The Cell, 5e
... degeneration in a variety of diseases • Radical damage occurs via e- extraction from biologic molecules • ROS include superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical • ROS can damage DNA, proteins, lipids, lead to cell death • Other radical species are NO and HOCl • NO reacts with oxygen or superoxi ...
... degeneration in a variety of diseases • Radical damage occurs via e- extraction from biologic molecules • ROS include superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical • ROS can damage DNA, proteins, lipids, lead to cell death • Other radical species are NO and HOCl • NO reacts with oxygen or superoxi ...
Biological Molecules
... a hydrolysis reaction, an —OH and — H group are added to two subunits when they are broken apart ...
... a hydrolysis reaction, an —OH and — H group are added to two subunits when they are broken apart ...
lecture08_08
... Different polypeptide chains run alongside each other and are linked together by hydrogen bonds. ...
... Different polypeptide chains run alongside each other and are linked together by hydrogen bonds. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 4. According to Stern’s model, how do ions congregate in solution? 5. Define potential of zero charge. 6. Derive the expression for the electrochemical reaction rate on the basis of Faraday’s laws of electrolysis. 7. Define exchange current density of and electrode. How is it related to its polarisa ...
... 4. According to Stern’s model, how do ions congregate in solution? 5. Define potential of zero charge. 6. Derive the expression for the electrochemical reaction rate on the basis of Faraday’s laws of electrolysis. 7. Define exchange current density of and electrode. How is it related to its polarisa ...
File
... Describe a chemical test to show that the fat is unsaturated. name of reagent ................................................................................................................ result of test .............................................................................................. ...
... Describe a chemical test to show that the fat is unsaturated. name of reagent ................................................................................................................ result of test .............................................................................................. ...
BIO 1109 – Principles of Biology Midterm examination 2
... 5.1 Various conditions can alter the activity of an enzyme, briefly what are these and what results? OR Why are plants green and how is this related to photosynthesis {substrate concentration – as it rises so does enzyme activity} {enzyme concentration – the more enzyme the more activity} {Temperatu ...
... 5.1 Various conditions can alter the activity of an enzyme, briefly what are these and what results? OR Why are plants green and how is this related to photosynthesis {substrate concentration – as it rises so does enzyme activity} {enzyme concentration – the more enzyme the more activity} {Temperatu ...
[edit]Occurrence in solution
... a tetrahedral environment, being surrounded by 4 oxygen centres. In these structures, the chemical bonds to silicon conform to the octet rule. These tetrahedra sometimes occur as isolated SiO44- centres, but most commonly, the tetrahedra are joined together in various ways, such as pairs (Si2O76-) a ...
... a tetrahedral environment, being surrounded by 4 oxygen centres. In these structures, the chemical bonds to silicon conform to the octet rule. These tetrahedra sometimes occur as isolated SiO44- centres, but most commonly, the tetrahedra are joined together in various ways, such as pairs (Si2O76-) a ...
1.4 enzymes 2014
... Add a small piece of liver and observe. Feel the side of the beaker during the reaction (be careful not to get solution on your hands – wash it ...
... Add a small piece of liver and observe. Feel the side of the beaker during the reaction (be careful not to get solution on your hands – wash it ...
Chemistry 1 Lectures
... Electron pairs align at 0, 120, and 360º around the central atom, A # of atoms bonded to central atom ...
... Electron pairs align at 0, 120, and 360º around the central atom, A # of atoms bonded to central atom ...
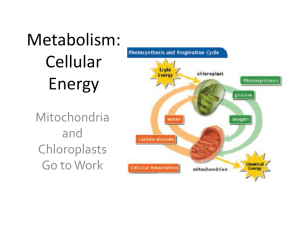
Cellular Energy
... • The life processes of all organisms require energy. • The potential energy held in the bonds of food molecules CANNOT be used directly by the cell. • Energy from food must be converted to the ONLY energy source that cells can use: ATP! ...
... • The life processes of all organisms require energy. • The potential energy held in the bonds of food molecules CANNOT be used directly by the cell. • Energy from food must be converted to the ONLY energy source that cells can use: ATP! ...
Lecture 7 - Columbus Labs
... Cleavage of the polypeptide chain from the tRNA and then the dissociation of the ribosome complex ...
... Cleavage of the polypeptide chain from the tRNA and then the dissociation of the ribosome complex ...
Chapter 2 - San Joaquin Memorial High School
... John Dalton (1766–1844), an Englishman, began teaching at a Quaker school when he was . His fascination with science included an intense interest in meteorology, which led to an interest in the gases of the air and their ultimate components, atoms. Dalton is best known for his atomic theory, in whic ...
... John Dalton (1766–1844), an Englishman, began teaching at a Quaker school when he was . His fascination with science included an intense interest in meteorology, which led to an interest in the gases of the air and their ultimate components, atoms. Dalton is best known for his atomic theory, in whic ...
INTRODUCING AMINO ACIDS
... acids such as alanine, the pI is an average of the pKa's of the carboxyl (2.34) and ammonium (9.69) groups. Thus, the pI for alanine is calculated to be: (2.34 + 9.69)/2 = 6.02, the experimentally determined value. If additional acidic or basic groups are present as side-chain functions, the pI is ...
... acids such as alanine, the pI is an average of the pKa's of the carboxyl (2.34) and ammonium (9.69) groups. Thus, the pI for alanine is calculated to be: (2.34 + 9.69)/2 = 6.02, the experimentally determined value. If additional acidic or basic groups are present as side-chain functions, the pI is ...
50695_1 - Griffith Research Online
... protein folding problem has been heavily sought after is due to their importance. Proteins carry out all of the main functionality within an organism on a cellular level. For example, red blood cells contain a protein known as the hemoglobin. This protein carries out the functionality of carrying ox ...
... protein folding problem has been heavily sought after is due to their importance. Proteins carry out all of the main functionality within an organism on a cellular level. For example, red blood cells contain a protein known as the hemoglobin. This protein carries out the functionality of carrying ox ...
Script
... Due to silicon’s strong bond enthalpy with oxygen, it will be oxidized if oxygen is present. The high abundance of silicates on many of the rocky planets is caused by the bonding of silicon with oxygen when the planets formed. The fully oxidized form of silicon, SiO2, forms four single bonds with fo ...
... Due to silicon’s strong bond enthalpy with oxygen, it will be oxidized if oxygen is present. The high abundance of silicates on many of the rocky planets is caused by the bonding of silicon with oxygen when the planets formed. The fully oxidized form of silicon, SiO2, forms four single bonds with fo ...
Solution
... Explanation: O=O bond energy greater than Cl–O, so the enthalpy contribution is favorable. Entropy chenge is negligible (unchanged number of gas moles). ...
... Explanation: O=O bond energy greater than Cl–O, so the enthalpy contribution is favorable. Entropy chenge is negligible (unchanged number of gas moles). ...
lecture09_09
... physics and chemistry alone Theoretically Ideal solution Practically nearly impossible WHY ? – Exceptionally complex calculations – Biophysics understanding incomplete ...
... physics and chemistry alone Theoretically Ideal solution Practically nearly impossible WHY ? – Exceptionally complex calculations – Biophysics understanding incomplete ...
Lecture 7 Citric acid cycle
... prokaryotes) as citrate synthase catalyzes its condensation with oxaloacetate to form citrate. ...
... prokaryotes) as citrate synthase catalyzes its condensation with oxaloacetate to form citrate. ...
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution
... Loss of the leaving group, the halide ion restores the aromaticity. Kinetics of the reaction are observed to be second order. The addition step is the rate determining step (loss of aromaticity). Nucleophilic substitution, and therefore reaction rate, is facilitated by the presence of a strong elect ...
... Loss of the leaving group, the halide ion restores the aromaticity. Kinetics of the reaction are observed to be second order. The addition step is the rate determining step (loss of aromaticity). Nucleophilic substitution, and therefore reaction rate, is facilitated by the presence of a strong elect ...
H 2 O 2
... Mammalian cytochromes are of three types – a, b, c. They differ in the substituents attached to the porphin ring. All these types of cytochromes occur in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Cytochromes type b (including cytochromes class P-450) occur also in membranes of endoplasmic reticulum and t ...
... Mammalian cytochromes are of three types – a, b, c. They differ in the substituents attached to the porphin ring. All these types of cytochromes occur in the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Cytochromes type b (including cytochromes class P-450) occur also in membranes of endoplasmic reticulum and t ...
AP Chemistry: Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) ---> 2 CaO (s) 2In this reaction the neutral O2 has gained electrons from the Ca to become O in CaO. 2We say O2 has been reduced to O . In all reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions, one species is reduced at the same time as ...
... When a substance gains electrons, it undergoes reduction: 2 Ca (s) + O2 (g) ---> 2 CaO (s) 2In this reaction the neutral O2 has gained electrons from the Ca to become O in CaO. 2We say O2 has been reduced to O . In all reduction-oxidation (redox) reactions, one species is reduced at the same time as ...
Slides - Websupport1
... • Two pyruvates = 34 ATP • The chemical formula for this process is C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ...
... • Two pyruvates = 34 ATP • The chemical formula for this process is C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O ...
Ch 9 Power Point - Cellular Respiration
... • Inner membrane of mitochondria • Multiprotein Complex (I, II, III, IV) • Many of the proteins are cytochromes – have a heme group (iron) which accepts protons • NADH and FADH2 enter and release e• e- are passed down the complexes until they reach oxygen (which also picks up 2 H atoms from surround ...
... • Inner membrane of mitochondria • Multiprotein Complex (I, II, III, IV) • Many of the proteins are cytochromes – have a heme group (iron) which accepts protons • NADH and FADH2 enter and release e• e- are passed down the complexes until they reach oxygen (which also picks up 2 H atoms from surround ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.







![[edit]Occurrence in solution](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009755146_1-58e56f0cc08d3d020872dbc6c3acbb66-300x300.png)