Assignment CHE-04 TMA-01,02 Year 2005
... 4. For nitrogen gas, the van der Waals constant, a, has the value 0.1408 Pa m6 mol─2. At 298.2 K, 1 mol of nitrogen gas is kept in a vessel of volume 4.894×10─2.m3. (i) Calculate pressure of the gas, assuming ideal behaviour. (ii) Assuming that the gas obeys van der Waals equation and that the van d ...
... 4. For nitrogen gas, the van der Waals constant, a, has the value 0.1408 Pa m6 mol─2. At 298.2 K, 1 mol of nitrogen gas is kept in a vessel of volume 4.894×10─2.m3. (i) Calculate pressure of the gas, assuming ideal behaviour. (ii) Assuming that the gas obeys van der Waals equation and that the van d ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... 2) Fairly unreactive, so used for pipes, pumps, reaction vessels 3) Usually found in Ti4+ state, no d-electrons, colorless/white 4) TiO2 (titanium(IV) oxide) used as white pigment in paper, paint, etc… 5) Ti3+ is stable: Ti(H2O)63+ complex ion is purple (1 d-electron) 6) Ti2+ is not very stable, but ...
... 2) Fairly unreactive, so used for pipes, pumps, reaction vessels 3) Usually found in Ti4+ state, no d-electrons, colorless/white 4) TiO2 (titanium(IV) oxide) used as white pigment in paper, paint, etc… 5) Ti3+ is stable: Ti(H2O)63+ complex ion is purple (1 d-electron) 6) Ti2+ is not very stable, but ...
CE3503 Expectations – Equilibrium Reactions that proceed to
... the other. The equilibrium position for a strong acid, for example, lies well to the right with little undissociated acid present, while that for a weak acid may lie more toward the middle, i.e. equal parts dissociated and undissociated acid. The general form of the equilibrium constant is written a ...
... the other. The equilibrium position for a strong acid, for example, lies well to the right with little undissociated acid present, while that for a weak acid may lie more toward the middle, i.e. equal parts dissociated and undissociated acid. The general form of the equilibrium constant is written a ...
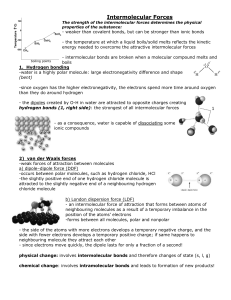
Intermolecular Forces
... side with fewer electrons develops a temporary positive charge; if same happens to neighbouring molecule they attract each other - since electrons move quickly, the dipole lasts for only a fraction of a second! physical change: involves intermolecular bonds and therefore changes of state (s, l, g) c ...
... side with fewer electrons develops a temporary positive charge; if same happens to neighbouring molecule they attract each other - since electrons move quickly, the dipole lasts for only a fraction of a second! physical change: involves intermolecular bonds and therefore changes of state (s, l, g) c ...
Final Study Questions - Porterville College Home
... D) Ketone. E) Carboxyl. 55. Identify the type of organic compound shown: (CH3)3N A) ester B) ketone C) aldehyde D) amine E) none of these 56. Why does octane have a higher boiling point than ethane, 126°C versus –89°C? A) Octane has stronger London dispersion forces than ethane. B) Octane exhibits h ...
... D) Ketone. E) Carboxyl. 55. Identify the type of organic compound shown: (CH3)3N A) ester B) ketone C) aldehyde D) amine E) none of these 56. Why does octane have a higher boiling point than ethane, 126°C versus –89°C? A) Octane has stronger London dispersion forces than ethane. B) Octane exhibits h ...
Size match between cation and host cavity Electrostatic charge
... In kinetic template effect the preorganised metal complex actually forms In thermodynamic template effect the effect is based on the ability of the metal cation to select the complementary ligand from the equilibrium mixture of products -> this way te equilibrium of the reaction can be driven toward ...
... In kinetic template effect the preorganised metal complex actually forms In thermodynamic template effect the effect is based on the ability of the metal cation to select the complementary ligand from the equilibrium mixture of products -> this way te equilibrium of the reaction can be driven toward ...
in-situ by 1,2,4-triazole schiff bases and different metal salts A. Mouadili
... spectra in Figures 4, it is clear that the catalytic conversion of catechol to o-quinone is influenced by the nature of the solvent. According to studies by Banu et al., [23] in 2012, the special properties of solvents, such as dielectric constant, dipole moment and polarity complex in these solvent ...
... spectra in Figures 4, it is clear that the catalytic conversion of catechol to o-quinone is influenced by the nature of the solvent. According to studies by Banu et al., [23] in 2012, the special properties of solvents, such as dielectric constant, dipole moment and polarity complex in these solvent ...
Answers to Topic 15 Exercises - A
... Add a small quantity of a suitable ligand to each in order to identify the colour. Choose the filter which gives the largest absorbance, and measure the absorbance of each sample using this filter. Plot a graph of absorbance against concentration. Take the sample of unknown concentration, add the li ...
... Add a small quantity of a suitable ligand to each in order to identify the colour. Choose the filter which gives the largest absorbance, and measure the absorbance of each sample using this filter. Plot a graph of absorbance against concentration. Take the sample of unknown concentration, add the li ...
Periodicity Notes
... a. definition: species that can donate a pair of electrons to the central metal ion. Most common examples are water, ammonia, and chloride ion (show that all these have unbonded electron pairs that may be donated to a metal (electron poor species) b. d-block metals have low energy unfilled d-orbital ...
... a. definition: species that can donate a pair of electrons to the central metal ion. Most common examples are water, ammonia, and chloride ion (show that all these have unbonded electron pairs that may be donated to a metal (electron poor species) b. d-block metals have low energy unfilled d-orbital ...
A study on the nickel(II)
... Calculations were carried out at the ab initio Hartree– Fock level with basis set CEP-31G implemented in GAUSSIAN ’98 program. Computations of square-planar nickel complex were done at the Academic Computer Center ‘Cyfronet’ in Cracow. First the geometry of the complex was optimized. Then the freque ...
... Calculations were carried out at the ab initio Hartree– Fock level with basis set CEP-31G implemented in GAUSSIAN ’98 program. Computations of square-planar nickel complex were done at the Academic Computer Center ‘Cyfronet’ in Cracow. First the geometry of the complex was optimized. Then the freque ...
Chemical Kinetics - Review
... Chemical Kinetics - Review Work should be shown for all calculations. ...
... Chemical Kinetics - Review Work should be shown for all calculations. ...
b - PianetaChimica
... Mass spectrometry is an important tool in the determination of the structures of organic compounds. The process begins with the ionisation of the sample to form a positively charged ion, the molecular ion. At this stage, the molecular ion commonly fragments to form additional cations. These cations ...
... Mass spectrometry is an important tool in the determination of the structures of organic compounds. The process begins with the ionisation of the sample to form a positively charged ion, the molecular ion. At this stage, the molecular ion commonly fragments to form additional cations. These cations ...
the nature of acids, bases, and salts
... can split apart to form a hydrogen ion and a hydroxide ion. H2O → H+ + OHSince it produces a hydrogen ion, water is an acid. However, the fact that it produces a hydroxide ion also makes it a base. This reaction occurs only to a very small extent. In pure water only one out of 10 million molecules o ...
... can split apart to form a hydrogen ion and a hydroxide ion. H2O → H+ + OHSince it produces a hydrogen ion, water is an acid. However, the fact that it produces a hydroxide ion also makes it a base. This reaction occurs only to a very small extent. In pure water only one out of 10 million molecules o ...
Chem 310 Lectures by: Dr. Muhammad D. Bala Office: Block H, 3
... Degenerate orbitals are filled according to Hund's rules: • One electron is added to each of the degenerate orbitals in a subshell before a second electron is added to any orbital in the subshell Î lowest energy subshell filled in first. • Electrons are added to a subshell with the same value of the ...
... Degenerate orbitals are filled according to Hund's rules: • One electron is added to each of the degenerate orbitals in a subshell before a second electron is added to any orbital in the subshell Î lowest energy subshell filled in first. • Electrons are added to a subshell with the same value of the ...
$doc.title
... with one oxygen atom to form one molecule of water. On the atomic scale, we never see an example of one and a half hydrogen atoms combining with an oxygen atom. This was one of the first observations of the early chemists who explored the properties of chemical elements. This observation is known as ...
... with one oxygen atom to form one molecule of water. On the atomic scale, we never see an example of one and a half hydrogen atoms combining with an oxygen atom. This was one of the first observations of the early chemists who explored the properties of chemical elements. This observation is known as ...
TFG_QU Gonzálvez Noguera, Miguel Agustín
... solvated electron. The reactions have been described (including two Nobel prices) as occurring via two types of mechanisms that have been labeled as inner- and outer- sphere, depending on the type of activation needed for the process to take place. 3.3.1. Inner-sphere electron transfer Inner sphere ...
... solvated electron. The reactions have been described (including two Nobel prices) as occurring via two types of mechanisms that have been labeled as inner- and outer- sphere, depending on the type of activation needed for the process to take place. 3.3.1. Inner-sphere electron transfer Inner sphere ...