File
... A) Hydrogen provides a pair of electrons to be shared with nitrogen. B) Nitrogen provides a pair of electrons to be shared with hydrogen. C) Hydrogen transfers a pair of electrons to nitrogen. D) Nitrogen transfers a pair of electrons to hydrogen. 29. Which type of bond would be formed when a hydrog ...
... A) Hydrogen provides a pair of electrons to be shared with nitrogen. B) Nitrogen provides a pair of electrons to be shared with hydrogen. C) Hydrogen transfers a pair of electrons to nitrogen. D) Nitrogen transfers a pair of electrons to hydrogen. 29. Which type of bond would be formed when a hydrog ...
AP Biology
... Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation: electron transport and ...
... Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation: electron transport and ...
Mass Spectrometers - Porto Conte Ricerche
... with 10-fold higher transfer efficiency in MS/MS mode and 3–5-fold in full scan spectra, by a dual pressure ion trap configuration, and by reduction of overhead times between scans. The first ion trap efficiently captures and fragments ions at relatively high pressure whereas the second ion trap rea ...
... with 10-fold higher transfer efficiency in MS/MS mode and 3–5-fold in full scan spectra, by a dual pressure ion trap configuration, and by reduction of overhead times between scans. The first ion trap efficiently captures and fragments ions at relatively high pressure whereas the second ion trap rea ...
Divergent or just different Rozeboom, Henriette
... 1974). However, in 1976 Rossmann & Argos recognized the structural similarity between hen egg-white lysozyme and phage-type lysozyme via rotation and translation superposition of the two structures (Rossmann et al., 1976). This study was the first example of the discovery of an evolutionary relation ...
... 1974). However, in 1976 Rossmann & Argos recognized the structural similarity between hen egg-white lysozyme and phage-type lysozyme via rotation and translation superposition of the two structures (Rossmann et al., 1976). This study was the first example of the discovery of an evolutionary relation ...
ch19 MSJ jlm
... H2O, CH4, H3N, HCl) = -1 for hydrogen when bonded to metals (e.g., NaH) = -1 for oxygen in peroxides (e.g., HOOH) Sum of O.N. = 0 for neutral compound (e.g., for Na2CO3, Na = +1, O = -2, C = +4) Sum of O.N. = ion charge for polyatomic ion (e.g., for CO3-2, O = -2, C = +4) ...
... H2O, CH4, H3N, HCl) = -1 for hydrogen when bonded to metals (e.g., NaH) = -1 for oxygen in peroxides (e.g., HOOH) Sum of O.N. = 0 for neutral compound (e.g., for Na2CO3, Na = +1, O = -2, C = +4) Sum of O.N. = ion charge for polyatomic ion (e.g., for CO3-2, O = -2, C = +4) ...
Protein foods - Deans Community High School
... Write a heading and try the work below. 1. What test is used to find out if a) sugar is in food - _____________________________ b) starch is in food - ____________________________ c) fat is in food - _______________________________ 2. The name of the test that is used to find out if protein is prese ...
... Write a heading and try the work below. 1. What test is used to find out if a) sugar is in food - _____________________________ b) starch is in food - ____________________________ c) fat is in food - _______________________________ 2. The name of the test that is used to find out if protein is prese ...
Give a brief account of drug protein binding and outline its
... 1995b(13): Give a brief account of drug protein binding and outline its significance General: Drug protein binding refers to the interaction a drug has with proteins. - Can be intravascular, interstitial, or intracellular proteins o Plasma proteins binding is most significant - Interaction is usuall ...
... 1995b(13): Give a brief account of drug protein binding and outline its significance General: Drug protein binding refers to the interaction a drug has with proteins. - Can be intravascular, interstitial, or intracellular proteins o Plasma proteins binding is most significant - Interaction is usuall ...
Expected paths Observed paths Nuclear atom • Rutherford
... • Polyatomic ions: two or more atoms joined by covalent bonds o Commonly contain only nonmetals o Number of polyatomic anions » number of polyatomic cations o Most end in –ite or –ate (oxoanions), a handful in –ide o Some have hypo- (least O) or per- (most O) prefixes o Oxoanion series occur; ex: C ...
... • Polyatomic ions: two or more atoms joined by covalent bonds o Commonly contain only nonmetals o Number of polyatomic anions » number of polyatomic cations o Most end in –ite or –ate (oxoanions), a handful in –ide o Some have hypo- (least O) or per- (most O) prefixes o Oxoanion series occur; ex: C ...
enzymes - MrsGorukhomework
... How do enzymes achieve this substrate specificity? Lock and Key model. Explains why cells have glycoproteins and peripheral proteins to allow for this. The body uses enzyme inhibition a lot to control enzymes. You don’t want them catalyzing everything they see. You want to control them and regulate ...
... How do enzymes achieve this substrate specificity? Lock and Key model. Explains why cells have glycoproteins and peripheral proteins to allow for this. The body uses enzyme inhibition a lot to control enzymes. You don’t want them catalyzing everything they see. You want to control them and regulate ...
Macromolecules PPT.
... - forms tough cell walls in plants because of the way its glucose monomers are linked and arranged in parallel fibres - linkages joining monomers cannot be hydrolyzed (broken) by most animals, so passes through the digestive tract as fibre. - cows and termites have cellulose hydrolyzing microorganis ...
... - forms tough cell walls in plants because of the way its glucose monomers are linked and arranged in parallel fibres - linkages joining monomers cannot be hydrolyzed (broken) by most animals, so passes through the digestive tract as fibre. - cows and termites have cellulose hydrolyzing microorganis ...
Sample Test
... c) mass number d) ionic charge e) ionic weight. 15. The number of electrons lost by an element in chemical reactions is its common ionic charge. This is also known as its: a) atomic number b) atomic weight c) mass number d) valence e) ionic weight. 16. Those elements of the periodic table that form ...
... c) mass number d) ionic charge e) ionic weight. 15. The number of electrons lost by an element in chemical reactions is its common ionic charge. This is also known as its: a) atomic number b) atomic weight c) mass number d) valence e) ionic weight. 16. Those elements of the periodic table that form ...
Ch. 9 Cellular Respiration
... therefore the initial acceptor for FADH2 must be stronger in order to pull the electrons away. ...
... therefore the initial acceptor for FADH2 must be stronger in order to pull the electrons away. ...
Biochemistry - Austin Community College
... more pairs of outer-shell electrons • Much stronger than ionic bonds – holds lots of Energy ...
... more pairs of outer-shell electrons • Much stronger than ionic bonds – holds lots of Energy ...
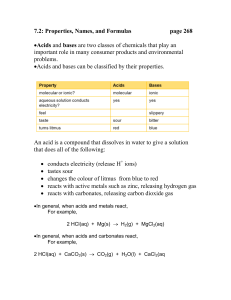
7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas page 268 •Acids and bases
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
... 7.2: Properties, Names, and Formulas ...
Chemistry 464 Biochemistry First Hour Exam
... add 15 mls of .1M HCl .015L x .1 mol/liter = .0015 moles You had 100 ml of .058 M A - = .0058 mole and 100 ml of .042M HA = .0042 moles H+ + A -6HA so A - = .0058-.0015, HA = .0042 + .0015; ...
... add 15 mls of .1M HCl .015L x .1 mol/liter = .0015 moles You had 100 ml of .058 M A - = .0058 mole and 100 ml of .042M HA = .0042 moles H+ + A -6HA so A - = .0058-.0015, HA = .0042 + .0015; ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2013
... 2H2O2 (aq) 2H2O (l) + O2 Which of the following will increase the rate of the reaction? a. Increasing pressure on the reaction b. Decreasing concentration of the reactants c. Adding a catalyst to the reaction d. Decreasing the temperature of the reaction 66. For a reaction, increasing the temperat ...
... 2H2O2 (aq) 2H2O (l) + O2 Which of the following will increase the rate of the reaction? a. Increasing pressure on the reaction b. Decreasing concentration of the reactants c. Adding a catalyst to the reaction d. Decreasing the temperature of the reaction 66. For a reaction, increasing the temperat ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in CH 001 at 8
... E. Insulin leads to activation of glycogen synthase. 7. Describe each cycle/transport system (compounds, compartments, tissues) and explain its purpose: A. malate/aspartate shuttle B. citrate transport system C. Cori cycle D. glucose/alanine cycle 8. For each of these cofactors, explain its chemical ...
... E. Insulin leads to activation of glycogen synthase. 7. Describe each cycle/transport system (compounds, compartments, tissues) and explain its purpose: A. malate/aspartate shuttle B. citrate transport system C. Cori cycle D. glucose/alanine cycle 8. For each of these cofactors, explain its chemical ...
Chapters 2-3 Problem Set 1. Please list the three subatomic
... Solution A: Increases the OH- concentration when added to water. Is Solution A an Acid or a Base? _____________________ Solution B: Decreases the pH when added to water. Is Solution B an Acid or a Base? _____________________ Solution C: Increases the pH when added to water. Is Solution C an Acid or ...
... Solution A: Increases the OH- concentration when added to water. Is Solution A an Acid or a Base? _____________________ Solution B: Decreases the pH when added to water. Is Solution B an Acid or a Base? _____________________ Solution C: Increases the pH when added to water. Is Solution C an Acid or ...
Macromolecules - Van Buren Public Schools
... – H bonds between polar side chains – Ionic bonds between +/- side chains – Disulfide Bridges between two cysteine monomers (those with –SH groups) • S of one bonds with S of another ...
... – H bonds between polar side chains – Ionic bonds between +/- side chains – Disulfide Bridges between two cysteine monomers (those with –SH groups) • S of one bonds with S of another ...
The Electron Transport Chain Chemiosmosis
... therefore the initial acceptor for FADH2 must be stronger in order to pull the electrons away. ...
... therefore the initial acceptor for FADH2 must be stronger in order to pull the electrons away. ...
Download PDF
... The goal of this course is to learn about general aspects of biochemical pathways from the perspective of the chemical principles and chemical reactions. We will cover: 1. Biochemical structures. We will study detailed aspects of the three-dimensional structure of proteins, and how this translates i ...
... The goal of this course is to learn about general aspects of biochemical pathways from the perspective of the chemical principles and chemical reactions. We will cover: 1. Biochemical structures. We will study detailed aspects of the three-dimensional structure of proteins, and how this translates i ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.