Explain advantages of Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
... which are necessary for life. They are called nucleic acids as they were discovered in the nucleus of the cell and contain phosphate groups which are associated with phosphoric acid. The term nucleic acid covers DNA and RNA which is present in all living cells. The nucleotide is the main component i ...
... which are necessary for life. They are called nucleic acids as they were discovered in the nucleus of the cell and contain phosphate groups which are associated with phosphoric acid. The term nucleic acid covers DNA and RNA which is present in all living cells. The nucleotide is the main component i ...
CH 17 PPT
... sequence is AATAAA. • Prokaryotic mRNA is ready for translation immediately; eukaryotic mRNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus and ...
... sequence is AATAAA. • Prokaryotic mRNA is ready for translation immediately; eukaryotic mRNA must be processed before it leaves the nucleus and ...
Improving protein fold recognition with hybrid
... structural information from solvent accessibility, secondary structure or backbone torsion angle can be used to improve sequencebased fold recognition. Such structural features have the advantage of being predictable, which addresses the absence of experimental model for the target protein. Thus, se ...
... structural information from solvent accessibility, secondary structure or backbone torsion angle can be used to improve sequencebased fold recognition. Such structural features have the advantage of being predictable, which addresses the absence of experimental model for the target protein. Thus, se ...
Expression of Human 21-Hydroxylase (P450c21) in Bacterial and
... phc21 (Fig. 4, lane 1). Mutant protein corresponding to mutation of He172 to His, Gin, Leu, or Asn was also produced and detectable by anti-P450c21 antisera after transfection with each mutant plasmid (Fig. 4, lanes 2 5). Multiple scannings of the intensity of the protein bands from four blots showe ...
... phc21 (Fig. 4, lane 1). Mutant protein corresponding to mutation of He172 to His, Gin, Leu, or Asn was also produced and detectable by anti-P450c21 antisera after transfection with each mutant plasmid (Fig. 4, lanes 2 5). Multiple scannings of the intensity of the protein bands from four blots showe ...
A toolbox for validation of mass spectrometry peptides identification
... in the significant category. Dynamic classification has an impact on protein hits: when a PSM is declared ambiguous, it becomes irrelevant to proteins identification. IRMa takes into account these changes to ensure consistency of information such as protein coverage and identification score and dyna ...
... in the significant category. Dynamic classification has an impact on protein hits: when a PSM is declared ambiguous, it becomes irrelevant to proteins identification. IRMa takes into account these changes to ensure consistency of information such as protein coverage and identification score and dyna ...
Response of Primary Human Airway Epithelial Cells to Influenza
... Research); all antibodies were diluted in 1% BSA and PBS. Coverslips were then mounted onto slides using DAPI-Prolong Gold Antifade, dried, and sealed. Fluorescent images were ...
... Research); all antibodies were diluted in 1% BSA and PBS. Coverslips were then mounted onto slides using DAPI-Prolong Gold Antifade, dried, and sealed. Fluorescent images were ...
Application Note #14 - GE Healthcare Life Sciences
... Heterologous recombinant proteins produced in E. coli can undergo intracellular proteolysis by action of cytoplasmic proteinases. Mass spectrometry has recently proven to be an important methodology for characterizing peptides and proteins, particularly when combined with other techniques, such as g ...
... Heterologous recombinant proteins produced in E. coli can undergo intracellular proteolysis by action of cytoplasmic proteinases. Mass spectrometry has recently proven to be an important methodology for characterizing peptides and proteins, particularly when combined with other techniques, such as g ...
Paper Title
... First approach was based on the idea of selecting a subset of properties with high orthogonality. To prove this idea, 544 properties from AAIndex were clustered by K-means algorithm [20] into {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} clusters and 20,000 of experiments were proceeded on MMP dataset for each cluster count ...
... First approach was based on the idea of selecting a subset of properties with high orthogonality. To prove this idea, 544 properties from AAIndex were clustered by K-means algorithm [20] into {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10} clusters and 20,000 of experiments were proceeded on MMP dataset for each cluster count ...
Ring, helix, sphere and cylinder: the basic geometry of prokaryotic
... confers rigidity to this structure. These enzymes are penicillinbinding proteins (PBPs) and belong to the SxxK superfamily of serine proteases. Class A SxxK peptidases act independently, whereas class B associate with either glycosyl transferases or acyl transferases. This latter class also associat ...
... confers rigidity to this structure. These enzymes are penicillinbinding proteins (PBPs) and belong to the SxxK superfamily of serine proteases. Class A SxxK peptidases act independently, whereas class B associate with either glycosyl transferases or acyl transferases. This latter class also associat ...
Protein Synthesis - Austin Community College
... This establishes the reading frame; subsequent codons are read in groups of three nucleotides. ...
... This establishes the reading frame; subsequent codons are read in groups of three nucleotides. ...
ppt - Avraham Samson`s Lab
... • Both Chou and Fasman and GOR have been assessed and their accuracy is estimated to be Q3=60-65%. (initially, higher scores were reported, but the experiments set to measure Q3 were flawed, as the test cases included proteins used to derive the propensities!) ...
... • Both Chou and Fasman and GOR have been assessed and their accuracy is estimated to be Q3=60-65%. (initially, higher scores were reported, but the experiments set to measure Q3 were flawed, as the test cases included proteins used to derive the propensities!) ...
Atom depth in protein structure and function
... several molecular, residue and atomic properties, such as average protein domain size, protein stability, free energy of formation of protein complexes, amino acid type hydrophobicity, residue conservation and hydrogen/deuterium amide proton exchange rates. Although the functional properties of a pr ...
... several molecular, residue and atomic properties, such as average protein domain size, protein stability, free energy of formation of protein complexes, amino acid type hydrophobicity, residue conservation and hydrogen/deuterium amide proton exchange rates. Although the functional properties of a pr ...
Advances in Natural and Applied Sciences Aedes aegypti Aulanni’am
... populations with 3 different kind of sera samples from endemic area. (A) SGE Lab. scale cultures, (B) SGE from landing population , (C) negative control, (M) Marker. The specific proteins of 56 and 31 kDa that were detected in this study (Fig. 3), were related to the immune response against SGE of A ...
... populations with 3 different kind of sera samples from endemic area. (A) SGE Lab. scale cultures, (B) SGE from landing population , (C) negative control, (M) Marker. The specific proteins of 56 and 31 kDa that were detected in this study (Fig. 3), were related to the immune response against SGE of A ...
The plastid division proteins, FtsZ1 and FtsZ2, differ in their
... thaliana and by a gene family of at least four members in Nicotiana tabacum (an allotetraploid species). In both plants, a small multigene family encodes FtsZ2, with two members in Arabidopsis thaliana. It was demonstrated recently that the classification of FtsZ proteins into two distinct groups al ...
... thaliana and by a gene family of at least four members in Nicotiana tabacum (an allotetraploid species). In both plants, a small multigene family encodes FtsZ2, with two members in Arabidopsis thaliana. It was demonstrated recently that the classification of FtsZ proteins into two distinct groups al ...
chapter 17 from gene to protein
... This establishes the reading frame; subsequent codons are read in groups of three nucleotides. ...
... This establishes the reading frame; subsequent codons are read in groups of three nucleotides. ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008.
... plays an important role in their function. There are many sequence of this protein are present in UniProt database. But due to their lack of structure, homology modeling is necessary. But this work is based on the insulin of the zebra fish. Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of pr ...
... plays an important role in their function. There are many sequence of this protein are present in UniProt database. But due to their lack of structure, homology modeling is necessary. But this work is based on the insulin of the zebra fish. Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of pr ...
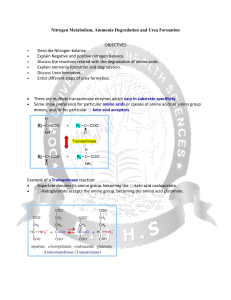
Nitrogen Metabolism, Ammonia Degradation and Urea Formation
... Normal concentration: 25-40 mol/l (0.4-0.7 mg/l) Ammonia must be removed from the organism ...
... Normal concentration: 25-40 mol/l (0.4-0.7 mg/l) Ammonia must be removed from the organism ...
3 | biological macromolecules
... Are carbohydrates good for you? People who wish to lose weight are often told that carbohydrates are bad for them and should be avoided. Some diets completely forbid carbohydrate consumption, claiming that a low-carbohydrate diet helps people to lose weight faster. However, carbohydrates have been a ...
... Are carbohydrates good for you? People who wish to lose weight are often told that carbohydrates are bad for them and should be avoided. Some diets completely forbid carbohydrate consumption, claiming that a low-carbohydrate diet helps people to lose weight faster. However, carbohydrates have been a ...
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs)
... Proteins (IDPs) and ID Regions (IDRs) • Whole proteins and regions of proteins are intrinsically disordered if they lack stable 3D structure under physiological conditions, • But exist instead as highly dynamic, rapidly interconverting ensembles without particular equilibrium values for their coordi ...
... Proteins (IDPs) and ID Regions (IDRs) • Whole proteins and regions of proteins are intrinsically disordered if they lack stable 3D structure under physiological conditions, • But exist instead as highly dynamic, rapidly interconverting ensembles without particular equilibrium values for their coordi ...
The families of pathogenesis-related proteins, their activities, and
... Individual family members are named by lower case letters in the order in which they are described. In the literature, besides proteins, newly defined mRNAs (cDNAs) are often considered as additional members of the existing families when shown to be induced by pathogens or specific elicitors. Howeve ...
... Individual family members are named by lower case letters in the order in which they are described. In the literature, besides proteins, newly defined mRNAs (cDNAs) are often considered as additional members of the existing families when shown to be induced by pathogens or specific elicitors. Howeve ...
Effective Scoring Function for Protein Sequence Design
... The modified backbone-dependent rotamer library of Dunbrack is used in this study.22,24 Polar hydrogen atoms are added. 2 of Ser, Thr, and 3 of Tyr are assigned values of ⫺60°, 60°, and 180°. Three protonation states of His with the same expected frequencies are considered: N␦1 protonated, N⑀2 prot ...
... The modified backbone-dependent rotamer library of Dunbrack is used in this study.22,24 Polar hydrogen atoms are added. 2 of Ser, Thr, and 3 of Tyr are assigned values of ⫺60°, 60°, and 180°. Three protonation states of His with the same expected frequencies are considered: N␦1 protonated, N⑀2 prot ...
MINI REVIEW Lectin-like proteins in model organisms: implications
... first three structural groups are located mostly intracellularly, in luminal compartments. They function in the trafficking, sorting, and targetting of glycoproteins in the secretory and other pathways. CRDs in the remaining structural groups are found in lectins that function largely outside the ce ...
... first three structural groups are located mostly intracellularly, in luminal compartments. They function in the trafficking, sorting, and targetting of glycoproteins in the secretory and other pathways. CRDs in the remaining structural groups are found in lectins that function largely outside the ce ...
Membrane-enclosed Crystals in Dictyostelium discoideum Cells
... multicellular body is formed which gives rise to a fruiting body, whereby the major portion of cells differentiates into spores and a minor one into stalk cells. The development ofD. discoideum is driven and accompanied by stage and cell-type specific gene expression. The expression of one group of ...
... multicellular body is formed which gives rise to a fruiting body, whereby the major portion of cells differentiates into spores and a minor one into stalk cells. The development ofD. discoideum is driven and accompanied by stage and cell-type specific gene expression. The expression of one group of ...
Vicia species belonging to the subgenus Cracca are
... Adams & Crooks, 2002; Jang, Jun, Rue, Han, Park & Kim 2002). ...
... Adams & Crooks, 2002; Jang, Jun, Rue, Han, Park & Kim 2002). ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... structures, resulting in a wide range of functions • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances ...
... structures, resulting in a wide range of functions • Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells • Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport, cellular communications, movement, and defense against foreign substances ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.