Amino_Acids_and_Protein_Background_Info_
... To make the meringue, slightly beat a room-temperature egg white with the cream of tartar. The acid will lower the pH of the white and makes it foam faster. Beat until foamy to start to denature the egg white protein. Slowly add sugar and beat until peaks form. The sugar makes the foam more stable. ...
... To make the meringue, slightly beat a room-temperature egg white with the cream of tartar. The acid will lower the pH of the white and makes it foam faster. Beat until foamy to start to denature the egg white protein. Slowly add sugar and beat until peaks form. The sugar makes the foam more stable. ...
Notes - Biological Molecules
... Polypeptide (abreviation = ppt): >2 amino acids joined together. Usually short: less than 20 amino acids or so. iv. Protein: a polypeptide chain is called a protein when it gets large (usually ~75 or more amino acids in length – though there is no absolute rule here) Proteins have 4 levels of organi ...
... Polypeptide (abreviation = ppt): >2 amino acids joined together. Usually short: less than 20 amino acids or so. iv. Protein: a polypeptide chain is called a protein when it gets large (usually ~75 or more amino acids in length – though there is no absolute rule here) Proteins have 4 levels of organi ...
Digestion 3 – Enzymes {PowerPoint}
... – It would take to long without them. They act as a catalyst to speed up the digestive process. ...
... – It would take to long without them. They act as a catalyst to speed up the digestive process. ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
Simple Life Forms: an Oxymoron “Then God said, “Let the land
... that can be read like a book. Every cell in the human body contains these same DNA strands. Therefore each cell has about three billion DNA base pairs comprising an estimated 20,000-25,000 genes. Compare that to an average page of text of 2,000 to 2,500 letters. Just the DNA letters in each individu ...
... that can be read like a book. Every cell in the human body contains these same DNA strands. Therefore each cell has about three billion DNA base pairs comprising an estimated 20,000-25,000 genes. Compare that to an average page of text of 2,000 to 2,500 letters. Just the DNA letters in each individu ...
Protein Molecules in Solution
... represents number of Zn++ (or Ca±±) ions bound by 1 molecule of protein; abscissa gives the logarithm of the concentration of free metal ion (in qvater) in equilibrium with the bound metal ion on the protein. in compounds such as tyrosine. On the other hand, Cu is bound more strongly to amine nitrog ...
... represents number of Zn++ (or Ca±±) ions bound by 1 molecule of protein; abscissa gives the logarithm of the concentration of free metal ion (in qvater) in equilibrium with the bound metal ion on the protein. in compounds such as tyrosine. On the other hand, Cu is bound more strongly to amine nitrog ...
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
... • Proteins are polymers of amino acid monomers. – Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms. – Amino acids differ in side groups, or R groups. – Amino acids are linked by peptide bonds. ...
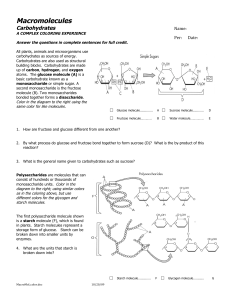
Macromolecule coloring
... Answer the questions in complete sentences for full credit. Lipids are a group of organic molecules that dissolve in oils, but not in water. Lipids come in three varieties: Fats, phospholipids and cholesterol. Fats are very efficient energy-storage molecules that yield about twice the amount of chem ...
... Answer the questions in complete sentences for full credit. Lipids are a group of organic molecules that dissolve in oils, but not in water. Lipids come in three varieties: Fats, phospholipids and cholesterol. Fats are very efficient energy-storage molecules that yield about twice the amount of chem ...
You find all these questions again in the ′Test
... Question 111: The slime mould mofope has a very small serine protease with the sequence: GSVEFKITSGGNGPAELLKALIQGSGSVTITWEVHGNGNSALELALQLLKGSGTVEFIDGNGN ...
... Question 111: The slime mould mofope has a very small serine protease with the sequence: GSVEFKITSGGNGPAELLKALIQGSGSVTITWEVHGNGNSALELALQLLKGSGTVEFIDGNGN ...
Assembly - The Open Academy
... region of the P protein. Coniments established that the Pon protein catalyzed both viral nthesis and genome replication, ...
... region of the P protein. Coniments established that the Pon protein catalyzed both viral nthesis and genome replication, ...
Open Reading Frames and Codon Bias in Streptomyces coelicolor
... known to code for different amino acids in different species including bacteria and the mitochondria of eukaryotes [6]. The majority of the codons having variable definitions are AT-only or AT-rich. These codons are not found in the genome of S. coelicolor (Fig. 1a) or in the MORFs of the protein fa ...
... known to code for different amino acids in different species including bacteria and the mitochondria of eukaryotes [6]. The majority of the codons having variable definitions are AT-only or AT-rich. These codons are not found in the genome of S. coelicolor (Fig. 1a) or in the MORFs of the protein fa ...
Biomolecules
... 30. Biomolecules of the general formula Cx(H2O)y are examples of … 31. Name the test or give the chemicals used to detect the presence of protein in a food sample. 32. Name a structural polysaccharide. 33. Name a group of biomolecules in the blood which are too large to pass through the filtration s ...
... 30. Biomolecules of the general formula Cx(H2O)y are examples of … 31. Name the test or give the chemicals used to detect the presence of protein in a food sample. 32. Name a structural polysaccharide. 33. Name a group of biomolecules in the blood which are too large to pass through the filtration s ...
Datasheet PDF - BioAssay Systems
... Bradford Colorimetric Protein Determination at 595 nm DESCRIPTION The protein is known as the "building blocks of life" and is one of the most important macromolecules in life science. Proteins are polypeptides made up of amino acids and play various key roles in all aspects of biology. Protein quan ...
... Bradford Colorimetric Protein Determination at 595 nm DESCRIPTION The protein is known as the "building blocks of life" and is one of the most important macromolecules in life science. Proteins are polypeptides made up of amino acids and play various key roles in all aspects of biology. Protein quan ...
PDF - Bioinformation
... structural and functional analyses of the gene responsible of their degradation are an important aspect for environmental studies and are important to human well-being. It has been shown that some haloacids are toxic and mutagenic. Microorganisms capable of degrading these haloacids can be found in ...
... structural and functional analyses of the gene responsible of their degradation are an important aspect for environmental studies and are important to human well-being. It has been shown that some haloacids are toxic and mutagenic. Microorganisms capable of degrading these haloacids can be found in ...
video slide
... of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
... of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
Chapter 5 The Structure & Function of Molecules
... of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
... of biological organization is reached when small organic molecules are joined together – Atom ---> molecule --- compound ...
Magic Numbers in Protein Structures
... The exhaustive enumeration in Fig. 2 and the unique description of folds on a cubic lattice are also relevant for the bead model of proteins, which is extensively studied; see a recent discussion, e.g., Ref. [13]. This model is, however, in fundamental principle very different from the present one. ...
... The exhaustive enumeration in Fig. 2 and the unique description of folds on a cubic lattice are also relevant for the bead model of proteins, which is extensively studied; see a recent discussion, e.g., Ref. [13]. This model is, however, in fundamental principle very different from the present one. ...
No Slide Title
... structure, we focus in finding these regular NOE patterns? • This is exactly what we do. We actually look for cyclic NOE patterns, which are normally found in regular secondary structure. • After we found these patterns, we try to match them with chunks of primary structure of our peptide. • This me ...
... structure, we focus in finding these regular NOE patterns? • This is exactly what we do. We actually look for cyclic NOE patterns, which are normally found in regular secondary structure. • After we found these patterns, we try to match them with chunks of primary structure of our peptide. • This me ...
How cells use DNA, part 1: TRANSCRIPTION
... Most commonly, what comes to mind is the process by which we take ideas expressed in one language, & make them intelligible in another language. Often this means a change of script, from one we don’t understand to another we can read. ...
... Most commonly, what comes to mind is the process by which we take ideas expressed in one language, & make them intelligible in another language. Often this means a change of script, from one we don’t understand to another we can read. ...
bch2ibm: molecular biology end of semester 1 exam notes 2014
... -‐ It’s the process by which the nucleotide sequence of an mRNA is used as a template to join the amino acids in a polypeptide chain in the correct order. Qu. What are the 3 types of RNA molecules involved in translation and what do they do? 1) Messenger RNA (mRNA) -‐ Carries genetic informatio ...
... -‐ It’s the process by which the nucleotide sequence of an mRNA is used as a template to join the amino acids in a polypeptide chain in the correct order. Qu. What are the 3 types of RNA molecules involved in translation and what do they do? 1) Messenger RNA (mRNA) -‐ Carries genetic informatio ...
anmol publications pvt. ltd.
... be created artificially. The dawn of biochemistry may have been the discovery of the first enzyme, diastase (today called amylase), in 1833 by Anselme Payen. Eduard Buchner contributed the first demonstration of a complex biochemical process outside of a cell in 1896: alcoholic fermentation in cell ...
... be created artificially. The dawn of biochemistry may have been the discovery of the first enzyme, diastase (today called amylase), in 1833 by Anselme Payen. Eduard Buchner contributed the first demonstration of a complex biochemical process outside of a cell in 1896: alcoholic fermentation in cell ...
Chapter 15
... Pathogenic Properties of Fungi • Fungal waste products may cause symptoms. • Chronic infections provoke an allergic response. • Tichothecene toxins inhibit protein synthesis. ...
... Pathogenic Properties of Fungi • Fungal waste products may cause symptoms. • Chronic infections provoke an allergic response. • Tichothecene toxins inhibit protein synthesis. ...
Prescribing Description - Healthcare Pharmaceuticals
... Energy content : 1,551 kJ/L (371.14 kcal/L) Nitrogen content : 7.2 gm/L Description Nutrilive® contains all 18 essential and non-essential amino acid needed for protein synthesis. The amino acid composition is such that positive nitrogen balance can be achieved in the postoperative period and during ...
... Energy content : 1,551 kJ/L (371.14 kcal/L) Nitrogen content : 7.2 gm/L Description Nutrilive® contains all 18 essential and non-essential amino acid needed for protein synthesis. The amino acid composition is such that positive nitrogen balance can be achieved in the postoperative period and during ...
Does intracrine amplification provide a unifying principle for the
... First, evidence of substrate protein amplification should be sought in all NDDs— and confirmed in Parkinson's disease where amplification has already been reported21. Second, prevention of amplification is a disease-controlling strategy; complete knock-down of substrate protein is unnecessary. Third ...
... First, evidence of substrate protein amplification should be sought in all NDDs— and confirmed in Parkinson's disease where amplification has already been reported21. Second, prevention of amplification is a disease-controlling strategy; complete knock-down of substrate protein is unnecessary. Third ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.