0.8V 1GHz Dynamic Comparator in Digital 90nm CMOS Technology
... voltage minus the common mode voltage. In general, the comparators can tolerate an offset up to ±VREF/2b for a bbit stage [6]. Using dynamic comparators may reduce the architectural complexity and reduce power dissipation, but tight control over variations and mismatch must be exercised to ensure th ...
... voltage minus the common mode voltage. In general, the comparators can tolerate an offset up to ±VREF/2b for a bbit stage [6]. Using dynamic comparators may reduce the architectural complexity and reduce power dissipation, but tight control over variations and mismatch must be exercised to ensure th ...
A LOW POWER AND FAST CMOS ARITHMETIC LOGIC UNIT NUR
... This thesis presents the design of a low power and fast Complimentary Metal-OxideSemiconductor (CMOS) Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). ALU is one of the most important parts of a digital computer which is designed to do the arithmetic and logic operations, including bit shifting operation that need to b ...
... This thesis presents the design of a low power and fast Complimentary Metal-OxideSemiconductor (CMOS) Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). ALU is one of the most important parts of a digital computer which is designed to do the arithmetic and logic operations, including bit shifting operation that need to b ...
CMOS, the Ideal Logic Family
... rather than step functions. Typically, rise and fall times tend to be 20 to 40% longer than the propagation delays. Last, but not least, the noise immunity approaches 50%, being typically 45% of the full logic swing. Besides the fact that it approaches the characteristics of an ideal logic family an ...
... rather than step functions. Typically, rise and fall times tend to be 20 to 40% longer than the propagation delays. Last, but not least, the noise immunity approaches 50%, being typically 45% of the full logic swing. Besides the fact that it approaches the characteristics of an ideal logic family an ...
Unit 7 : A/D and D/A Converter
... within a continuous range of values. Examples include temperature, pressure, light intensity, audio signals, position, rotational speed, and flow rate. Digital systems perform all of their internal operations using digital circuitry and digital operations. Any information that has to be inputted to ...
... within a continuous range of values. Examples include temperature, pressure, light intensity, audio signals, position, rotational speed, and flow rate. Digital systems perform all of their internal operations using digital circuitry and digital operations. Any information that has to be inputted to ...
Subscriber access provided by UNIV OF
... devices built on a 4 in. Si/SiO2 wafer, and a typical chip consisted of five different types of devices, including backgated transistors, top-gated transistors, CMOS inverters, and CMOS, NOR, and NAND logic gates. We first characterized the electrical properties of nanotube transistors as basic comp ...
... devices built on a 4 in. Si/SiO2 wafer, and a typical chip consisted of five different types of devices, including backgated transistors, top-gated transistors, CMOS inverters, and CMOS, NOR, and NAND logic gates. We first characterized the electrical properties of nanotube transistors as basic comp ...
Chap007-2011
... Introduce CMOS logic concepts Explore the voltage transfer characteristics of CMOS inverters Learn to design basic and complex CMOS logic gates Discuss the static and dynamic power in CMOS logic Present expressions for dynamic performance of CMOS logic devices Present noise margins for CMOS logic In ...
... Introduce CMOS logic concepts Explore the voltage transfer characteristics of CMOS inverters Learn to design basic and complex CMOS logic gates Discuss the static and dynamic power in CMOS logic Present expressions for dynamic performance of CMOS logic devices Present noise margins for CMOS logic In ...
Dual 10-Bit TxDAC+ with 2 AD9761 ®
... well as some additional control logic. The data is de-interleaved back into its original I and Q data. An on-chip state machine ensures the proper pairing of I and Q data. The data output from each latch is then processed by a 2 digital interpolation filter that eases the reconstruction filter requ ...
... well as some additional control logic. The data is de-interleaved back into its original I and Q data. An on-chip state machine ensures the proper pairing of I and Q data. The data output from each latch is then processed by a 2 digital interpolation filter that eases the reconstruction filter requ ...
Design of MOS Current-Mode Logic Standard Cells Technology
... This report describes how MOS Current-Mode Logic (MCML) standard cells where designed and created, in order to create a cell library. A short introduction about MCML circuits is given, as well as a complete description of the design process, including all the analysis involved in achieving the trans ...
... This report describes how MOS Current-Mode Logic (MCML) standard cells where designed and created, in order to create a cell library. A short introduction about MCML circuits is given, as well as a complete description of the design process, including all the analysis involved in achieving the trans ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE) e-ISSN: 2278-0661, p-ISSN: 2278-8727 PP 29-36 www.iosrjournals.org
... Pulsewidth control loops (PWCLs) can be used to overcome this problem. A conventional PWCL was produced using a built ring oscillator. Due to the variations in PVT the duty cycle of the ring oscillator deviated widely. Locking time of the circuit was also an important factor. Although a low- voltage ...
... Pulsewidth control loops (PWCLs) can be used to overcome this problem. A conventional PWCL was produced using a built ring oscillator. Due to the variations in PVT the duty cycle of the ring oscillator deviated widely. Locking time of the circuit was also an important factor. Although a low- voltage ...
FED 101: Computer Engineering Module Version 1.3
... As mentioned, the binary number system is used in digital computers. But it is readily apparent that the notation for binary numbers is awkward in that even small numbers are represented by long strings of zeros and ones. Over the years two closely related number systems were used to shorten the rep ...
... As mentioned, the binary number system is used in digital computers. But it is readily apparent that the notation for binary numbers is awkward in that even small numbers are represented by long strings of zeros and ones. Over the years two closely related number systems were used to shorten the rep ...
EL2003 - Electric Circuits#
... elements, sinusoidal steady state analysis, AC steady state power, three phase circuits, frequency response, Introduction to electric machines. To develop skills in obtaining steady state and transient solutions to electrical ...
... elements, sinusoidal steady state analysis, AC steady state power, three phase circuits, frequency response, Introduction to electric machines. To develop skills in obtaining steady state and transient solutions to electrical ...
AD7813 数据手册DataSheet下载
... ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the AD7813 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to h ...
... ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the AD7813 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to h ...
AD669 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... is the measure of the change in the analog output, normalized to full scale, associated with a 1 LSB change in the digital input code. Monotonic behavior requires that the differential linearity error be within ± 1 LSB over the temperature range of interest. MONOTONICITY: A DAC is monotonic if the o ...
... is the measure of the change in the analog output, normalized to full scale, associated with a 1 LSB change in the digital input code. Monotonic behavior requires that the differential linearity error be within ± 1 LSB over the temperature range of interest. MONOTONICITY: A DAC is monotonic if the o ...
An Intelligent Technique for Generating Equivalent TT Circuits Using
... number of original nodes, the number of diagonal elements represent the number of grounded elements, and the reminder elements are thus the floating ones.Secondly, all the passive elements are to be encoded in genes, and the floating passive elements are to be expanded as follows: Each element is re ...
... number of original nodes, the number of diagonal elements represent the number of grounded elements, and the reminder elements are thus the floating ones.Secondly, all the passive elements are to be encoded in genes, and the floating passive elements are to be expanded as follows: Each element is re ...
Chapter 13
... Equation (13.35) indicates that to minimize dynamic power dissipation: Capacitance should be minimal. This shortens length of transients. VDD should be minimal. This is why modern devices use 5V supplies, as opposed to 12 or 15V. Although reduction of f is possible, it goes against the n ...
... Equation (13.35) indicates that to minimize dynamic power dissipation: Capacitance should be minimal. This shortens length of transients. VDD should be minimal. This is why modern devices use 5V supplies, as opposed to 12 or 15V. Although reduction of f is possible, it goes against the n ...
G. H. RAISONI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, NAGPUR Department
... Theory: Digital circuits are different from analog circuits. Almost all digital circuits are designed for two state operations. This means using only two non-adjacent points on the load line, typically saturation and cutoff. As a result the output voltage has only two states, either low or high. Thu ...
... Theory: Digital circuits are different from analog circuits. Almost all digital circuits are designed for two state operations. This means using only two non-adjacent points on the load line, typically saturation and cutoff. As a result the output voltage has only two states, either low or high. Thu ...
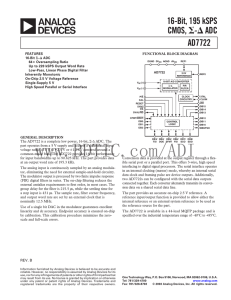
16-Bit, 195 kSPS CMOS, AD7722 -
... simultaneously sample its analog input and update its output data register. A rising edge resets the AD7722 digital filter sequencer counter to zero. After a SYNC, conversion data is not valid until after the digital filter settles (see Figure 7). DVAL goes low in the serial mode. When the rising ed ...
... simultaneously sample its analog input and update its output data register. A rising edge resets the AD7722 digital filter sequencer counter to zero. After a SYNC, conversion data is not valid until after the digital filter settles (see Figure 7). DVAL goes low in the serial mode. When the rising ed ...
IG3415411546
... from T1 as the final first four low power outputs 1010. Note that the clock to the last four bits of the LP-TPG is also disabled. The last four bits however are the outputs from the injector circuits. The injector circuit compares the next value (at the input of the Dflip-flop) with the current valu ...
... from T1 as the final first four low power outputs 1010. Note that the clock to the last four bits of the LP-TPG is also disabled. The last four bits however are the outputs from the injector circuits. The injector circuit compares the next value (at the input of the Dflip-flop) with the current valu ...
ADG711 数据手册DataSheet下载
... The ADG711, ADG712, and ADG713 are monolithic CMOS devices containing four independently selectable switches. These switches are designed on an advanced submicron process that provides low power dissipation yet gives high switching speed, low on resistance, low leakage currents, and high bandwidth. ...
... The ADG711, ADG712, and ADG713 are monolithic CMOS devices containing four independently selectable switches. These switches are designed on an advanced submicron process that provides low power dissipation yet gives high switching speed, low on resistance, low leakage currents, and high bandwidth. ...
Digital electronics

Digital electronics or digital (electronic) circuits are electronics that handle digital signals- discrete bands of analog levels, rather than by continuous ranges (as used in analogue electronics). All levels within a band of values represent the same numeric value. Because of this discretization, relatively small changes to the analog signal levels due to manufacturing tolerance, signal attenuation or parasitic noise do not leave the discrete envelope, and as a result are ignored by signal state sensing circuitry.In most cases the number of these states is two, and they are represented by two voltage bands: one near a reference value (typically termed as ""ground"" or zero volts), and the other a value near the supply voltage. These correspond to the ""false"" (""0"") and ""true"" (""1"") values of the Boolean domain, respectively, yielding binary code.Digital techniques are useful because it is easier to get an electronic device to switch into one of a number of known states than to accurately reproduce a continuous range of values.Digital electronic circuits are usually made from large assemblies of logic gates, simple electronic representations of Boolean logic functions.