Nervous Systems II PPT
... 3 basic function of all neurons: ◦ Receive and integrate incoming signals ◦ Conduct these signals through the cell ◦ Transmit these signals to other cells ...
... 3 basic function of all neurons: ◦ Receive and integrate incoming signals ◦ Conduct these signals through the cell ◦ Transmit these signals to other cells ...
Nervous System Lecture- Part II
... Nerve impulses are called action potentials Other special characteristics Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose, neurons die af ...
... Nerve impulses are called action potentials Other special characteristics Longevity – can live and function for a lifetime Do not divide – fetal neurons lose their ability to undergo mitosis; neural stem cells are an exception High metabolic rate – require abundant oxygen and glucose, neurons die af ...
초록리스트
... afferent inputs and taking up the sole output of the cerebellar cortex. PCs are known to generate high-frequency action potentials. The pattern and rate of firing are under the control of both synaptic input and intrinsic ion channels that allow the neurons to fire spontaneously in the absence of sy ...
... afferent inputs and taking up the sole output of the cerebellar cortex. PCs are known to generate high-frequency action potentials. The pattern and rate of firing are under the control of both synaptic input and intrinsic ion channels that allow the neurons to fire spontaneously in the absence of sy ...
E4 - Neurotransmitters and Synapses - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... potential at its axon hillock, it will produce an action potential pre-synaptic neurons can vary in the frequency, but not intensity of their input, since action potentials are "all-or-none“ rule ...
... potential at its axon hillock, it will produce an action potential pre-synaptic neurons can vary in the frequency, but not intensity of their input, since action potentials are "all-or-none“ rule ...
The Importance of the Nervous System
... • http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__ chemical_synapse__quiz_1_.html ...
... • http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter8/animation__ chemical_synapse__quiz_1_.html ...
Chapter 17
... presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft which act on the postsynaptic cell - there are numerous neurotransmitters including acetylcholine (ACh), glutamate, aspartate, glycine, norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), serotonin, endorphins, nitric oxide (NO), etc. Structural ...
... presynaptic neuron releases neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft which act on the postsynaptic cell - there are numerous neurotransmitters including acetylcholine (ACh), glutamate, aspartate, glycine, norepinephrine (NE), dopamine (DA), serotonin, endorphins, nitric oxide (NO), etc. Structural ...
מצגת של PowerPoint
... Excitatory GABA currents are essential (necessary) for proper dendritic development ...
... Excitatory GABA currents are essential (necessary) for proper dendritic development ...
Nervous System Chapter 11 Answers
... Axon diameter (Larger diameter results in faster conduction of impulse) Degree of myelination (Continuous conduction vs. Saltatory conduction) 17. Describe the events of the propagation of an action potential through a synapse to the next dendrite. 1. Propagation of impulse to the axon terminal ...
... Axon diameter (Larger diameter results in faster conduction of impulse) Degree of myelination (Continuous conduction vs. Saltatory conduction) 17. Describe the events of the propagation of an action potential through a synapse to the next dendrite. 1. Propagation of impulse to the axon terminal ...
Artificial Neural Networks - Introduction -
... Artificial neural networks Tasks to be solved by artificial neural networks: • controlling the movements of a robot based on selfperception and other information (e.g., visual information); • deciding the category of potential food items (e.g., edible or non-edible) in an artificial world; ...
... Artificial neural networks Tasks to be solved by artificial neural networks: • controlling the movements of a robot based on selfperception and other information (e.g., visual information); • deciding the category of potential food items (e.g., edible or non-edible) in an artificial world; ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I
... PP. A neurilemma is a portion of a Schwann cell outside of the myelin sheath. QQ. A node of Ranvier is a narrow gap between myelin sheaths. RR. Myelinated axons have myelin sheaths. SS. Unmyelinated axons have no myelin sheaths. TT. White matter is composed of myelinated axons. UU. Gray matter is c ...
... PP. A neurilemma is a portion of a Schwann cell outside of the myelin sheath. QQ. A node of Ranvier is a narrow gap between myelin sheaths. RR. Myelinated axons have myelin sheaths. SS. Unmyelinated axons have no myelin sheaths. TT. White matter is composed of myelinated axons. UU. Gray matter is c ...
Excitatory_Inhibitory_Neural_Network_1
... Excitatory-Inhibitory Neural Network 1 From: Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected netw ...
... Excitatory-Inhibitory Neural Network 1 From: Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected netw ...
A quantitative theory of neural computation Cambridge, MA 02138
... formation, where association is defined as follows: Given two items A and B already represented the task is to make modifications in the circuit so that whenever in the future A fires so will B also. 5. Correspondences with Experimental Findings The classical model of vision in cortex is as a hierar ...
... formation, where association is defined as follows: Given two items A and B already represented the task is to make modifications in the circuit so that whenever in the future A fires so will B also. 5. Correspondences with Experimental Findings The classical model of vision in cortex is as a hierar ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-30
... Lower Motor Neuron (LMN, alpha motor neuron): -Cell body in spinal cord (spinal nerve) or in brainstem (cranial nerve) -Axon terminates on muscles Upper Motor Neuron (UMN): -Cell body in brainstem or cortex -Synapses on lower motor neuron -Strong influence on lower motor neuron Reflex: 2 neurons and ...
... Lower Motor Neuron (LMN, alpha motor neuron): -Cell body in spinal cord (spinal nerve) or in brainstem (cranial nerve) -Axon terminates on muscles Upper Motor Neuron (UMN): -Cell body in brainstem or cortex -Synapses on lower motor neuron -Strong influence on lower motor neuron Reflex: 2 neurons and ...
Protocadherin mediates collective axon extension of neurons
... migration using live-imaging and found that, in wild-type conditions, when the elongating axons came into contact with an axon from other neurons of the same subtype, it continued to elongate along the other axon, whereas in the Pcdh17 mutant, the axon stopped elongating when it came into contact wi ...
... migration using live-imaging and found that, in wild-type conditions, when the elongating axons came into contact with an axon from other neurons of the same subtype, it continued to elongate along the other axon, whereas in the Pcdh17 mutant, the axon stopped elongating when it came into contact wi ...
A zebrafish model exemplifies the long preclinical period of motor
... disease (MND) and demonstrated that zebrafish, like mice and humans, show hallmark features of ALS, suggesting that the zebrafish provides an excellent model system to study motor neuron disease.2 Additionally, the transparency and ex vivo development of embryos enables one to trace early embryonic ch ...
... disease (MND) and demonstrated that zebrafish, like mice and humans, show hallmark features of ALS, suggesting that the zebrafish provides an excellent model system to study motor neuron disease.2 Additionally, the transparency and ex vivo development of embryos enables one to trace early embryonic ch ...
The Nervous System
... “jump”. They are just too far apart. When the signal reaches the end of the axon and wants to go to the next cell in line, it must change to a chemical messenger instead of an electrical impulse. These chemical messengers are called neurotransmitters ...
... “jump”. They are just too far apart. When the signal reaches the end of the axon and wants to go to the next cell in line, it must change to a chemical messenger instead of an electrical impulse. These chemical messengers are called neurotransmitters ...
Outline10 Action Potl
... B. Action Potentials (= nerve impulses) large change in membrane potential actively conducted along the axon rapid depolarization followed by repolarization “all or none” - constant size, does not depend on stimulus strength ...
... B. Action Potentials (= nerve impulses) large change in membrane potential actively conducted along the axon rapid depolarization followed by repolarization “all or none” - constant size, does not depend on stimulus strength ...
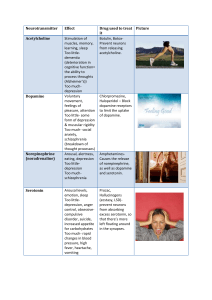
Neurotransmitter - Pamoja Education Blogs
... form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
... form of depression & muscular rigidity Too much- social anxiety, schizophrenia (breakdown of thought processes) Arousal, alertness, eating, depression Too littledepression Too muchschizophrenia ...
www.sakshieducation.com
... 8) An involuntary response by the nervous system to a stimulus is a A) Synapse B) Reflex C) Motor response D) Smooth muscle ...
... 8) An involuntary response by the nervous system to a stimulus is a A) Synapse B) Reflex C) Motor response D) Smooth muscle ...
Pre-Bötzinger complex

The pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC) is a cluster of interneurons in the ventrolateral medulla of the brainstem. This complex has been proven to be essential for the generation of respiratory rhythm in mammals. The exact mechanism of the rhythm generation and transmission to motor nuclei remains controversial and the topic of much present research.Several synthetic compounds have been shown to act on neurons specific to the preBötC, most being selective agonists or antagonists to receptor subtypes on neurons in the vicinity. Since many of these neurons express GABA, glutamate, serotonin and adenosine receptors, chemicals custom tailored to bind at these sites are most effective at altering respiratory rhythm.Adenosine modulates the preBötC output via activation of the A1 and A2A receptor subtypes. An adenosine A1 receptor agonist has been shown to depress preBötC rhythmogenesis independent of the neurotransmitters GABA and glycine in ""in vitro"" preparations from 0-7 day old mice. Another synthetic drug specific to the adenosine A2A receptor subtype is CGS-21680 that has been shown to cause apneas in 14-21 day old rat pups in vivo. For this reason, it has been used as a model to study pathological conditions such as apnea of prematurity and SIDS in neonatal infants.