Integrated model of visual processing
... 2 1 / 2 D sketch that encodes the position and orientation in depth of small surface elements in 3D and the final stage is the 3D representation that corresponds to the representation of objects in three dimensions. Thus, it is a model based on a cascade of filters, that starts from a local analysis ...
... 2 1 / 2 D sketch that encodes the position and orientation in depth of small surface elements in 3D and the final stage is the 3D representation that corresponds to the representation of objects in three dimensions. Thus, it is a model based on a cascade of filters, that starts from a local analysis ...
Spinal nerves
... receptors, muscles, and glands and are part of the peripheral nervous system. – The 31 pairs of spinal nerves are named and numbered according to the region and level of the spinal cord from which they emerge (Figure 13.2). – Roots of the lower lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal nerves are not in line wi ...
... receptors, muscles, and glands and are part of the peripheral nervous system. – The 31 pairs of spinal nerves are named and numbered according to the region and level of the spinal cord from which they emerge (Figure 13.2). – Roots of the lower lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal nerves are not in line wi ...
The Constructive Nature of Visual Processing
... Beyond the optic chiasm the axons from nasal and temporal hemiretinas carrying input from one hemifield join in the optic tract, which extends to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus. The lateral geniculate nucleus in primates consists of six layers, each of which receives input from eithe ...
... Beyond the optic chiasm the axons from nasal and temporal hemiretinas carrying input from one hemifield join in the optic tract, which extends to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus. The lateral geniculate nucleus in primates consists of six layers, each of which receives input from eithe ...
Robotic/Human Loops - Computer Science & Engineering
... Ripplinger MC, Wilson CJ, King JG, Frye J, Drewes R, Harris FC, and Goodman PH, “Computational Model of Interacting Brain Networks,” Journal of Investigative Medicine, Vol. 52, No. 1, Jan 2004, pp. S155. ...
... Ripplinger MC, Wilson CJ, King JG, Frye J, Drewes R, Harris FC, and Goodman PH, “Computational Model of Interacting Brain Networks,” Journal of Investigative Medicine, Vol. 52, No. 1, Jan 2004, pp. S155. ...
Biological Basis of behavior
... neuron. A specific neurotransmitter can bind only to receptor sites that its molecular structure will fit into, much like a key must fit a lock. ...
... neuron. A specific neurotransmitter can bind only to receptor sites that its molecular structure will fit into, much like a key must fit a lock. ...
Schwann cells
... Myelin Sheaths in the PNS Schwann cells wraps many times around the axon Myelin sheath—concentric layers of Schwann cell membrane ...
... Myelin Sheaths in the PNS Schwann cells wraps many times around the axon Myelin sheath—concentric layers of Schwann cell membrane ...
Encoding Information in Neuronal Activity
... In one example the correlated firing between two neurons during the GO tasks was highest during the first second after the onset of the stimulus and lower during the next second. During the NO- GO tasks the pattern of correlated firing was reversed. The correlation was low in the first second and hi ...
... In one example the correlated firing between two neurons during the GO tasks was highest during the first second after the onset of the stimulus and lower during the next second. During the NO- GO tasks the pattern of correlated firing was reversed. The correlation was low in the first second and hi ...
Animal Response to Stimuli
... reflex arc: The pathway from the point of stimulation to the responding effector. A reflex arc has five components. The stimulus is picked up by a receptor that sends the message along an afferent (sensory) neuron to the spinal cord. The reply to this stimulus is sent from the spinal cord along an e ...
... reflex arc: The pathway from the point of stimulation to the responding effector. A reflex arc has five components. The stimulus is picked up by a receptor that sends the message along an afferent (sensory) neuron to the spinal cord. The reply to this stimulus is sent from the spinal cord along an e ...
Presentation 14 - Foundations of Human Social
... Lack of accuracy: differences detected only at macroscopic scale ...
... Lack of accuracy: differences detected only at macroscopic scale ...
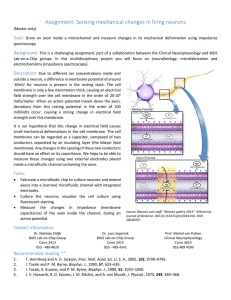
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... membrane is only a few nanometers thick, causing an electrical field strength over the cell membrane in the order of 20∙106 Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical ...
... membrane is only a few nanometers thick, causing an electrical field strength over the cell membrane in the order of 20∙106 Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical ...
Thalamus 1
... Lies between lateral thalamic surface and external medullary lamina Reticular nucleus is developmentally not a part of thalamus. It has distinct anatomical and physiological properties. Considered a part of thalamus because of location and extensive involvement in thalamic function. ...
... Lies between lateral thalamic surface and external medullary lamina Reticular nucleus is developmentally not a part of thalamus. It has distinct anatomical and physiological properties. Considered a part of thalamus because of location and extensive involvement in thalamic function. ...
OCULAR HEMORRHAGE IN CHILDREN
... cells undergo mitoses to produce neurons and glia. After mitoses, some of the newly generated cells will remain in the germinal zone and undergo further divisions, while others will migrate outward to their final destinations. At 8 gw, the first young neurons begin to migrate outward. Initially, sim ...
... cells undergo mitoses to produce neurons and glia. After mitoses, some of the newly generated cells will remain in the germinal zone and undergo further divisions, while others will migrate outward to their final destinations. At 8 gw, the first young neurons begin to migrate outward. Initially, sim ...
CHAPTER 2 –OUTLINE I. Introduction: Neuroscience and Behavior
... and carries information from the neuron to other neurons, glands, and muscles. Axons vary in length from a few thousandths of an inch to about four feet. a. Many axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath, a white, fatty covering that insulates axons from one another and increases the neuron’s communic ...
... and carries information from the neuron to other neurons, glands, and muscles. Axons vary in length from a few thousandths of an inch to about four feet. a. Many axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath, a white, fatty covering that insulates axons from one another and increases the neuron’s communic ...
download file
... and the parameters derived from it, including threshold and bandwidth. A range of tuning curve shapes were observed, although the basic V-shape predominated (Fig. 1B). The `best frequency' is the frequency that evokes a consistent neural response at the lowest tone intensity. We recorded from units ...
... and the parameters derived from it, including threshold and bandwidth. A range of tuning curve shapes were observed, although the basic V-shape predominated (Fig. 1B). The `best frequency' is the frequency that evokes a consistent neural response at the lowest tone intensity. We recorded from units ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 34.1 Somatic and autonomic styles of
... project through ventral roots to either paravertebral chain ganglia or prevertebral ganglia, as illustrated for the splanchnic nerve (A). Visceral sensory neurons located in the dorsal root ganglia transmit information from innervated visceral organs to interneurons in the spinal cord to complete au ...
... project through ventral roots to either paravertebral chain ganglia or prevertebral ganglia, as illustrated for the splanchnic nerve (A). Visceral sensory neurons located in the dorsal root ganglia transmit information from innervated visceral organs to interneurons in the spinal cord to complete au ...
Chapter 48 Nervous Systems
... EK than to ENa is that the membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+. If something causes the membrane’s permeability to Na+ to increase, the membrane potential will move toward ENa and away from EK. This is the basis of nearly all electrical signals in the nervous system. The membrane potential ...
... EK than to ENa is that the membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+. If something causes the membrane’s permeability to Na+ to increase, the membrane potential will move toward ENa and away from EK. This is the basis of nearly all electrical signals in the nervous system. The membrane potential ...
Presynaptic Questions
... 8. What types of amino acids (and how many?) generally signal a site in a neuropeptide precursor at which it will be cleaved by an endopeptidase? Dibasic amino acids generally signal cleavage sites o Lysine (K) and arginine (R) o Sequences are generally KK, KR or RR 9. In what ways can the same DNA ...
... 8. What types of amino acids (and how many?) generally signal a site in a neuropeptide precursor at which it will be cleaved by an endopeptidase? Dibasic amino acids generally signal cleavage sites o Lysine (K) and arginine (R) o Sequences are generally KK, KR or RR 9. In what ways can the same DNA ...
Specification of Cerebral Cortical Areas
... remarkable product of brain evolution, not only because it makes up two-thirds of the neuronal mass and contains about three-quarters of all our synapses, but also because it is the structure that most distinctively sets us apart from other species. One of the most prominent features of the cerebral ...
... remarkable product of brain evolution, not only because it makes up two-thirds of the neuronal mass and contains about three-quarters of all our synapses, but also because it is the structure that most distinctively sets us apart from other species. One of the most prominent features of the cerebral ...
Page 1 - Rochester Community Schools
... B) range of traits that contribute to reproductive success. C) set of genetic material in an organism's chromosomes. D) set of interactions between genes and environments. E) collection of genetic and hormonal influences on behavior. 29. Compared with identical twins, fraternal twins are A) less lik ...
... B) range of traits that contribute to reproductive success. C) set of genetic material in an organism's chromosomes. D) set of interactions between genes and environments. E) collection of genetic and hormonal influences on behavior. 29. Compared with identical twins, fraternal twins are A) less lik ...
Composition of the Nervous System
... •Neurons are structural and functional unit responsible for transfer of information via electrical (ionic movement) and chemical communication. •Neurons are excitable cells that are capable of transmitting signals along cell membrane by action potentials to other excitable cells (other neurons or mu ...
... •Neurons are structural and functional unit responsible for transfer of information via electrical (ionic movement) and chemical communication. •Neurons are excitable cells that are capable of transmitting signals along cell membrane by action potentials to other excitable cells (other neurons or mu ...
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
... • You Tube video animations – Neuron Synapse: EPSP and IPSP – Neural Communication: EPSP and IPSP ...
... • You Tube video animations – Neuron Synapse: EPSP and IPSP – Neural Communication: EPSP and IPSP ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Ribbon synapses of photoreceptor cells and bipolar neurons in the retina signal graded changes in light intensity via sustained release of neurotransmitter. One molecular specialization of retinal ribbon synapses is the expression of complexin protein subtypes Cplx3 and Cplx4, whereas conventional s ...
... Ribbon synapses of photoreceptor cells and bipolar neurons in the retina signal graded changes in light intensity via sustained release of neurotransmitter. One molecular specialization of retinal ribbon synapses is the expression of complexin protein subtypes Cplx3 and Cplx4, whereas conventional s ...
Signal Integration in Thalamus: Labeled Lines Go
... The brain creates perceptions from incoming sensory information in two main ways. The first way is to maintain a given quality of information about the outside world in its pure, unadulterated form (sometimes called a ‘‘labeled line’’) as it is passed from one stage of neural processing to the next. ...
... The brain creates perceptions from incoming sensory information in two main ways. The first way is to maintain a given quality of information about the outside world in its pure, unadulterated form (sometimes called a ‘‘labeled line’’) as it is passed from one stage of neural processing to the next. ...