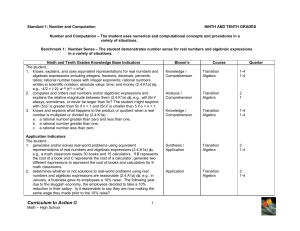
Ninth and Tenth Grades Knowledge Base Indicators
... 1. explains and illustrates the relationship between the subsets of the real number system [natural (counting) numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers] using mathematical models (2.4.K1a), e.g., number lines or Venn diagrams. 2. identifies all the subsets of the real n ...
... 1. explains and illustrates the relationship between the subsets of the real number system [natural (counting) numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers] using mathematical models (2.4.K1a), e.g., number lines or Venn diagrams. 2. identifies all the subsets of the real n ...
lalg1_fl_ch03_03
... left side of the equation. Because –4(x – 3) = –4x + 12, Step 2 should be 5x – 4x + 12 = 17. ANSWER The correct answer is D. A B ...
... left side of the equation. Because –4(x – 3) = –4x + 12, Step 2 should be 5x – 4x + 12 = 17. ANSWER The correct answer is D. A B ...
Common Factoring Using Algebra Tiles as a Tool and Patterning as
... each term and find their GCF. ♦ Look at the variables of each term and find the greatest variable term that could be factored out. ♦ This is the GCMF, write it on the next line after =. ♦ Put in the brackets and fill the brackets with the leftovers (what you would have to multiply the GCMF by to ...
... each term and find their GCF. ♦ Look at the variables of each term and find the greatest variable term that could be factored out. ♦ This is the GCMF, write it on the next line after =. ♦ Put in the brackets and fill the brackets with the leftovers (what you would have to multiply the GCMF by to ...