DSD Code (continued)
... The plasma does not appear except as the source of Debye shielding. The simulations show strongly coupled plasma crystals, but the force is isotropic, and leads to isotropic structures (bcc & fcc). Experiments can show a strong anisotropy between flow direction and the transverse plane. In s ...
... The plasma does not appear except as the source of Debye shielding. The simulations show strongly coupled plasma crystals, but the force is isotropic, and leads to isotropic structures (bcc & fcc). Experiments can show a strong anisotropy between flow direction and the transverse plane. In s ...
Absorption of High-frequency Electromagnetic Energy in a High
... in a frequency range where Re N ^> 1, Cherenkov absorption will also occur when the thermal motion of charged particles across the magnetic field is taken into account. Formally, this result follows from the fact that with со ^> œce it can be assumed in Eq. (7) that sin cocei — CJOCQÍ and, as a cons ...
... in a frequency range where Re N ^> 1, Cherenkov absorption will also occur when the thermal motion of charged particles across the magnetic field is taken into account. Formally, this result follows from the fact that with со ^> œce it can be assumed in Eq. (7) that sin cocei — CJOCQÍ and, as a cons ...
On the anomalous mass defect of strange stars in the Field
... defects characterized by energy excesses with respect to the energies they would have to be (stable) bound systems. Anomalous mass defects were interpreted in terms of a catastrophic additivity violation of the internal energy due to the very intense gravitational fields in the interior of such supe ...
... defects characterized by energy excesses with respect to the energies they would have to be (stable) bound systems. Anomalous mass defects were interpreted in terms of a catastrophic additivity violation of the internal energy due to the very intense gravitational fields in the interior of such supe ...
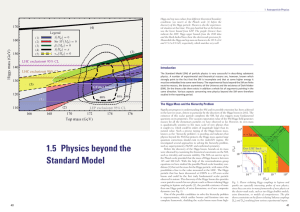
1.5 physics beyond the Standard Model
... physics beyond the SM that protects the Higgs mass against large quantum corrections should exist in the multi-TeV regime. We investigated several approaches to solving the hierarchy problem, such as supersymmetry (SUSY) and conformal symmetry. Before the discovery of the Higgs boson, bounds on its ...
... physics beyond the SM that protects the Higgs mass against large quantum corrections should exist in the multi-TeV regime. We investigated several approaches to solving the hierarchy problem, such as supersymmetry (SUSY) and conformal symmetry. Before the discovery of the Higgs boson, bounds on its ...
chemical potential dependence of particle ratios within a
... number, i. e., the higher the strangeness quantum number is, the smaller the difference between antibaryons and baryons. It is interesting to note that even the yield of very rarely produced strange particles like Ω is well described by the model. The particle ratios are found to be consistent with u ...
... number, i. e., the higher the strangeness quantum number is, the smaller the difference between antibaryons and baryons. It is interesting to note that even the yield of very rarely produced strange particles like Ω is well described by the model. The particle ratios are found to be consistent with u ...
681_1.PDF
... In this Section we propose another scheme of a microwave-driven plasma accelerator. As in the case of BIT, the goal is to create an accelerating medium (magnetized plasma) with the following electromagnetic properties with respect to the accelerating electromagnetic wave propagating in x— direction, ...
... In this Section we propose another scheme of a microwave-driven plasma accelerator. As in the case of BIT, the goal is to create an accelerating medium (magnetized plasma) with the following electromagnetic properties with respect to the accelerating electromagnetic wave propagating in x— direction, ...
How to teach the Standard Model
... Early Particle Physics J.J. Thomson at work on his electron l t discovery. ...
... Early Particle Physics J.J. Thomson at work on his electron l t discovery. ...
The Interacting Gluon Model: a review
... to study energy deposition, connecting it with the apparent dominance of multiparticle production processes by the gluonic content of the impinging hadrons, hence its name: Interacting Gluon Model (IGM) [11]. Its original application to the description of inelasticity [12] and multiparticle producti ...
... to study energy deposition, connecting it with the apparent dominance of multiparticle production processes by the gluonic content of the impinging hadrons, hence its name: Interacting Gluon Model (IGM) [11]. Its original application to the description of inelasticity [12] and multiparticle producti ...
Document
... Example 4 In the preceding example, what is the frequency, wavelength of the emitted photon, and in what part of the EM spectrum is it in? E = 12.1 [eV]. First convert this to [J]. ...
... Example 4 In the preceding example, what is the frequency, wavelength of the emitted photon, and in what part of the EM spectrum is it in? E = 12.1 [eV]. First convert this to [J]. ...
Experimental and numerical study of modulation of ionization front propagation velocity in ?s helium plasma gun discharge with nitrogen admixture
... coincides with the higher production of N 2 +* lines in the penning mixtures while for higher N 2 amounts, electron impact excitation of N 2 second positive system becomes predominant and consistent with a lower ionization degree of the plasma. While no detailed analysis has for yet been performed, ...
... coincides with the higher production of N 2 +* lines in the penning mixtures while for higher N 2 amounts, electron impact excitation of N 2 second positive system becomes predominant and consistent with a lower ionization degree of the plasma. While no detailed analysis has for yet been performed, ...
Jun Takahashi for the STAR collaboration, SQM2008 Beijing, China
... arXiv:nucl-th/0612033v1: Local and Global strangeness inhomogenuities at freeze-out conditions. PRC_73_024902: Inhomogeneous freeze-out in relativistic heavy ion collisions. Jun Takahashi for the STAR collaboration, SQM2008 Beijing, China ...
... arXiv:nucl-th/0612033v1: Local and Global strangeness inhomogenuities at freeze-out conditions. PRC_73_024902: Inhomogeneous freeze-out in relativistic heavy ion collisions. Jun Takahashi for the STAR collaboration, SQM2008 Beijing, China ...
Plasma Physics Definitions
... Before application of the potential, gas molecules are electrically neutral and the gas at room temperature will contain very few if any charged particles. Occasionally however, a free electron may be released from a molecule by the interaction of, for example, a cosmic ray or other natural radiatio ...
... Before application of the potential, gas molecules are electrically neutral and the gas at room temperature will contain very few if any charged particles. Occasionally however, a free electron may be released from a molecule by the interaction of, for example, a cosmic ray or other natural radiatio ...
Strangeness production
Strangeness production is a signature and a diagnostic tool of quark–gluon plasma (or QGP) formation and properties. Unlike up and down quarks, from which everyday matter is made, strange quarks are formed in pair-production processes in collisions between constituents of the plasma. The dominant mechanism of production involves gluons only present when matter has become a quark–gluon plasma. When quark–gluon plasma disassembles into hadrons in a breakup process, the high availability of strange antiquarks helps to produce antimatter containing multiple strange quarks, which is otherwise rarely made. Similar considerations are at present made for the heavier charm flavor, which is made at the beginning of the collision process in the first interactions and is only abundant in the high-energy environments of CERN's Large Hadron Collider.