CMM/BIO4350
... peripheral nervous system (PNS) • Neural tube becomes central nervous system (CNS) • Somites become spinal vertebrae. Somites ...
... peripheral nervous system (PNS) • Neural tube becomes central nervous system (CNS) • Somites become spinal vertebrae. Somites ...
Normal Edema
... • Not all cells in the CNS are ‘equal’: while some disease processes affect some groups of cells more than others (‘selective vulnerability’), other disease processes could affect other areas more. • Not all areas in the brain are equal: most areas in the brain have specific functions: a same diseas ...
... • Not all cells in the CNS are ‘equal’: while some disease processes affect some groups of cells more than others (‘selective vulnerability’), other disease processes could affect other areas more. • Not all areas in the brain are equal: most areas in the brain have specific functions: a same diseas ...
The Nervous System - Marshall Middle
... responsible for the body functions which are not under conscious control like the heartbeat or the digestive system. The smooth operation of the peripheral nervous system is achieved by dividing it into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. These are opposing actions and check on each other to pr ...
... responsible for the body functions which are not under conscious control like the heartbeat or the digestive system. The smooth operation of the peripheral nervous system is achieved by dividing it into sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. These are opposing actions and check on each other to pr ...
Ch. 35 Nervous System ppt - Jamestown Public Schools
... muscles attach to the lens to change its shape, to help you adjust your eyes’ focus to see near or distant objects Retina - where light is focused onto from the lens; here, light energy is converted into nerve impulses that are carried to the CNS ...
... muscles attach to the lens to change its shape, to help you adjust your eyes’ focus to see near or distant objects Retina - where light is focused onto from the lens; here, light energy is converted into nerve impulses that are carried to the CNS ...
Nervous System
... from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor (Efferent) Neurons carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
... from the sense receptors to the CNS. Motor (Efferent) Neurons carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscles and glands. Interneurons connect the two neurons. ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 48.1: Neuron
... o Current that depolarizes axon membrane ahead of action potential can’t produce another action potential behind it Evolutionary Adaptations of Axon Structure Axon diameter impacts speed of action potentials o Increased width = increased speed o Because resistance to electrical current flow is inv ...
... o Current that depolarizes axon membrane ahead of action potential can’t produce another action potential behind it Evolutionary Adaptations of Axon Structure Axon diameter impacts speed of action potentials o Increased width = increased speed o Because resistance to electrical current flow is inv ...
The Nervous System
... • Impulse goes from neuronal axon to another neuron or a receptor – This junction called ---synapse – neurotransmitters ...
... • Impulse goes from neuronal axon to another neuron or a receptor – This junction called ---synapse – neurotransmitters ...
A1987K582900002
... y-aminobutyric acid. Immunocytochemical methods were used to localize GAD within neuronal sornata and dendrites that had the features of aspinous and sparsely-spinous stellate cells. In addition, GAD-immunoreactive axon terminals formed symmetric synapses with every neuronal type in the cerebral cor ...
... y-aminobutyric acid. Immunocytochemical methods were used to localize GAD within neuronal sornata and dendrites that had the features of aspinous and sparsely-spinous stellate cells. In addition, GAD-immunoreactive axon terminals formed symmetric synapses with every neuronal type in the cerebral cor ...
TECHNIQUES2001
... • High resolution images constructed from measurements of waves that H-atoms emit when activated by radio-frequency waves in a magnetic field. • Higher the density of Hydrogen atoms, the higher the density of tissue. ...
... • High resolution images constructed from measurements of waves that H-atoms emit when activated by radio-frequency waves in a magnetic field. • Higher the density of Hydrogen atoms, the higher the density of tissue. ...
TEST REVIEW FOR NERVOUS SYSTEM
... o Study drawings in worksheet packet and ID’s I have given you. I will/could give you the picture from your book or in the packet. o IF you did a good chart…study that!! o Make sure you can answer the following questions and/or finish the statement…..TODAY…you need to review today in class by answer ...
... o Study drawings in worksheet packet and ID’s I have given you. I will/could give you the picture from your book or in the packet. o IF you did a good chart…study that!! o Make sure you can answer the following questions and/or finish the statement…..TODAY…you need to review today in class by answer ...
action potential
... Be able to identify the following morphological features of the neuron and to describe the role they play in receiving and transmitting neural impulses. (basic cell of brain and peripheral nervous system) a. neuron (contains nucleus with RNA and metabolic components) b. cell body (soma) (processes t ...
... Be able to identify the following morphological features of the neuron and to describe the role they play in receiving and transmitting neural impulses. (basic cell of brain and peripheral nervous system) a. neuron (contains nucleus with RNA and metabolic components) b. cell body (soma) (processes t ...
Nervous System - teacherver.com
... Three Overlapping Functions 1) Much like a sentry, it uses its millions of sensory receptors to monitor changes occurring both inside and outside the body. These changes are called stimuli and the gathered information is called sensory input. 2) It processes and interprets the sensory input and mak ...
... Three Overlapping Functions 1) Much like a sentry, it uses its millions of sensory receptors to monitor changes occurring both inside and outside the body. These changes are called stimuli and the gathered information is called sensory input. 2) It processes and interprets the sensory input and mak ...
Can an Injured Spinal Cord Be Fixed?
... epithelial cells organized into taste buds, which are scattered on the tongue. Binding of a sugar molecule to a receptor cell initiates a signal transduction pathway. Sodium channels open, Na+ ions diffuse into the cell, and the membrane depolarizes. ...
... epithelial cells organized into taste buds, which are scattered on the tongue. Binding of a sugar molecule to a receptor cell initiates a signal transduction pathway. Sodium channels open, Na+ ions diffuse into the cell, and the membrane depolarizes. ...
Communication as an emergent metaphor for neuronal operation
... practical problems [4]. At the same time the same devices were proposed as models of cognition capable of explaining both higher level mental processes [5] and low level information processing in the brain [6]. However, these promises were based on the assumption that the computational model capture ...
... practical problems [4]. At the same time the same devices were proposed as models of cognition capable of explaining both higher level mental processes [5] and low level information processing in the brain [6]. However, these promises were based on the assumption that the computational model capture ...
Science - edl.io
... messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord inside your backbone. Motor nerves carry messages back from the brain to all the muscles and glands in your body. So how do they pass along messages? Through the marvels of chemistry and a kind of electricity! Neurons a ...
... messages to the brain and generally connect to the brain through the spinal cord inside your backbone. Motor nerves carry messages back from the brain to all the muscles and glands in your body. So how do they pass along messages? Through the marvels of chemistry and a kind of electricity! Neurons a ...
The Peripheral and Autonomic Nervous Systems
... body. The parasympathetic division innervates only visceral structures serviced by cranial nerves or lying within the ...
... body. The parasympathetic division innervates only visceral structures serviced by cranial nerves or lying within the ...
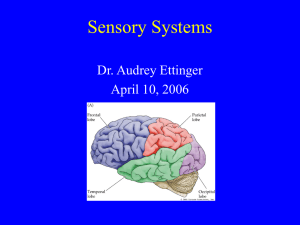
Sensory Systems - Cedar Crest College
... • “What kind” information is transmitted by which neurons respond to the signal • “How much” information is transmitted by the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
... • “What kind” information is transmitted by which neurons respond to the signal • “How much” information is transmitted by the number of action potentials sent – The action potential is an “all or none” signal ...
Brain Organization or, why everyone should have some
... Temporal Occipital In general they have function but remember this is in general ...
... Temporal Occipital In general they have function but remember this is in general ...
The Nervous System
... Purpose - Nerve Impulse Impulse - electrical signals carried by nervous system An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. The Nerve Impulse is like a chain of dominoes Ions pass through the cell membrane, passing the message along ...
... Purpose - Nerve Impulse Impulse - electrical signals carried by nervous system An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the environment. The Nerve Impulse is like a chain of dominoes Ions pass through the cell membrane, passing the message along ...
Mathematical neuroscience: from neurons to circuits to systems
... gating mechanisms were sufficient to explain the generation of action potentials, i.e. explosive all or none voltage spikes that initiate synaptic signaling between neurons. Using the same set of current-balance equations, Hodgkin and Huxley demonstrated how action potentials result from a stereotyped ...
... gating mechanisms were sufficient to explain the generation of action potentials, i.e. explosive all or none voltage spikes that initiate synaptic signaling between neurons. Using the same set of current-balance equations, Hodgkin and Huxley demonstrated how action potentials result from a stereotyped ...
Slides - gserianne.com
... Intro to Cell Response/Signaling • How does a neuron “know” its being stimulated? • When stimulated by multiple inputs, how does a neuron “know” whether it should send a nerve impulse (action potential) or not? Answer: Changes in cellular ionic composition But recall that ions are ‘hydrated’ and ca ...
... Intro to Cell Response/Signaling • How does a neuron “know” its being stimulated? • When stimulated by multiple inputs, how does a neuron “know” whether it should send a nerve impulse (action potential) or not? Answer: Changes in cellular ionic composition But recall that ions are ‘hydrated’ and ca ...
Slide ()
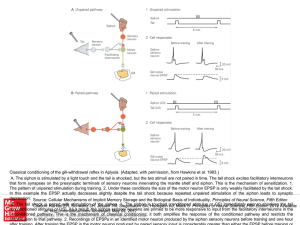
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...