Supplement: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... Supplementary Figure 1. Layer 5 pyramidal cells are interconnected by several synaptic boutons that are within one length constant of the axon. Simultaneous patch clamp recording from three layer 5 pyramidal neurons revealed synaptic connections as illustrated in the lower left schematic. Anatomical ...
... Supplementary Figure 1. Layer 5 pyramidal cells are interconnected by several synaptic boutons that are within one length constant of the axon. Simultaneous patch clamp recording from three layer 5 pyramidal neurons revealed synaptic connections as illustrated in the lower left schematic. Anatomical ...
handout
... control state and the task state. Researchers carefully choose each state so as to isolate as best as possible a limited number of ...
... control state and the task state. Researchers carefully choose each state so as to isolate as best as possible a limited number of ...
Group Redundancy Measures Reveal Redundancy Reduction in the
... auditory modality. Under two different coding paradigms, we show differences in both information content and group redundancies between Ie and cortical auditory neurons. Single Ie neurons carry more information about the presented stimulus, but are also more redundant. On the other hand, auditory co ...
... auditory modality. Under two different coding paradigms, we show differences in both information content and group redundancies between Ie and cortical auditory neurons. Single Ie neurons carry more information about the presented stimulus, but are also more redundant. On the other hand, auditory co ...
The Brain - Wando High School
... Neuron- a nerve cell that transmits electrical and chemical information. --Dendrites: part of the neuron that receives info. from the axon. --Axons: carries messages to dendrites of another neuron. --Synapse: junction point of two or more neurons. --Vesicles: bubble-like containers of neurotransmitt ...
... Neuron- a nerve cell that transmits electrical and chemical information. --Dendrites: part of the neuron that receives info. from the axon. --Axons: carries messages to dendrites of another neuron. --Synapse: junction point of two or more neurons. --Vesicles: bubble-like containers of neurotransmitt ...
... Question 9: What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism? Answer: The maintenance of the body functions in response to changes in the body by working together of various integrated body systems is known as coordination. All the movements that occur in response to stimuli ...
THE NeurobiologyOF “We”
... the two middle fingers) is especially important because it touches all three major parts of our brain: the cortex, limbic area, and brainstem as well as the body-proper. “It’s the middle prefrontal fibers which map out the internal states of others,” he adds. “And they do this not only within one br ...
... the two middle fingers) is especially important because it touches all three major parts of our brain: the cortex, limbic area, and brainstem as well as the body-proper. “It’s the middle prefrontal fibers which map out the internal states of others,” he adds. “And they do this not only within one br ...
Newswire Newswire - Rockefeller University
... of Merck Research Laboratories and is now a member of the Broad Institute, the annual award is given for work in any field of neuroscience. The prize is endowed through a gift from Merck and includes a $125,000 grant. Bargmann studies the relationships between genes, experience, the nervous system, ...
... of Merck Research Laboratories and is now a member of the Broad Institute, the annual award is given for work in any field of neuroscience. The prize is endowed through a gift from Merck and includes a $125,000 grant. Bargmann studies the relationships between genes, experience, the nervous system, ...
Chapter 9-中樞神經系統檔案
... Figure 9.20 Withdrawal and crossextensor reflexes. In responses to the activation of a nociceptors, an afferent neuron synapses on an excitatory interneuron and an inhibitory interneuron , ultimately producing contraction of the hamstrings and relaxation of the quadriceps in the affected leg, and ...
... Figure 9.20 Withdrawal and crossextensor reflexes. In responses to the activation of a nociceptors, an afferent neuron synapses on an excitatory interneuron and an inhibitory interneuron , ultimately producing contraction of the hamstrings and relaxation of the quadriceps in the affected leg, and ...
Chapter 9-中樞神經系統檔案
... Figure 9.20 Withdrawal and crossextensor reflexes. In responses to the activation of a nociceptors, an afferent neuron synapses on an excitatory interneuron and an inhibitory interneuron , ultimately producing contraction of the hamstrings and relaxation of the quadriceps in the affected leg, and ...
... Figure 9.20 Withdrawal and crossextensor reflexes. In responses to the activation of a nociceptors, an afferent neuron synapses on an excitatory interneuron and an inhibitory interneuron , ultimately producing contraction of the hamstrings and relaxation of the quadriceps in the affected leg, and ...
resting membrane potential
... Figure 7.4 Functional classes of neurons. Afferent neurons originate in the periphery with sensory or visceral receptors. The peripheral axons of afferent neurons are part of the peripheral nervous system, but the axon terminals are located in the central nervous system, where they communicate with ...
... Figure 7.4 Functional classes of neurons. Afferent neurons originate in the periphery with sensory or visceral receptors. The peripheral axons of afferent neurons are part of the peripheral nervous system, but the axon terminals are located in the central nervous system, where they communicate with ...
Sensation
... one another, allowing the vibrations of the eardrum to be carried to the inner ear. Vibrations then travel to the Oval Window, Cochlea, and Basilar Membrane before they reach the receptor cells in the Organ of Corti and finally reach the brain. ...
... one another, allowing the vibrations of the eardrum to be carried to the inner ear. Vibrations then travel to the Oval Window, Cochlea, and Basilar Membrane before they reach the receptor cells in the Organ of Corti and finally reach the brain. ...
Mechanism for propagation of rate signals through a 10
... 3.3. Network activity modulated by the synaptic time constant It is worth noting that the synaptic time constant, τsyn , remarkably affects the network dynamics. Figure 4(a) shows f10 versus τsyn for different noise intensities. The curves are unimodal with a peak at τsyn = 3 ms. This is related to th ...
... 3.3. Network activity modulated by the synaptic time constant It is worth noting that the synaptic time constant, τsyn , remarkably affects the network dynamics. Figure 4(a) shows f10 versus τsyn for different noise intensities. The curves are unimodal with a peak at τsyn = 3 ms. This is related to th ...
Cortical and subcortical anatomy: basics and applied
... This disclosure form must be included as the third page of your Course Notes and the third slide of your presentation. It is the policy of the Canadian Neurological Sciences Federation to insure balance, independence, objectivity and scientific rigor in all of its education programs. Faculty partici ...
... This disclosure form must be included as the third page of your Course Notes and the third slide of your presentation. It is the policy of the Canadian Neurological Sciences Federation to insure balance, independence, objectivity and scientific rigor in all of its education programs. Faculty partici ...
(580.422) Lecture 7, Synaptic Transmission
... is a simplification; usually more than one T must bind and there are additional TR and D states. ...
... is a simplification; usually more than one T must bind and there are additional TR and D states. ...
NEUROSCIENCE 2. THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM 2.1
... stand for the cognitive capabilities of the brain. Connecting each of the hemispheres is the corpus callosum as well as several additional commissures. One of the most important parts of the cerebral hemispheres is the cortex, which is made up of gray matter covering the surface of the brain. Functi ...
... stand for the cognitive capabilities of the brain. Connecting each of the hemispheres is the corpus callosum as well as several additional commissures. One of the most important parts of the cerebral hemispheres is the cortex, which is made up of gray matter covering the surface of the brain. Functi ...
Introduction
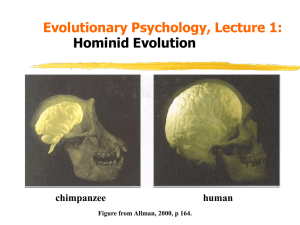
... Horrobin (1998) proposed that during the course of human evolution specific biochemical alterations led to changes in metabolism which enabled the human brain to expand in size and function more efficiently. Neural connectivity is determined by the availability of phospholipids, which make up 60 ...
... Horrobin (1998) proposed that during the course of human evolution specific biochemical alterations led to changes in metabolism which enabled the human brain to expand in size and function more efficiently. Neural connectivity is determined by the availability of phospholipids, which make up 60 ...
Accurate Reconstruction of Neuronal Morphology
... • Model for the development of interneuronal connectivity: competition for neurotrophic factors. ...
... • Model for the development of interneuronal connectivity: competition for neurotrophic factors. ...
Poster
... According to the National Institutes of Health, 5.1 million Americans have Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which affects memory and the ability to learn. In long-term potentiation (LTP), a correlate of learning and memory, the number of receptors at the synapse between neurons, increases. Calcium/calmodul ...
... According to the National Institutes of Health, 5.1 million Americans have Alzheimer’s disease (AD), which affects memory and the ability to learn. In long-term potentiation (LTP), a correlate of learning and memory, the number of receptors at the synapse between neurons, increases. Calcium/calmodul ...
Drugs and the Brain
... We know that the same sort of mechanisms involved in the development of tolerance can eventually lead to profound changes in neurons and brain circuits, with the potential to severely compromise the long-term health of the brain. For example, glutamate is another neurotransmitter that influences the ...
... We know that the same sort of mechanisms involved in the development of tolerance can eventually lead to profound changes in neurons and brain circuits, with the potential to severely compromise the long-term health of the brain. For example, glutamate is another neurotransmitter that influences the ...
Voltage-sensitive dye Glowing thoughts RUB
... special section of the journal Neurophotonics that honors Prof. Amiram Grinvald, one of the most influencing researchers in this field. Boosting the voltage Dirk Jancke has given the phrase “a light-bulb moment” a whole new meaning. In his laboratory he turns the activity of brain cells into light, ...
... special section of the journal Neurophotonics that honors Prof. Amiram Grinvald, one of the most influencing researchers in this field. Boosting the voltage Dirk Jancke has given the phrase “a light-bulb moment” a whole new meaning. In his laboratory he turns the activity of brain cells into light, ...
123COM.CHP:Corel VENTURA
... f low within the vascular network. These findings have notable implications for functional brain mapping using hemodynamic changes as a ‘proxy’ for neural activity. On the one hand, the finding that intrinsic signals identif y reasonably well the area of activation, assessed by electrophysiological ...
... f low within the vascular network. These findings have notable implications for functional brain mapping using hemodynamic changes as a ‘proxy’ for neural activity. On the one hand, the finding that intrinsic signals identif y reasonably well the area of activation, assessed by electrophysiological ...
PoNS Fact Sheet - Helius Medical Technologies
... activates two major cranial nerves – the lingual nerve (part of the trigeminal nerve) and the chorda tympani (part of the facial nerve). Electrical stimulation of the cranial nerves creates a flow of neural impulses that are then delivered directly into the brain stem and cerebellum – the main contr ...
... activates two major cranial nerves – the lingual nerve (part of the trigeminal nerve) and the chorda tympani (part of the facial nerve). Electrical stimulation of the cranial nerves creates a flow of neural impulses that are then delivered directly into the brain stem and cerebellum – the main contr ...
Activity Overview Continued - The University of Texas Health
... different regions of the human body: brain, spinal cord, hands, arms, legs, and feet. It is recommended that the teacher draw a simple outline of the human body on butcher paper or use masking tape or chalk to outline the human body on the floor as shown in the diagram. The teacher may wish to do th ...
... different regions of the human body: brain, spinal cord, hands, arms, legs, and feet. It is recommended that the teacher draw a simple outline of the human body on butcher paper or use masking tape or chalk to outline the human body on the floor as shown in the diagram. The teacher may wish to do th ...
Nervous System PPT
... • Neural plasticity describes the ability of the nervous system to be modified after birth • Changes can strengthen or weaken signaling at a synapse ...
... • Neural plasticity describes the ability of the nervous system to be modified after birth • Changes can strengthen or weaken signaling at a synapse ...