Bittinger_PA_5_8_draft1a
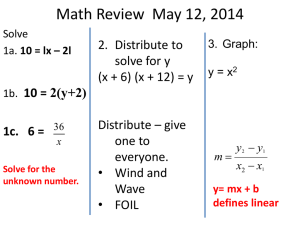
... (e) 5 times the difference of two numbers let x and y = the numbers 5(x – y) SAY: Next we consider solving applied problems. We will use the Five Steps for Problem Solving learned earlier in the text. SAY: Let’s work an example. READ Exercise 25 ...
... (e) 5 times the difference of two numbers let x and y = the numbers 5(x – y) SAY: Next we consider solving applied problems. We will use the Five Steps for Problem Solving learned earlier in the text. SAY: Let’s work an example. READ Exercise 25 ...
... • The y−coordinate of the vertex is –3. This means that the graph has undergone a vertical translation of –3. The vertex is easy to pick out from the tables since it is the point around which the corresponding points appear. • The points from the vertex are plotted left and right one and up two, lef ...
M340L Unique number 53280
... 7) If A is an invertible nxn matrix, then the equation Ax = b is consistent for each b in Rn. ……T…………………… 8) If an nxn matrix A is invertible, then its columns are linearly independent . 9) If A is an nxn matrix such that the equation Ax = 0 has a non trivial solution, then A has fewer than n pivot ...
... 7) If A is an invertible nxn matrix, then the equation Ax = b is consistent for each b in Rn. ……T…………………… 8) If an nxn matrix A is invertible, then its columns are linearly independent . 9) If A is an nxn matrix such that the equation Ax = 0 has a non trivial solution, then A has fewer than n pivot ...
Math/116 Final
... (Type an ordered pair. Type an integer or a fraction. Type N if there is no solution. Type I if there are in infinitely many solution) ...
... (Type an ordered pair. Type an integer or a fraction. Type N if there is no solution. Type I if there are in infinitely many solution) ...