Representation of naturalistic image structure in the primate visual
... Visual texture: models and human perception “Visual texture” refers to portions of an image that are filled with repeated elements, often subject to some randomization in their location, size, color, orientation, etc; for example, an image of leaves, or pebbles, or tree bark (Fig. 1a). Lettvin (1976 ...
... Visual texture: models and human perception “Visual texture” refers to portions of an image that are filled with repeated elements, often subject to some randomization in their location, size, color, orientation, etc; for example, an image of leaves, or pebbles, or tree bark (Fig. 1a). Lettvin (1976 ...
dendritic integration
... that capture the essential processing power of the real thing. A paper by Polsky and colleagues1 in this issue represents a large step in this direction by providing experimental insight into what kinds of computations real neurons perform and how they do it. For many decades now, neural network mod ...
... that capture the essential processing power of the real thing. A paper by Polsky and colleagues1 in this issue represents a large step in this direction by providing experimental insight into what kinds of computations real neurons perform and how they do it. For many decades now, neural network mod ...
Chapter 12 Notes - Las Positas College
... cell bodies are located within the CNS; those in the PNS are termed ganglia. 2. Dendrites are branching processes extending from the cell body. Dendrites function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons. 3. Neurons have only one axon. An axon is an “impulse generator,” which take ...
... cell bodies are located within the CNS; those in the PNS are termed ganglia. 2. Dendrites are branching processes extending from the cell body. Dendrites function as receptive sites for receiving signals from other neurons. 3. Neurons have only one axon. An axon is an “impulse generator,” which take ...
PCL - mmc7
... Lower motor neurons: these carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord (or brainstem for cranial nerves) to the muscle Decussation: the crossing over of upper motor neurons Suppose that left-sided facial weakness arises. Where could this pathology be? 1. Left side lower-motor neuron 2. Right side uppe ...
... Lower motor neurons: these carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord (or brainstem for cranial nerves) to the muscle Decussation: the crossing over of upper motor neurons Suppose that left-sided facial weakness arises. Where could this pathology be? 1. Left side lower-motor neuron 2. Right side uppe ...
Parietal cortex neurons of the monkey related to the visual guidance
... objects connected with microswitches that required different patterns of hand movement (object-manipulation task). They were also trained to fixate their gaze on the object without manipulating it, in order to assess visual responses of cells to the sight of the object (object-fixation task). In bot ...
... objects connected with microswitches that required different patterns of hand movement (object-manipulation task). They were also trained to fixate their gaze on the object without manipulating it, in order to assess visual responses of cells to the sight of the object (object-fixation task). In bot ...
Chapter 3
... Sections of the Brain Note whether views are – Axial (Horizontal) Views – Coronal Views – Less need for familiarity with sagittal view ...
... Sections of the Brain Note whether views are – Axial (Horizontal) Views – Coronal Views – Less need for familiarity with sagittal view ...
The Mammalian Nervous System: Structure and
... in the adrenal gland. Preganglionic sympathetic neurons send axons to the adrenal. Hormone-secreting cells in the adrenal are actually modified neurons— secrete neurotransmitters that act as hormones into the circulation. ...
... in the adrenal gland. Preganglionic sympathetic neurons send axons to the adrenal. Hormone-secreting cells in the adrenal are actually modified neurons— secrete neurotransmitters that act as hormones into the circulation. ...
The Neuron
... - Cell membrane open and the positive ions rush in when enough has entered to make the inside more positive than the outside. The cell membrane closes again. This opens/close of cell membrane occurs along the length of the neural membrane creating the neural impulse that travels down the axon = like ...
... - Cell membrane open and the positive ions rush in when enough has entered to make the inside more positive than the outside. The cell membrane closes again. This opens/close of cell membrane occurs along the length of the neural membrane creating the neural impulse that travels down the axon = like ...
Document
... and many other shaped somata. - the cells are small to medium sized. - this layer blends with the white matter. ...
... and many other shaped somata. - the cells are small to medium sized. - this layer blends with the white matter. ...
Neural Oscillators on the Edge: Harnessing Noise to Promote Stability
... Abnormal neural oscillations are implicated in certain disease states, for example repetitive firing of injured axons evoking painful paresthesia, and rhythmic discharges of cortical neurons in patients with epilepsy. In other clinical conditions, the pathological state manifests as a vulnerability ...
... Abnormal neural oscillations are implicated in certain disease states, for example repetitive firing of injured axons evoking painful paresthesia, and rhythmic discharges of cortical neurons in patients with epilepsy. In other clinical conditions, the pathological state manifests as a vulnerability ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Concept 7: Transportation of sensory information to the brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s ow ...
... Concept 7: Transportation of sensory information to the brain • Sensory neural pathway (ascending track) – Passes through the spinal cord to brain stem to thalamus to the sensory areas of cerebral cortex and to the cerebellum – There are different specific ascending tracks: • Vision has it’s ow ...
The central nervous system, or CNS for short, is composed of the
... neurons (Brosamle, et al., 2000). This is caused by chemicals called proteoglycans that are released by neurons (Cafferty, et al., 2007). Proteoglycans are proteins that have multiple sugars attached to them, making them resemble a tangled mess (Cafferty, et al., 2007; Krekoski, et al., 2001). Altho ...
... neurons (Brosamle, et al., 2000). This is caused by chemicals called proteoglycans that are released by neurons (Cafferty, et al., 2007). Proteoglycans are proteins that have multiple sugars attached to them, making them resemble a tangled mess (Cafferty, et al., 2007; Krekoski, et al., 2001). Altho ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
... Also called neuroglia or simply glia Non-excitable – do not transmit electrical signals ...
chapter 8 lecture ppt
... organ, or other neuron - involved with release of neurotransmitters - Ex. Neuromuscular junction ...
... organ, or other neuron - involved with release of neurotransmitters - Ex. Neuromuscular junction ...
Can the ophthalmologist repair the Brain in Infantile ET
... The reach of V1 horizontal axons and Park ' s 8 pd rule FIG 9. Distance spanned by the average V1 horizontal axon in normal and strabismic primates. Normal: In a primate with normal eye alignment, the ODC representing the foveola (or 0 deg eccentricity) of the left eye (L) is immediately adjacent t ...
... The reach of V1 horizontal axons and Park ' s 8 pd rule FIG 9. Distance spanned by the average V1 horizontal axon in normal and strabismic primates. Normal: In a primate with normal eye alignment, the ODC representing the foveola (or 0 deg eccentricity) of the left eye (L) is immediately adjacent t ...
Chapter 6
... Physical site of the stimulated receptor Acuity - precision of stimulus location Greater receptive field size and overlap decreases acuity Lateral inhibition increases acuity Intensity Stronger stimuli result in higher frequency of receptor potentials leading to a higher frequency of action potentia ...
... Physical site of the stimulated receptor Acuity - precision of stimulus location Greater receptive field size and overlap decreases acuity Lateral inhibition increases acuity Intensity Stronger stimuli result in higher frequency of receptor potentials leading to a higher frequency of action potentia ...
Sensation and Perception
... from the bathroom and plunked myself down in the wrong booth, facing the wrong man. I remained unaware he was not my date even as my date (a stranger to me) accosted Wrong Booth Guy, and then stormed out of the Station. I can’t distinguish actors in movies and on TV. I do not recognize myself in pho ...
... from the bathroom and plunked myself down in the wrong booth, facing the wrong man. I remained unaware he was not my date even as my date (a stranger to me) accosted Wrong Booth Guy, and then stormed out of the Station. I can’t distinguish actors in movies and on TV. I do not recognize myself in pho ...
brain - Austin Community College
... - Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints - Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs 2. Efferent - transmit motor impulses from CNS to PNS - Somatic nervous system – provides conscious control of skeletal muscles - Autonomic nervous s ...
... - Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, and joints - Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs 2. Efferent - transmit motor impulses from CNS to PNS - Somatic nervous system – provides conscious control of skeletal muscles - Autonomic nervous s ...
nervous quiz RG
... __________ 2. The central nervous system is composed of the a. brain and spinal cord b. spinal cord and peripheral nerves c. brain and peripheral nerves __________ 3. What part of the neuron is responsible form increased nerve conduction? a. myelin ...
... __________ 2. The central nervous system is composed of the a. brain and spinal cord b. spinal cord and peripheral nerves c. brain and peripheral nerves __________ 3. What part of the neuron is responsible form increased nerve conduction? a. myelin ...
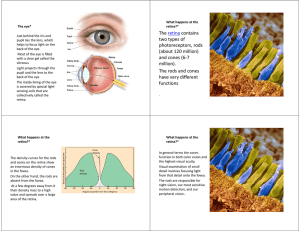
The retina contains two types of photoreceptors, rods (about 120
... The rods are the most numerous of the photoreceptors, some 120 million, and are the more light sensitive than the cones. However, they are not sensitive to color. They are responsible for our dark‐adapted, or scotopic, vision. ...
... The rods are the most numerous of the photoreceptors, some 120 million, and are the more light sensitive than the cones. However, they are not sensitive to color. They are responsible for our dark‐adapted, or scotopic, vision. ...
Lecture 7 (Jan 31): BRAIN DEVELOPMENT and EVOLUTION
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
... New cells migrate outwardly towards the cortical surface. (Along radial glia) ...
science guide 2016-Final2.indd
... The Problem Every time you look at the world around you, pay attention to something new, anticipate the future or recall a memory, a unique set of electrical signals sweeps through your brain. How do these pulses contain all the information necessary to form a thought or memory? The sheer quantity o ...
... The Problem Every time you look at the world around you, pay attention to something new, anticipate the future or recall a memory, a unique set of electrical signals sweeps through your brain. How do these pulses contain all the information necessary to form a thought or memory? The sheer quantity o ...
Neurotox I
... Erks, and involves blockade of death pathways at multiple points. Developmental neuron death is transcription dependent. Induction of death involves multiple pro-apoptotic signaling pathways, some of which converge on induction of BH3domain proteins. ...
... Erks, and involves blockade of death pathways at multiple points. Developmental neuron death is transcription dependent. Induction of death involves multiple pro-apoptotic signaling pathways, some of which converge on induction of BH3domain proteins. ...