Econ 101A – Midterm 2 Th 5 April 2012. You have approximately 1
... that is, what the quantity supplied q ∗ is as a function of p. (5 points) 3. Assume now that in perfect competition there are 5 firms, all with the same cost function Ci (qi ) = cqi . How does the aggregate supply function differ from the individual supply function, if at all? Plot, and write analyt ...
... that is, what the quantity supplied q ∗ is as a function of p. (5 points) 3. Assume now that in perfect competition there are 5 firms, all with the same cost function Ci (qi ) = cqi . How does the aggregate supply function differ from the individual supply function, if at all? Plot, and write analyt ...
The perfectly competitive firm`s supply curve is its Marginal cost
... A. only on what price to charge, taking output as fixed. B. both what price to charge and how much to produce. C. only on how much to produce, taking price as fixed. D. only on which industry to join, taking price and output as fixed. E. only on how much revenue it wishes to collect. ...
... A. only on what price to charge, taking output as fixed. B. both what price to charge and how much to produce. C. only on how much to produce, taking price as fixed. D. only on which industry to join, taking price and output as fixed. E. only on how much revenue it wishes to collect. ...
Document
... set of performance benchmarks against which firms’ actual performance can be compared – Even though profit maximization models are important, we will stress that for much of the healthcare industry other theories will be more appropriate ...
... set of performance benchmarks against which firms’ actual performance can be compared – Even though profit maximization models are important, we will stress that for much of the healthcare industry other theories will be more appropriate ...
Chapter 11: General Equilibrium and the Efficiency of
... • In all imperfectly competitive industries, output is lower—the product is underproduced—and price is higher ...
... • In all imperfectly competitive industries, output is lower—the product is underproduced—and price is higher ...
Lecture Week 12
... is a situation where a family’s income is too low to be able to buy the quantities of food, shelter, and clothing that are deemed necessary. is a relative concept. In Canada, poverty is measured by using a lowincome cutoff. low-income cutoff is the income level at which a family spends 54.7 pe ...
... is a situation where a family’s income is too low to be able to buy the quantities of food, shelter, and clothing that are deemed necessary. is a relative concept. In Canada, poverty is measured by using a lowincome cutoff. low-income cutoff is the income level at which a family spends 54.7 pe ...
A Multidisciplinary-economic Framework of Analysis
... develop analyses of real-life economies. We now call their approach Classical Political Economy. Other economists began to develop analyses of real-life economies, placed in their real-life societal context. This approach is now called Classical Sociology3. In the second half of the 19th century, a ...
... develop analyses of real-life economies. We now call their approach Classical Political Economy. Other economists began to develop analyses of real-life economies, placed in their real-life societal context. This approach is now called Classical Sociology3. In the second half of the 19th century, a ...
Inferior good - Installation is NOT complete
... For all normal goods and most inferior goods, a price drop results in an increase in the quantity demanded by consumers. The demand for a good is relatively inelastic when the quantity demanded does not change much with the price change. Goods and services for which no substitutes exist are generall ...
... For all normal goods and most inferior goods, a price drop results in an increase in the quantity demanded by consumers. The demand for a good is relatively inelastic when the quantity demanded does not change much with the price change. Goods and services for which no substitutes exist are generall ...
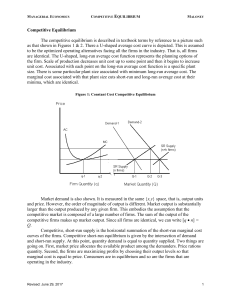
Competitive Equilibrium
... For all industry over large ranges of output, the industry supply curve is positively sloped. As industry output increases by a large margin, the unit cost of production will increase. There is a substantial difference between industries in terms of the relative flatness of the long-run industry ...
... For all industry over large ranges of output, the industry supply curve is positively sloped. As industry output increases by a large margin, the unit cost of production will increase. There is a substantial difference between industries in terms of the relative flatness of the long-run industry ...
Advertising and Integrated Brand Promotion 4e.
... role as part of the product differentiation strategy because the consumer will have to be convinced that the difference is meaningful. Copyright © 2006 Thomson Business and Economics. All rights reserved. ...
... role as part of the product differentiation strategy because the consumer will have to be convinced that the difference is meaningful. Copyright © 2006 Thomson Business and Economics. All rights reserved. ...
Aalborg Universitet Globalization and the Next Economy Li, Xing; Clark, Woodrow W.
... impact upon developing nations. We utilize an integrated historical-economicpolitical approach to study the concepts and inherent logic, primarily from the USA and UK as they steer international finance organizations toward their particular definition of globalization and the “Next Economy”. Globali ...
... impact upon developing nations. We utilize an integrated historical-economicpolitical approach to study the concepts and inherent logic, primarily from the USA and UK as they steer international finance organizations toward their particular definition of globalization and the “Next Economy”. Globali ...
Prices and Work in The New Economy
... The impetus for this paper is the urgent need is to figure out how a non-growing – even a shrinking – economy may be able to provide human well-being while beginning to restore the health of the natural world. Twentieth century economic theory is not well able to conceptualize this problem, especial ...
... The impetus for this paper is the urgent need is to figure out how a non-growing – even a shrinking – economy may be able to provide human well-being while beginning to restore the health of the natural world. Twentieth century economic theory is not well able to conceptualize this problem, especial ...
View/Open
... The impetus for this paper is the urgent need is to figure out how a non-growing – even a shrinking – economy may be able to provide human well-being while beginning to restore the health of the natural world. Twentieth century economic theory is not well able to conceptualize this problem, especial ...
... The impetus for this paper is the urgent need is to figure out how a non-growing – even a shrinking – economy may be able to provide human well-being while beginning to restore the health of the natural world. Twentieth century economic theory is not well able to conceptualize this problem, especial ...
x - Shelton State
... Typically, there is an inverse relationship between supply and demand in that as one increases, the other usually decreases. ...
... Typically, there is an inverse relationship between supply and demand in that as one increases, the other usually decreases. ...
Marketing X Finance = Product with High Return and Low Risk Profile
... – May complement cash flow stream from internal channel relation with external third part financial service, if…………. – How should we organize or marketing activities and financial product design to accomplish this? Faculty of Economics and Business Administration ...
... – May complement cash flow stream from internal channel relation with external third part financial service, if…………. – How should we organize or marketing activities and financial product design to accomplish this? Faculty of Economics and Business Administration ...
Unit 1 Market Mechanisms And Price Elasticity - Beck-Shop
... and price elasticity When goods are scarce, prices rise, but when goods are plentiful, prices fall. In this unit, you will find out why this happens. It is important to be able to distinguish between the different structures or types of markets. You will learn more about supply and demand, and you wi ...
... and price elasticity When goods are scarce, prices rise, but when goods are plentiful, prices fall. In this unit, you will find out why this happens. It is important to be able to distinguish between the different structures or types of markets. You will learn more about supply and demand, and you wi ...
Deadweight loss is the decrease in economic efficiency
... With the price ceiling, instead of the producer's surplus going all the way to the pareto optimal price line, it only goes as high as the price ceiling.The consumer surplus extends down to the price ceiling, but it is limited on the right by Harberger's triangle. In this case, the reason for that l ...
... With the price ceiling, instead of the producer's surplus going all the way to the pareto optimal price line, it only goes as high as the price ceiling.The consumer surplus extends down to the price ceiling, but it is limited on the right by Harberger's triangle. In this case, the reason for that l ...
Process and Emergence in the Economy
... contribute to that construction process. Indeed, the authors of the essays in this volume by no means share a single, coherent vision of the meaning and significance of complexity in economics. What we will find instead is a family resemblance, based upon an interrelated set of themes that together ...
... contribute to that construction process. Indeed, the authors of the essays in this volume by no means share a single, coherent vision of the meaning and significance of complexity in economics. What we will find instead is a family resemblance, based upon an interrelated set of themes that together ...
Revision_on_Changes_in_Costs.pdf
... In the example above, there is a rise in fixed costs - as a result, the AC curve shifts up from AC1 to AC2 There is no change in profit maximizing price or output Profits fall as the gap between price and average cost has declined (i.e. a lower profit margin is made) ...
... In the example above, there is a rise in fixed costs - as a result, the AC curve shifts up from AC1 to AC2 There is no change in profit maximizing price or output Profits fall as the gap between price and average cost has declined (i.e. a lower profit margin is made) ...
cm24e perfect competition
... risk. The tricky part of this analysis is that economists call this normal rate of return on capital "normal profit" but treat it as part of the firms' total costs because it is the opportunity cost ...
... risk. The tricky part of this analysis is that economists call this normal rate of return on capital "normal profit" but treat it as part of the firms' total costs because it is the opportunity cost ...
Lecture 12
... Two Steps to Maximize Profit To maximize its profit, any firm (not just a competitive firm) must answer two questions: The output decision: If the firm produces, what output level, q*, maximizes its profit or minimizes its loss? The shut-down decision: Is it more profitable to produce q* or to ...
... Two Steps to Maximize Profit To maximize its profit, any firm (not just a competitive firm) must answer two questions: The output decision: If the firm produces, what output level, q*, maximizes its profit or minimizes its loss? The shut-down decision: Is it more profitable to produce q* or to ...
Basic Economic Problems
... should be produced and in what quantities. If they require more of consumer goods, then consumer goods should be produced in larger quantity. But if they desire for more of the capital goods, society will have to act upon accordingly. The second question is how to produce. Due to scarcity, resources ...
... should be produced and in what quantities. If they require more of consumer goods, then consumer goods should be produced in larger quantity. But if they desire for more of the capital goods, society will have to act upon accordingly. The second question is how to produce. Due to scarcity, resources ...
Physics - Virginia Community College System
... means that the firm can sell either a low quantity (Ql) or a high quantity (Qh) at exactly the same price (P). (b) A monopolist perceives the demand curve that it faces to be the same as the market demand curve, which for most goods is downward-sloping. Thus, if the monopolist chooses a high level o ...
... means that the firm can sell either a low quantity (Ql) or a high quantity (Qh) at exactly the same price (P). (b) A monopolist perceives the demand curve that it faces to be the same as the market demand curve, which for most goods is downward-sloping. Thus, if the monopolist chooses a high level o ...
Supply and Demand - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... • The amount of goods and services that producers are willing and able to sell at any one time • Reflects producer behavior, not consumer behavior – Does not take demand into consideration – Motto: “On Planet supply, they will always buy.” ...
... • The amount of goods and services that producers are willing and able to sell at any one time • Reflects producer behavior, not consumer behavior – Does not take demand into consideration – Motto: “On Planet supply, they will always buy.” ...
Labor
... Economic Rent For a factor market, economic rent is the difference between the payments made to a factor of production and the minimum amount that must be spent to obtain the use of that factor. ...
... Economic Rent For a factor market, economic rent is the difference between the payments made to a factor of production and the minimum amount that must be spent to obtain the use of that factor. ...
PDF
... management technologies, many of these are not applicable under the field conditions because of the high application cost. This necessitates the need to develop low cost technologies for their greater commercialisation and use. To promulgate widespread bio-inputs adoption, the extension system shoul ...
... management technologies, many of these are not applicable under the field conditions because of the high application cost. This necessitates the need to develop low cost technologies for their greater commercialisation and use. To promulgate widespread bio-inputs adoption, the extension system shoul ...
Economics
Economics is the social science that seeks to describe the factors which determine the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services.The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek οἰκονομία from οἶκος (oikos, ""house"") and νόμος (nomos, ""custom"" or ""law""), hence ""rules of the house (hold for good management)"". 'Political economy' was the earlier name for the subject, but economists in the late 19th century suggested ""economics"" as a shorter term for ""economic science"" to establish itself as a separate discipline outside of political science and other social sciences.Economics focuses on the behavior and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Consistent with this focus, primary textbooks often distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines the behavior of basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the entire economy (meaning aggregated production, consumption, savings, and investment) and issues affecting it, including unemployment of resources (labor, capital, and land), inflation, economic growth, and the public policies that address these issues (monetary, fiscal, and other policies).Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing ""what is,"" and normative economics, advocating ""what ought to be""; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational and behavioral economics; and between mainstream economics (more ""orthodox"" and dealing with the ""rationality-individualism-equilibrium nexus"") and heterodox economics (more ""radical"" and dealing with the ""institutions-history-social structure nexus"").Besides the traditional concern in production, distribution, and consumption in an economy, economic analysis may be applied throughout society, as in business, finance, health care, and government. Economic analyses may also be applied to such diverse subjects as crime, education, the family, law, politics, religion, social institutions, war, science, and the environment. Education, for example, requires time, effort, and expenses, plus the foregone income and experience, yet these losses can be weighted against future benefits education may bring to the agent or the economy. At the turn of the 21st century, the expanding domain of economics in the social sciences has been described as economic imperialism.The ultimate goal of economics is to improve the living conditions of people in their everyday life.