Response to David Rosnick`s “Toward an Understanding of Keen
... The Cournot outcome has an unstable manifold, where overall production is declining leading to rising profits for all. The only way to prevent the system from taking that path is to explicitly inhibit it in some way – it might be said that prevention of collusion is sufficient to prohibit this from ...
... The Cournot outcome has an unstable manifold, where overall production is declining leading to rising profits for all. The only way to prevent the system from taking that path is to explicitly inhibit it in some way – it might be said that prevention of collusion is sufficient to prohibit this from ...
Lecture
... – To the extent that buyers or sellers don’t trust each other, quantity sold would go to zero -- unless remedied by trust in a brand or third-party certification – To the extent that buyers or sellers are protected from competition by barriers to entry, they won’t act competitively -- won’t be “pric ...
... – To the extent that buyers or sellers don’t trust each other, quantity sold would go to zero -- unless remedied by trust in a brand or third-party certification – To the extent that buyers or sellers are protected from competition by barriers to entry, they won’t act competitively -- won’t be “pric ...
The AS-AD Model
... • Quantity supplied in an economy depends on labor employed, amount of capital used, technological level, human capital (health, knowledge) of its workers, efficiency in production, institutional support (such as good government or well defined property rights) and so on. ...
... • Quantity supplied in an economy depends on labor employed, amount of capital used, technological level, human capital (health, knowledge) of its workers, efficiency in production, institutional support (such as good government or well defined property rights) and so on. ...
HOW THE DYNAMICS OF THE FREE MARKET CREATES
... The economy is initially at or close to equilibrium. A disturbance redistributes incomes (at time an−1 ). This causes a shift in the demand structure of the economy at time bn raising demand in some markets and causing demand deficiency in others. Prices and transactions adjust to the new demand pat ...
... The economy is initially at or close to equilibrium. A disturbance redistributes incomes (at time an−1 ). This causes a shift in the demand structure of the economy at time bn raising demand in some markets and causing demand deficiency in others. Prices and transactions adjust to the new demand pat ...
full paper - Sustainability – Missing Points in the
... market for whatever external reasons fails to deliver what in principle it could have delivered, and once the market disturbance is eliminated, the market will return to its equilibrium mechanisms and thus solve the problem. Whoever considers the failure of sustainable development to be a market fai ...
... market for whatever external reasons fails to deliver what in principle it could have delivered, and once the market disturbance is eliminated, the market will return to its equilibrium mechanisms and thus solve the problem. Whoever considers the failure of sustainable development to be a market fai ...
Document
... • No close substitutes for product • Significant barriers to resource mobility – Control of an essential input – Patents or copyrights – Economies of scale: Natural monopoly – Government franchise: Post office ...
... • No close substitutes for product • Significant barriers to resource mobility – Control of an essential input – Patents or copyrights – Economies of scale: Natural monopoly – Government franchise: Post office ...
Economics of Ideas
... than marginal cost and hence marginal cost pricing results in negative profits. No firm will enter this market and pay the fixed cost The production of new ideas requires the possibility of earning profits and therefore necessitates a move from perfect competition. ...
... than marginal cost and hence marginal cost pricing results in negative profits. No firm will enter this market and pay the fixed cost The production of new ideas requires the possibility of earning profits and therefore necessitates a move from perfect competition. ...
Monopoly 2 and Monopsony
... P2 1 + 1 ε 1 This says that the relative price difference in the two markets only depends on their demand elasticities. ...
... P2 1 + 1 ε 1 This says that the relative price difference in the two markets only depends on their demand elasticities. ...
The Ecology of Markets William D. Nordhaus Proceedings of the
... the final goods, the Pi terms are the marginal costs of production, and the qi terms are new variables that are scarcity values or "shadow prices" that represent the social scarcity of the different goods. The key point of Eq. 8 is that the marginal utilities of the different goods are proportional ...
... the final goods, the Pi terms are the marginal costs of production, and the qi terms are new variables that are scarcity values or "shadow prices" that represent the social scarcity of the different goods. The key point of Eq. 8 is that the marginal utilities of the different goods are proportional ...
APEC and the New Economy
... Australia). Here is an economy that is using e-commerce in the domestic market to enhance resource usage and gains in productivity and welfare. The tallish import cone indicates that imports are in e-commerce intensive sectors, which, when combined with a tall readiness cylinder, implies that domest ...
... Australia). Here is an economy that is using e-commerce in the domestic market to enhance resource usage and gains in productivity and welfare. The tallish import cone indicates that imports are in e-commerce intensive sectors, which, when combined with a tall readiness cylinder, implies that domest ...
Allocative efficiency
... that a person is willing to give up to get one more unit of it. decreasing marginal benefit implies that as more of a good or service is consumed, its marginal benefit decreases. ...
... that a person is willing to give up to get one more unit of it. decreasing marginal benefit implies that as more of a good or service is consumed, its marginal benefit decreases. ...
II.1. Critique of MPT/MDT
... concerning the functional distribution Wages are not determined by marginal productivity of labor) (critique of MPT) Market (current) level of wages is a magnitude which is secondary with respect to the rate of profit and results from the following (theoretical) reasoning: 1. There exists a histor ...
... concerning the functional distribution Wages are not determined by marginal productivity of labor) (critique of MPT) Market (current) level of wages is a magnitude which is secondary with respect to the rate of profit and results from the following (theoretical) reasoning: 1. There exists a histor ...
introductory economics: tools for clear thinking, or
... certainly do systematically omit any deeply critical leftist views and analyses from our introductory courses. We may not be a part of any "conspiracy" to omit these ideas, but nonetheless as graduates of the institutions in which teaching economists are properly "certified" for their work, most of ...
... certainly do systematically omit any deeply critical leftist views and analyses from our introductory courses. We may not be a part of any "conspiracy" to omit these ideas, but nonetheless as graduates of the institutions in which teaching economists are properly "certified" for their work, most of ...
Prices - Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis
... As discussed previously, the laws of supply and demand determine prices, at least insofar as government rules permit them to do so. Governments sometimes intervene to control prices for a variety of reasons. For example, the government may control prices for political reasons or in an attempt to ens ...
... As discussed previously, the laws of supply and demand determine prices, at least insofar as government rules permit them to do so. Governments sometimes intervene to control prices for a variety of reasons. For example, the government may control prices for political reasons or in an attempt to ens ...
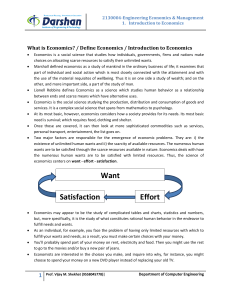
Introduction to Economics
... Economics is a science: Science is a structured body of knowledge that traces the relationship between cause and effect. Another attribute of science is that its phenomena should be open to measurement. Applying these characteristics, we find that economics is a branch of knowledge where the various ...
... Economics is a science: Science is a structured body of knowledge that traces the relationship between cause and effect. Another attribute of science is that its phenomena should be open to measurement. Applying these characteristics, we find that economics is a branch of knowledge where the various ...
Report on the CREATe panels
... sharing of expertise in product development between different contributors with no commercial incentive in mind (another type of intrinsic motivation). What the role of copyright in this mode of supply is or should be is something that economists need to research. The economic aspects of the effect ...
... sharing of expertise in product development between different contributors with no commercial incentive in mind (another type of intrinsic motivation). What the role of copyright in this mode of supply is or should be is something that economists need to research. The economic aspects of the effect ...
is the issue `competition vis-à-vis development`
... because of the initial arrangements that both companies had with MTL to use MTL’s Microwave Backbone Links (MBLs) that were to connect their networks to consumers across the country. After some research, it was discovered that Celtel had purchased its own MBL system towards the end of 2005 and no lo ...
... because of the initial arrangements that both companies had with MTL to use MTL’s Microwave Backbone Links (MBLs) that were to connect their networks to consumers across the country. After some research, it was discovered that Celtel had purchased its own MBL system towards the end of 2005 and no lo ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... Bureau of Economic Research
... To summarize briefly: In the, context of a set of household production functions, human capital is viewed as affecting the efficiency of the production process. By assuming Hicks-neutral productivity shifts, the effect of education on real income through nonmarket efficiency is examined, and it is s ...
... To summarize briefly: In the, context of a set of household production functions, human capital is viewed as affecting the efficiency of the production process. By assuming Hicks-neutral productivity shifts, the effect of education on real income through nonmarket efficiency is examined, and it is s ...
4.1.8.3 Public goods, private goods and quasi
... o They are non-excludable so by consuming the good, someone else is not prevented from consuming the good as well, and they are non-rival, so the benefit other people get from the good does not diminish if more people consume the good. o The non-excludable nature of public goods gives rise to the fr ...
... o They are non-excludable so by consuming the good, someone else is not prevented from consuming the good as well, and they are non-rival, so the benefit other people get from the good does not diminish if more people consume the good. o The non-excludable nature of public goods gives rise to the fr ...
Consumer and Producer Surplus
... • The difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good or service and what they actually have to pay ...
... • The difference between what a consumer is willing to pay for a good or service and what they actually have to pay ...
In economics, a circular flow model is a diagram that is
... The circular flow of income follows a specific pattern: Production → Income → Expenditure → Production. This circular flow is ongoing between households and firms. The circular flow of income can also be analyzed using the production possibility frontier (PPF). The PPF is a graph that shows the vari ...
... The circular flow of income follows a specific pattern: Production → Income → Expenditure → Production. This circular flow is ongoing between households and firms. The circular flow of income can also be analyzed using the production possibility frontier (PPF). The PPF is a graph that shows the vari ...
Demand
... – Based on assumption that prices may differ but everything else will remain constant, however, not always true. – People’s preference may change, substitutes may become available, or number of people in marketplace may fluctuate. ...
... – Based on assumption that prices may differ but everything else will remain constant, however, not always true. – People’s preference may change, substitutes may become available, or number of people in marketplace may fluctuate. ...
2. Management as a process of making choice. Human needs
... 2. Management as a process of making choice. Human needs – state of impregnation, absence, unfulfilled. People feels many needs and aims to maximal satisfaction them, which is equivalent with lay-out definite aim of operation it can favor different kind of needs: physiological, safety, social contac ...
... 2. Management as a process of making choice. Human needs – state of impregnation, absence, unfulfilled. People feels many needs and aims to maximal satisfaction them, which is equivalent with lay-out definite aim of operation it can favor different kind of needs: physiological, safety, social contac ...
ENV 536: Environmental Economics and Policy (Lecture 4
... Nobel laureate, Ronald Coase, proposed that the assignment of property rights alone can provide for an efficient solution even in the presence of an externality. Coase Theorem with two assumptions – Transaction costs are costless – Damages are accessible and measurable. ...
... Nobel laureate, Ronald Coase, proposed that the assignment of property rights alone can provide for an efficient solution even in the presence of an externality. Coase Theorem with two assumptions – Transaction costs are costless – Damages are accessible and measurable. ...
Economics
Economics is the social science that seeks to describe the factors which determine the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek οἰκονομία from οἶκος (oikos, ""house"") and νόμος (nomos, ""custom"" or ""law""), hence ""rules of the house (hold for good management)"". 'Political economy' was the earlier name for the subject, but economists in the late 19th century suggested ""economics"" as a shorter term for ""economic science"" to establish itself as a separate discipline outside of political science and other social sciences.Economics focuses on the behavior and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Consistent with this focus, primary textbooks often distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines the behavior of basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the entire economy (meaning aggregated production, consumption, savings, and investment) and issues affecting it, including unemployment of resources (labor, capital, and land), inflation, economic growth, and the public policies that address these issues (monetary, fiscal, and other policies).Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing ""what is,"" and normative economics, advocating ""what ought to be""; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational and behavioral economics; and between mainstream economics (more ""orthodox"" and dealing with the ""rationality-individualism-equilibrium nexus"") and heterodox economics (more ""radical"" and dealing with the ""institutions-history-social structure nexus"").Besides the traditional concern in production, distribution, and consumption in an economy, economic analysis may be applied throughout society, as in business, finance, health care, and government. Economic analyses may also be applied to such diverse subjects as crime, education, the family, law, politics, religion, social institutions, war, science, and the environment. Education, for example, requires time, effort, and expenses, plus the foregone income and experience, yet these losses can be weighted against future benefits education may bring to the agent or the economy. At the turn of the 21st century, the expanding domain of economics in the social sciences has been described as economic imperialism.The ultimate goal of economics is to improve the living conditions of people in their everyday life.