cp_kellermann_launay_17092010
... Lariboisière, Paris and the mental health network, Santé Mentale), sheds new light on the mechanisms of action of these drugs which have been used for more than 30 years and are heavily consumed in France. In particular, the researchers have revealed, for the first time, a sequence of reactions caus ...
... Lariboisière, Paris and the mental health network, Santé Mentale), sheds new light on the mechanisms of action of these drugs which have been used for more than 30 years and are heavily consumed in France. In particular, the researchers have revealed, for the first time, a sequence of reactions caus ...
Time-delay-induced phase-transition to synchrony in coupled
... Massachusetts Institute of Technology, by permission of The MIT Press. ...
... Massachusetts Institute of Technology, by permission of The MIT Press. ...
A5: Neuropharamcology (student) - Ms De Souza`s Super Awesome
... neuromodulators and take hundreds of milliseconds to act on the post-synaptic membrane. ...
... neuromodulators and take hundreds of milliseconds to act on the post-synaptic membrane. ...
Types of Neuron and their function - Click here
... Synaptic transmission is the process for transmitting messages from neuron to neuron. Since neurons form a network, they somehow have to be interconnected. When a nerve signal, or impulse reaches the ends of its axon, it has travelled as an action potential, or a pulse of electricity. However, there ...
... Synaptic transmission is the process for transmitting messages from neuron to neuron. Since neurons form a network, they somehow have to be interconnected. When a nerve signal, or impulse reaches the ends of its axon, it has travelled as an action potential, or a pulse of electricity. However, there ...
Molecular and Cellular aspects of a Sacred Disease `Epilepsy`
... current, resulting in burst of spikes (Ditcher, 1997). There are functional as well as structural changes occur in epileptic foci. Functional include metabolic alterations, concentration of cations and anions and changes in neurotransmitter level whereas structural changes involve neurons and glia. ...
... current, resulting in burst of spikes (Ditcher, 1997). There are functional as well as structural changes occur in epileptic foci. Functional include metabolic alterations, concentration of cations and anions and changes in neurotransmitter level whereas structural changes involve neurons and glia. ...
PDF
... miR172 levels increase when potato plants are grown under tuber-inducing short-day conditions. At the onset of tuberisation, miR172 levels increase specifically in stolons, the stems from which tubers arise. miR172 overexpression promotes not only flowering, as seen in other plants, but also tuberis ...
... miR172 levels increase when potato plants are grown under tuber-inducing short-day conditions. At the onset of tuberisation, miR172 levels increase specifically in stolons, the stems from which tubers arise. miR172 overexpression promotes not only flowering, as seen in other plants, but also tuberis ...
PDF
... miR172 levels increase when potato plants are grown under tuber-inducing short-day conditions. At the onset of tuberisation, miR172 levels increase specifically in stolons, the stems from which tubers arise. miR172 overexpression promotes not only flowering, as seen in other plants, but also tuberis ...
... miR172 levels increase when potato plants are grown under tuber-inducing short-day conditions. At the onset of tuberisation, miR172 levels increase specifically in stolons, the stems from which tubers arise. miR172 overexpression promotes not only flowering, as seen in other plants, but also tuberis ...
PDF
... miR172 levels increase when potato plants are grown under tuber-inducing short-day conditions. At the onset of tuberisation, miR172 levels increase specifically in stolons, the stems from which tubers arise. miR172 overexpression promotes not only flowering, as seen in other plants, but also tuberis ...
... miR172 levels increase when potato plants are grown under tuber-inducing short-day conditions. At the onset of tuberisation, miR172 levels increase specifically in stolons, the stems from which tubers arise. miR172 overexpression promotes not only flowering, as seen in other plants, but also tuberis ...
Chapter 4: The Cytology of Neurons
... inputs from… Excitatory input from primary sensory neurons Recurrent collateral branches of its own Recurrent excitatory input from other motor neuron Both excitatory and inhibitory input from interneurons driven by descending fibers from brain that control and coordinate movement Inhibitory input f ...
... inputs from… Excitatory input from primary sensory neurons Recurrent collateral branches of its own Recurrent excitatory input from other motor neuron Both excitatory and inhibitory input from interneurons driven by descending fibers from brain that control and coordinate movement Inhibitory input f ...
Neural Tissue – Chapter 12
... Step One: Sodium ions enter the cell and are attracted to the negative charges along the inner surface of the membrane. The arrival of positive charges shifts the transmembrane potential toward 0 mV. This is called depolarization. Step Two: At the resting potential, sodium ions are drawn to the oute ...
... Step One: Sodium ions enter the cell and are attracted to the negative charges along the inner surface of the membrane. The arrival of positive charges shifts the transmembrane potential toward 0 mV. This is called depolarization. Step Two: At the resting potential, sodium ions are drawn to the oute ...
Ch 15: Autonomic Division of NS
... stimulates specialized 2nd order neurons with very short axons in adrenal medulla to release NT into blood stream (= hormones) Epinephrine (adrenaline) ~ 80% and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Endocrine effects are longer lasting than nervous system effects ...
... stimulates specialized 2nd order neurons with very short axons in adrenal medulla to release NT into blood stream (= hormones) Epinephrine (adrenaline) ~ 80% and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Endocrine effects are longer lasting than nervous system effects ...
AUTONOMIC REFLEX - Semmelweis University
... sympathetic trunk and form the splanchnic nerves, these fibers travel to a prevertebral gaglion 4. some preganglionic axons in the splanchnic nerve innervate chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla ...
... sympathetic trunk and form the splanchnic nerves, these fibers travel to a prevertebral gaglion 4. some preganglionic axons in the splanchnic nerve innervate chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla ...
ppt - UK College of Arts & Sciences
... disciplines to the integrative nature of science so that they can better prepare themselves with the appropriate training during the remaining years of undergraduate schooling and help to direct their efforts and thus competitiveness towards particular graduate programs. By the end of this course, o ...
... disciplines to the integrative nature of science so that they can better prepare themselves with the appropriate training during the remaining years of undergraduate schooling and help to direct their efforts and thus competitiveness towards particular graduate programs. By the end of this course, o ...
Nervous System Reading from SparkNotes
... Neurons cannot directly pass an action potential from one to the next because of the synapses between them. Instead, neurons communicate across the synaptic clefts by the means of chemical signals known as neurotransmitters. When an action potential reaches the synapse, it causes the release of vesi ...
... Neurons cannot directly pass an action potential from one to the next because of the synapses between them. Instead, neurons communicate across the synaptic clefts by the means of chemical signals known as neurotransmitters. When an action potential reaches the synapse, it causes the release of vesi ...
PAC01 Pulmonary Physiology
... and air rushes into the thorax through all available openings (In healthy people, only the mouth and nose are open. In traumautic openings, air rushes into the pleura) 2.Contraction of the external intercostal muscles elevates the rib cage and increases the anteriorposterior dimension of the thorax. ...
... and air rushes into the thorax through all available openings (In healthy people, only the mouth and nose are open. In traumautic openings, air rushes into the pleura) 2.Contraction of the external intercostal muscles elevates the rib cage and increases the anteriorposterior dimension of the thorax. ...
The Languages of Neurons: An Analysis of Coding Mechanisms by
... While information processing in the brain is highly complex, each neuron uses a simple code mechanism for transmitting information. This is in the form of temporal electrophysiological action potentials or spikes (S) of about a 1 millisecond (ms) duration that, along with pauses (P) between spikes c ...
... While information processing in the brain is highly complex, each neuron uses a simple code mechanism for transmitting information. This is in the form of temporal electrophysiological action potentials or spikes (S) of about a 1 millisecond (ms) duration that, along with pauses (P) between spikes c ...
Neural Axis Representing Target Range in the Auditory
... three major clusters of delay-sensitive neurons: FM,-FM2, FMi-FM3, and FM,-FM4 facilitation neurons. Each cluster shows odotopic representation. Iso-BD contours and range axes are schematically shown by dashed lines and solid arrows, respectively. Best delays of 0.4 and 18 msec correspond to best ra ...
... three major clusters of delay-sensitive neurons: FM,-FM2, FMi-FM3, and FM,-FM4 facilitation neurons. Each cluster shows odotopic representation. Iso-BD contours and range axes are schematically shown by dashed lines and solid arrows, respectively. Best delays of 0.4 and 18 msec correspond to best ra ...
YAPAY SİNİR AĞLARINA GİRİŞ
... This can potentially help us understand the nature of human intelligence, formulate better teaching strategies, or better remedial actions for brain damaged patients. Artificial System Building : The engineering goal of building efficient systems for real world applications. This may make machines m ...
... This can potentially help us understand the nature of human intelligence, formulate better teaching strategies, or better remedial actions for brain damaged patients. Artificial System Building : The engineering goal of building efficient systems for real world applications. This may make machines m ...
ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels in the Brain: Sensors of
... gic SNc neurons express different types of KATP channel with differing sensitivities to metabolic inhibition and proposed a novel mechanism of the selective vulnerability of some dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. They showed that neurons with --cell-type KATP channels, which comprise Kir ...
... gic SNc neurons express different types of KATP channel with differing sensitivities to metabolic inhibition and proposed a novel mechanism of the selective vulnerability of some dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. They showed that neurons with --cell-type KATP channels, which comprise Kir ...
Optogenetics
... Parkinson's disease. Deep brain stimulation devices have been efficacious in correcting movement disorders in patients with advanced stage Parkinson's disease. High frequency stimulation is thought to suppress firing of neurons in the subthalamic nucleus (STN). Optical neuromodulation could be used ...
... Parkinson's disease. Deep brain stimulation devices have been efficacious in correcting movement disorders in patients with advanced stage Parkinson's disease. High frequency stimulation is thought to suppress firing of neurons in the subthalamic nucleus (STN). Optical neuromodulation could be used ...
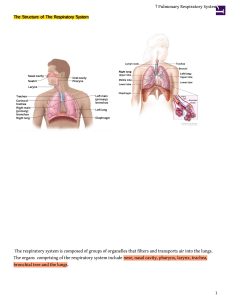
① Pulmonary Respiratory System
... The diaphragm is the most important muscle of inspiration, it inserts into the lower ribs, and is innervated by the phrenic nerves (Cervial plexus, brachial plexus C3-5). During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and the abdomen moves downward and forward causing ribs to lift outward. This causes ...
... The diaphragm is the most important muscle of inspiration, it inserts into the lower ribs, and is innervated by the phrenic nerves (Cervial plexus, brachial plexus C3-5). During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and the abdomen moves downward and forward causing ribs to lift outward. This causes ...
No Slide Title
... ARTERIAL pH • VARIATIONS OF PaO2 <3-4 mm Hg AND EVEN LESS FOR PaCO2 • TO EXPEND MINIMAL ENERGY IN THE WORK OF BREATHING ...
... ARTERIAL pH • VARIATIONS OF PaO2 <3-4 mm Hg AND EVEN LESS FOR PaCO2 • TO EXPEND MINIMAL ENERGY IN THE WORK OF BREATHING ...
Insights from models of rhythmic motor systems
... stagnalis [16]. Interactions between neuronal circuits involved in motor control — the pons and the medulla — have also recently been included in a model of respiratory pattern generation. This model suggests that the rhythmic activity produced by the reduced medullary preparations used in many stud ...
... stagnalis [16]. Interactions between neuronal circuits involved in motor control — the pons and the medulla — have also recently been included in a model of respiratory pattern generation. This model suggests that the rhythmic activity produced by the reduced medullary preparations used in many stud ...
Pre-Bötzinger complex

The pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC) is a cluster of interneurons in the ventrolateral medulla of the brainstem. This complex has been proven to be essential for the generation of respiratory rhythm in mammals. The exact mechanism of the rhythm generation and transmission to motor nuclei remains controversial and the topic of much present research.Several synthetic compounds have been shown to act on neurons specific to the preBötC, most being selective agonists or antagonists to receptor subtypes on neurons in the vicinity. Since many of these neurons express GABA, glutamate, serotonin and adenosine receptors, chemicals custom tailored to bind at these sites are most effective at altering respiratory rhythm.Adenosine modulates the preBötC output via activation of the A1 and A2A receptor subtypes. An adenosine A1 receptor agonist has been shown to depress preBötC rhythmogenesis independent of the neurotransmitters GABA and glycine in ""in vitro"" preparations from 0-7 day old mice. Another synthetic drug specific to the adenosine A2A receptor subtype is CGS-21680 that has been shown to cause apneas in 14-21 day old rat pups in vivo. For this reason, it has been used as a model to study pathological conditions such as apnea of prematurity and SIDS in neonatal infants.