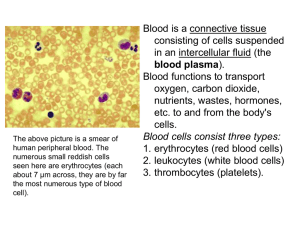
Ready for Review
... Ready for Review This chapter covers human anatomy and the function of body systems. To understand the location of specific signs or symptoms, it is necessary to examine topographic anatomy. The respiratory system consists of the lungs and the airway. This system functions to take in air through ...
... Ready for Review This chapter covers human anatomy and the function of body systems. To understand the location of specific signs or symptoms, it is necessary to examine topographic anatomy. The respiratory system consists of the lungs and the airway. This system functions to take in air through ...
PowerPoint - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web Pages
... your blood) due to their high content of the iron protein complex called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the molecule that allows erythrocytes to bind oxygen and carry it throughout the body. ...
... your blood) due to their high content of the iron protein complex called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is the molecule that allows erythrocytes to bind oxygen and carry it throughout the body. ...
1 Unit 1: The Body as a Whole
... These cellular requirements are reflected in the air we breathe, the food we eat, and the waste we excrete. Homeostasis is the maintenance of relatively constant conditions within the body's internal environment. Many physiological parameters, such as blood glucose and body temperature, are precisel ...
... These cellular requirements are reflected in the air we breathe, the food we eat, and the waste we excrete. Homeostasis is the maintenance of relatively constant conditions within the body's internal environment. Many physiological parameters, such as blood glucose and body temperature, are precisel ...
Chapter 15-1 Body Organization and Homeostasis • Levels of
... - organ – different kinds of tissues doing a job; ex. heart, blood vessels - organ system – group of organs working together; ex. circulatory • Homeostasis: body’s tendency to keep internal balance in spite of changes in external environment; ex. when body needs food, the brain sends signals that yo ...
... - organ – different kinds of tissues doing a job; ex. heart, blood vessels - organ system – group of organs working together; ex. circulatory • Homeostasis: body’s tendency to keep internal balance in spite of changes in external environment; ex. when body needs food, the brain sends signals that yo ...
File
... • At constant temperature, the volume of a compressible fluid is inversely proportional to pressure o V ↑ then P↓ Think about when your breathe o V ↓ then P↑ ...
... • At constant temperature, the volume of a compressible fluid is inversely proportional to pressure o V ↑ then P↓ Think about when your breathe o V ↓ then P↑ ...
UNIT 3 PART 1 LIFE FUNCTIONS
... to maintain homeostasis. The nervous system acts quickly and sends its message to specific parts of the body. • The endocrine system helps to maintain homeostasis by releasing chemicals into the blood. When the chemicals reach the target organ, a reaction occurs. This is slower than the nervous syst ...
... to maintain homeostasis. The nervous system acts quickly and sends its message to specific parts of the body. • The endocrine system helps to maintain homeostasis by releasing chemicals into the blood. When the chemicals reach the target organ, a reaction occurs. This is slower than the nervous syst ...
The Carbonic-Acid-Bicarbonate Buffer in the Blood
... equilibria in Equation 10), and the kidneys remove excess HCO 3- from the body (helping to lower the pH). The lungs' removal of CO2 from the blood is somewhat impeded during exercise when the heart rate is very rapid; the blood is pumped through the capillaries very quickly, and so there is little t ...
... equilibria in Equation 10), and the kidneys remove excess HCO 3- from the body (helping to lower the pH). The lungs' removal of CO2 from the blood is somewhat impeded during exercise when the heart rate is very rapid; the blood is pumped through the capillaries very quickly, and so there is little t ...
Resp. Circ. Systems
... (spaces surrounding organs) Closed circulatory: blood confined to vessels Cardiovascular system •heart (atria/ventricles) •blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillary beds, venules, veins) •blood ...
... (spaces surrounding organs) Closed circulatory: blood confined to vessels Cardiovascular system •heart (atria/ventricles) •blood vessels (arteries, arterioles, capillary beds, venules, veins) •blood ...
The Circulatory System
... Transportation system by which oxygen and nutrients reach the body's cells, and waste materials are carried away. ...
... Transportation system by which oxygen and nutrients reach the body's cells, and waste materials are carried away. ...
Excretion - Mr. Baravarian's Wide World of Science
... by releasing SWEAT which evaporates and cools our body. The skin also removes some of the same substances as urine including urea and salts. ...
... by releasing SWEAT which evaporates and cools our body. The skin also removes some of the same substances as urine including urea and salts. ...
Circulatory System
... Blood –a fluid that carries all materials and wastes, delivers oxygen and removes CO2. made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells of the body. Plasma 60% is plasma – A fluid that contains proteins, glucose, hormones, gases and oth ...
... Blood –a fluid that carries all materials and wastes, delivers oxygen and removes CO2. made up of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells of the body. Plasma 60% is plasma – A fluid that contains proteins, glucose, hormones, gases and oth ...
6.5 Nerves, Hormones and Homeostasis
... 6.5.7 State that the endocrine system consists of glands that release hormones that are transported in the blood. 6.5.8 State that homeostasis involves maintaining the internal environment between limits, including blood pH, carbon dioxide concentration, blood glucose concentration, body temperature ...
... 6.5.7 State that the endocrine system consists of glands that release hormones that are transported in the blood. 6.5.8 State that homeostasis involves maintaining the internal environment between limits, including blood pH, carbon dioxide concentration, blood glucose concentration, body temperature ...
Circulatory System
... DIASTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE: lowest arterial pressure, occurs while ventricles relax. Normal resting blood pressure is 120 mm Hg over 80 mm Hg in brachial artery of arm ...
... DIASTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE: lowest arterial pressure, occurs while ventricles relax. Normal resting blood pressure is 120 mm Hg over 80 mm Hg in brachial artery of arm ...
2.2 Notes #1
... o Active muscles have a low partial pressure so O2 detaches from hemoglobin easily and diffuses in. • CO2 is produced during exercise and is transported to the lungs via the veins, partly dissolved in blood but mostly in the temporary form of bicarbonate ...
... o Active muscles have a low partial pressure so O2 detaches from hemoglobin easily and diffuses in. • CO2 is produced during exercise and is transported to the lungs via the veins, partly dissolved in blood but mostly in the temporary form of bicarbonate ...
Give Once to Live Twice, pp 4,5
... Have you donated blood recently? Some people __________ their blood to help hospitals keep a supply in case of __________. But blood isn’t the only thing you can donate to help sick people. In addition to donating blood, people also donate their __________. Organ donors promise that when they die th ...
... Have you donated blood recently? Some people __________ their blood to help hospitals keep a supply in case of __________. But blood isn’t the only thing you can donate to help sick people. In addition to donating blood, people also donate their __________. Organ donors promise that when they die th ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... • The interior of body, the environment of cells inside the body • Mostly water (~67%) – Liquid – High heat capacity • does not change temperature easily ...
... • The interior of body, the environment of cells inside the body • Mostly water (~67%) – Liquid – High heat capacity • does not change temperature easily ...
Circulatory System
... Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells of the body. Plasma 60% of blood is plasma (and 92% of plasma is water!) – A fluid that contains proteins, glucose, hormones, gases and other substances dissolved in water. – White Blood cells – help body fight infection. – Red blood cells – more numerous, ...
... Blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells of the body. Plasma 60% of blood is plasma (and 92% of plasma is water!) – A fluid that contains proteins, glucose, hormones, gases and other substances dissolved in water. – White Blood cells – help body fight infection. – Red blood cells – more numerous, ...
Unit 3 part 1 PPT
... maintain homeostasis. The nervous system acts quickly and sends its message to specific parts of the body. • The endocrine system helps to maintain homeostasis by releasing chemicals into the blood. When the chemicals reach the target organ, a reaction occurs. This is slower than the nervous system, ...
... maintain homeostasis. The nervous system acts quickly and sends its message to specific parts of the body. • The endocrine system helps to maintain homeostasis by releasing chemicals into the blood. When the chemicals reach the target organ, a reaction occurs. This is slower than the nervous system, ...
Respiration
... The alveoli give the lungs a large surface area so that oxygen can quickly diffuse from the air inside the lungs into the blood contained in capillaries. The walls of the alveoli and the walls of the capillaries are only one cell thick which also makes it easy for oxygen to diffuse into the blood. T ...
... The alveoli give the lungs a large surface area so that oxygen can quickly diffuse from the air inside the lungs into the blood contained in capillaries. The walls of the alveoli and the walls of the capillaries are only one cell thick which also makes it easy for oxygen to diffuse into the blood. T ...
Human Body Systems Part 2
... deliver messages into bloodstream. • These chemical products are called hormones. ...
... deliver messages into bloodstream. • These chemical products are called hormones. ...
Body Systems Powerpoint
... Purpose: produces electrical messages for communication within the body – one of the most complex yet smallest systems of the body-- Composed of the brain, spinal cord, nerves and special sense organs. ...
... Purpose: produces electrical messages for communication within the body – one of the most complex yet smallest systems of the body-- Composed of the brain, spinal cord, nerves and special sense organs. ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.