... psychology is the study of behavior and mental processes, understanding how the nervous system works provides fundamental information about what is going on inside your body when you engage in a specific behavior, feel a particular emotion, or have an abstract thought. The field of study that deals ...
... psychology is the study of behavior and mental processes, understanding how the nervous system works provides fundamental information about what is going on inside your body when you engage in a specific behavior, feel a particular emotion, or have an abstract thought. The field of study that deals ...
t1review
... 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What structures are located in the Brain Stem and what are their functions? 13. What could result if each of these structures were af ...
... 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What structures are located in the Brain Stem and what are their functions? 13. What could result if each of these structures were af ...
File
... ___________________ The branching filaments that conduct nerve impulses towards the cell. ___________________ The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from within and outside the body. ___________________ The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. ___________________ The part of the nerve ...
... ___________________ The branching filaments that conduct nerve impulses towards the cell. ___________________ The sense organ or cells that receive stimuli from within and outside the body. ___________________ The reaction to a stimulus by a muscle or gland. ___________________ The part of the nerve ...
Neurons: A fish-eye view of the brain
... most activity in its brain when it’s watching a screen with moving spots the same size as its favorite food, and less activity when watching bigger or smaller spots. These results imply that neurons in the fish’s visual system are programmed to detect certain movements more readily than others—a spe ...
... most activity in its brain when it’s watching a screen with moving spots the same size as its favorite food, and less activity when watching bigger or smaller spots. These results imply that neurons in the fish’s visual system are programmed to detect certain movements more readily than others—a spe ...
Psychology 300 Instructor: Sylvia S. Spencer Ph.D. TEST 1 REVIEW
... 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What structures are located in the Brain Stem and what are their functions? 13. What could result if each of these structures were af ...
... 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What structures are located in the Brain Stem and what are their functions? 13. What could result if each of these structures were af ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Forebrain – emotion, complex thought – thalamus, limbic system, cerebrum, cerebral cortex ...
... Forebrain – emotion, complex thought – thalamus, limbic system, cerebrum, cerebral cortex ...
temporal lobe
... Changes shape for precise focusing of light on retina Onion-like avascular fibers, increase through life Cataract if becomes clouded Note lens below, but in life it is clear ...
... Changes shape for precise focusing of light on retina Onion-like avascular fibers, increase through life Cataract if becomes clouded Note lens below, but in life it is clear ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
3-1-neuron _1
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
... The brain is both specialized and integrated. The nervous system is “plastic” especially at early ages of development. ...
Control of Movement
... Somatotopic Organization topographic representation of body Distorted Homunculus disproportionate amount of cortex for body parts high sensitivity: large cortical area ~ ...
... Somatotopic Organization topographic representation of body Distorted Homunculus disproportionate amount of cortex for body parts high sensitivity: large cortical area ~ ...
AHD Legault Visual system Apr 1
... – Complex: sensitive to position and angle – Hypercomplex: also sensitive to lenght of stimulus (if extends into inhibitory zone, will ↓ the response) ...
... – Complex: sensitive to position and angle – Hypercomplex: also sensitive to lenght of stimulus (if extends into inhibitory zone, will ↓ the response) ...
The Nervous System
... Control center for all body activities Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... Control center for all body activities Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
The Special Senses and Functional Aspects of the Nervous System
... Pressure waves in the perilymph cause pressure on the endolymph in the membranous labyrinth These pressure waves cause movement of hair cells which releases neurotransmitters The neurotransmitters stimulate sensory neurons in cochlear nerve to generate an action potential ...
... Pressure waves in the perilymph cause pressure on the endolymph in the membranous labyrinth These pressure waves cause movement of hair cells which releases neurotransmitters The neurotransmitters stimulate sensory neurons in cochlear nerve to generate an action potential ...
Slide ()
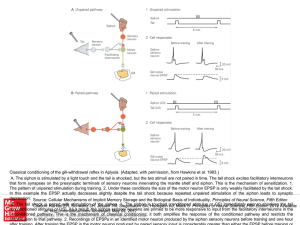
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
primary visual cortex - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
action potential
... – transplants of fetal dopamineproducing substantia nigra cells – adrenal gland transplants – electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors ...
... – transplants of fetal dopamineproducing substantia nigra cells – adrenal gland transplants – electrical stimulation of the thalamus has been used to stop tremors ...
Attenuating GABAA Receptor Signaling in Dopamine Neurons
... Excitation of DA neurons by Glu and ACh is modulated by GABAA-R ...
... Excitation of DA neurons by Glu and ACh is modulated by GABAA-R ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
Organization and Development of the Nervous System
... NEURON: Mitosis (Make New Cells/Neurons) and ...
... NEURON: Mitosis (Make New Cells/Neurons) and ...