PDF file
... Developmental Network is the basis of a series of WhereWhat Networks, whose 4th version WWN-4 appeared in [12]. A simplest version of a Developmental Network (DN) has three areas, the sensory area X, the internal area Y and the motor area Z, with an example in Fig. 1(b). The internal neurons in Y ha ...
... Developmental Network is the basis of a series of WhereWhat Networks, whose 4th version WWN-4 appeared in [12]. A simplest version of a Developmental Network (DN) has three areas, the sensory area X, the internal area Y and the motor area Z, with an example in Fig. 1(b). The internal neurons in Y ha ...
Unsupervised models and clustering.
... This shows that there is a kind of cerebral selforganization, that develops the brain power to classify and easily recognize some “common” patterns, which is also confirmed by the difficulty of reading a text upside down or containing attached ...
... This shows that there is a kind of cerebral selforganization, that develops the brain power to classify and easily recognize some “common” patterns, which is also confirmed by the difficulty of reading a text upside down or containing attached ...
Neural Networks
... body are called excitatory. Synapses which lower the potential are called inhibitory. • It has been found that synapses exhibit plasticity. This means that long-term changes in the strengths of the connections can be formed depending on the firing patterns of other neurons. This is thought to be the ...
... body are called excitatory. Synapses which lower the potential are called inhibitory. • It has been found that synapses exhibit plasticity. This means that long-term changes in the strengths of the connections can be formed depending on the firing patterns of other neurons. This is thought to be the ...
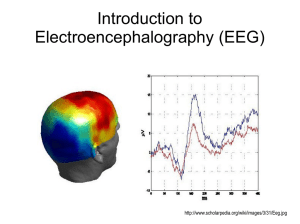
Introduction to Electroencephalography (EEG)
... http://www.scholarpedia.org/wiki/images/1/10/Electroencephalogram_figHead.jpg ...
... http://www.scholarpedia.org/wiki/images/1/10/Electroencephalogram_figHead.jpg ...
Chapter 8 & 5 powerpoint file
... segment of the membrane depolarizes Positive charge spreads along adjacent sections of axon by local current flow – as the signal moves away the currently stimulated area returns to its resting potential Local current flow causes new section of the membrane to depolarize – this new section is cr ...
... segment of the membrane depolarizes Positive charge spreads along adjacent sections of axon by local current flow – as the signal moves away the currently stimulated area returns to its resting potential Local current flow causes new section of the membrane to depolarize – this new section is cr ...
Branched nanostructures represent unique, 3D building blocks for
... investigate extracellular electron transfer in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, where an array of nanoholes precludes or single window allows for direct microbeelectrode contacts. The ability to control and image cell/electrode interactions down to the single-cell level provide a powerful approach for ad ...
... investigate extracellular electron transfer in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, where an array of nanoholes precludes or single window allows for direct microbeelectrode contacts. The ability to control and image cell/electrode interactions down to the single-cell level provide a powerful approach for ad ...
Principles of Neural Science
... A. At electrical synapses two cells are structurally connected by gap-junction channels. A gap-junction channel is actually a pair of hemichannels, one in each apposite cell, that match up in the gap junction through homophilic interactions. The channel thus connects the cytoplasm of the two cells a ...
... A. At electrical synapses two cells are structurally connected by gap-junction channels. A gap-junction channel is actually a pair of hemichannels, one in each apposite cell, that match up in the gap junction through homophilic interactions. The channel thus connects the cytoplasm of the two cells a ...
8th Grade Information Processing
... • Basic structural unit of the nervous system is the Neuron • Neurons are microscopic nerve cells that make up the brain, spinal cord, and nerves ...
... • Basic structural unit of the nervous system is the Neuron • Neurons are microscopic nerve cells that make up the brain, spinal cord, and nerves ...
Neural Axis Representing Target Range in the Auditory
... areas. (B) The FM processing area consists of Distance from theoretical 5.0-msec iso-BD contour line (x 100 umn) three major clusters of delay-sensitive neurons: FM,-FM2, FMi-FM3, and FM,-FM4 facilitation neurons. Each cluster shows odotopic representation. Iso-BD contours and range axes are schemat ...
... areas. (B) The FM processing area consists of Distance from theoretical 5.0-msec iso-BD contour line (x 100 umn) three major clusters of delay-sensitive neurons: FM,-FM2, FMi-FM3, and FM,-FM4 facilitation neurons. Each cluster shows odotopic representation. Iso-BD contours and range axes are schemat ...
The Nervous System Organization of the Nervous System
... and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of communication pathways from CNS to rest of the body. Communication occurs via electrical impulses (high speed pathway). Functions of the nervous system. Monitors the internal and external environments. Integrates sensory information. C ...
... and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system consisting of communication pathways from CNS to rest of the body. Communication occurs via electrical impulses (high speed pathway). Functions of the nervous system. Monitors the internal and external environments. Integrates sensory information. C ...
Myotatic Reflex
... 2) locations of source synapses on the target neuron. • for an individual synapse, effectiveness is related to synaptic location on the target neuron most effective {axon hillock >> soma >> proximal dendrite >> distal dendrite} least effective • a given amount of synaptic input will have more effect ...
... 2) locations of source synapses on the target neuron. • for an individual synapse, effectiveness is related to synaptic location on the target neuron most effective {axon hillock >> soma >> proximal dendrite >> distal dendrite} least effective • a given amount of synaptic input will have more effect ...
Module 4 SG - HallquistCPHS.com
... Module 4 is concerned with the functions of the body's neural and hormonal systems, which provide the basis for all human behavior. Under the direction of the brain, the nervous and endocrine systems coordinate a variety of voluntary and involuntary behaviors and serve as the body's mechanisms for c ...
... Module 4 is concerned with the functions of the body's neural and hormonal systems, which provide the basis for all human behavior. Under the direction of the brain, the nervous and endocrine systems coordinate a variety of voluntary and involuntary behaviors and serve as the body's mechanisms for c ...
Cellular Components of Nervous Tissue
... Whereas dendrites and the cell body can be characterized as domains of the neuron that receive afferents, the axon, at the other pole of the neuron, is responsible for transmitting neural information. This information may be primary, in the case of a sensory receptor, or processed information that h ...
... Whereas dendrites and the cell body can be characterized as domains of the neuron that receive afferents, the axon, at the other pole of the neuron, is responsible for transmitting neural information. This information may be primary, in the case of a sensory receptor, or processed information that h ...
Note
... Estimating the discriminability of two stimuli from the neural responses proceeds by calculating the distribution of responses to the two stimuli P(n|v) from data (where n = NT , the number of spikes); the stimuli v are noise (n) and tone plus noise (t). The discrimination task is to detect the ton ...
... Estimating the discriminability of two stimuli from the neural responses proceeds by calculating the distribution of responses to the two stimuli P(n|v) from data (where n = NT , the number of spikes); the stimuli v are noise (n) and tone plus noise (t). The discrimination task is to detect the ton ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs122.wordpress.com Pathways in
... 2nd order neuron Fibres of the 1st order neuron ends when it enters the brain stem and synapse with the 2nd order neuron The fibres pass through the brainstem 1st – through the (mid 5th) crus cerebri of midbrain 2nd – through the anterior part of the pons 3rd – in the medulla oblongata 80-85% of the ...
... 2nd order neuron Fibres of the 1st order neuron ends when it enters the brain stem and synapse with the 2nd order neuron The fibres pass through the brainstem 1st – through the (mid 5th) crus cerebri of midbrain 2nd – through the anterior part of the pons 3rd – in the medulla oblongata 80-85% of the ...
Intelligence and Patterns - Paradigm Shift International
... The cerebral cortex, the convoluted "grey matter" that makes up 80% of the human brain, is responsible for our ability to remember, think, reflect, empathize, communicate, adapt to new situations and plan for the future. The cortex first appeared in mammals, and it has a fundamentally simple repetit ...
... The cerebral cortex, the convoluted "grey matter" that makes up 80% of the human brain, is responsible for our ability to remember, think, reflect, empathize, communicate, adapt to new situations and plan for the future. The cortex first appeared in mammals, and it has a fundamentally simple repetit ...
Neurons
... Largely the result of negatively charged organic molecules within the cell. Limited diffusion of positively charged inorganic ions. Electrochemical gradients of Na+ and K+. ...
... Largely the result of negatively charged organic molecules within the cell. Limited diffusion of positively charged inorganic ions. Electrochemical gradients of Na+ and K+. ...
PDF file
... can serve as class supervision [7], attention [2], [3], and storage of time information [33]. Foreseeably, there are many other functions to which we can attribute feed-backward connections to. Gallistel reviewed [5]: “This problem-specific structure, they argue, is what makes learning possible.” “N ...
... can serve as class supervision [7], attention [2], [3], and storage of time information [33]. Foreseeably, there are many other functions to which we can attribute feed-backward connections to. Gallistel reviewed [5]: “This problem-specific structure, they argue, is what makes learning possible.” “N ...
Nervous System PPT 4 - PNS
... • sensory receptors impulse to interneurons in the spinal cord interneurons signal motor neurons impulses to skeletal muscle contracts, giving the response to the stimulus. • Pain is not felt until the brain receives nerve impulses. ...
... • sensory receptors impulse to interneurons in the spinal cord interneurons signal motor neurons impulses to skeletal muscle contracts, giving the response to the stimulus. • Pain is not felt until the brain receives nerve impulses. ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... Center for the study of Adaptive Control in Brain and Behavior (Acacia), University of Amsterdam, 1018 XA Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and 3Amsterdam Brain & Cognition, University of Amsterdam, 1018 WB Amsterdam, the Netherlands ...
... Center for the study of Adaptive Control in Brain and Behavior (Acacia), University of Amsterdam, 1018 XA Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and 3Amsterdam Brain & Cognition, University of Amsterdam, 1018 WB Amsterdam, the Netherlands ...
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE, CERE BRAL EDEMA
... Increased intracranial pressure results from either localized or generalized cerebral edema. The types of cerebral edema are vasogenic, cytotoxic, or interstitial. Increased capillary permeability causes vasogenic edema; this occurs with brain tumor, abscess, trauma, and hemorrhage. The fluid is loc ...
... Increased intracranial pressure results from either localized or generalized cerebral edema. The types of cerebral edema are vasogenic, cytotoxic, or interstitial. Increased capillary permeability causes vasogenic edema; this occurs with brain tumor, abscess, trauma, and hemorrhage. The fluid is loc ...
Optic Glomeruli and Their Inputs inDrosophilaShare an
... Hemisection through the brain labeled with anti-␣-tubulin and anti-GFP, showing the ensemble of type Col A LCN neurons in the lobula Animal preparation. Our animal setup (Fig. with converging axons to its corresponding Col A glomerulus. This lies ventral and medial to a glomerulus receiving terminal ...
... Hemisection through the brain labeled with anti-␣-tubulin and anti-GFP, showing the ensemble of type Col A LCN neurons in the lobula Animal preparation. Our animal setup (Fig. with converging axons to its corresponding Col A glomerulus. This lies ventral and medial to a glomerulus receiving terminal ...
Chapter Two
... Neuroscience Contributions to Psychopathology The Field of Neuroscience The role of the nervous system in disease and behavior The Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Somatic and autonomic branches ...
... Neuroscience Contributions to Psychopathology The Field of Neuroscience The role of the nervous system in disease and behavior The Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and spinal cord The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Somatic and autonomic branches ...
Self Organizing Maps: Fundamentals
... So far we have looked at networks with supervised training techniques, in which there is a target output for each input pattern, and the network learns to produce the required outputs. We now turn to unsupervised training, in which the networks learn to form their own classifications of the training ...
... So far we have looked at networks with supervised training techniques, in which there is a target output for each input pattern, and the network learns to produce the required outputs. We now turn to unsupervised training, in which the networks learn to form their own classifications of the training ...
Unit 2, the Brain
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... Action Potential Properties All-or-None Response: A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...