video slide - Your School
... 1 When a ribosome reaches a stop 2 The release factor hydrolyzes 3 The two ribosomal subunits codon on mRNA, the A site of the the bond between the tRNA in and the other components of ribosome accepts a protein called the P site and the last amino the assembly dissociate. a release factor instead of ...
... 1 When a ribosome reaches a stop 2 The release factor hydrolyzes 3 The two ribosomal subunits codon on mRNA, the A site of the the bond between the tRNA in and the other components of ribosome accepts a protein called the P site and the last amino the assembly dissociate. a release factor instead of ...
Inorganic Molecular Capsules: From Structure to
... The assembly of nanoscale capsules or cages using metal coordination represents one of the most interesting and challenging areas of chemical nanoscience. These high-symmetry capsules are invariably comprised of many metal–ligand components, which often selfassemble rapidly and in high yield into a ...
... The assembly of nanoscale capsules or cages using metal coordination represents one of the most interesting and challenging areas of chemical nanoscience. These high-symmetry capsules are invariably comprised of many metal–ligand components, which often selfassemble rapidly and in high yield into a ...
Cellular Respiration
... Acetyl coA is stripped via enzymes: coA is recycle and the remaining acetyl (2-C) is combined with oxaloacetate already present in the mitochondria forming citrate (6-C) Step 2 and 3 Redox reactions take place stripping hydrogen atoms from organic intermediates producing NADH molecules and dispo ...
... Acetyl coA is stripped via enzymes: coA is recycle and the remaining acetyl (2-C) is combined with oxaloacetate already present in the mitochondria forming citrate (6-C) Step 2 and 3 Redox reactions take place stripping hydrogen atoms from organic intermediates producing NADH molecules and dispo ...
Functional Mimics of Superoxide Dismutase Enzymes as
... play in maintaining the health of organisms. The SOD enzymes are a class of oxidoreductases which contain either Cu/Zn, Fe, or Mn at the active site and catalyze this dismutation of the free radical superoxide, the one-electron reduction product of molecular oxygen (eq 1) (eqs 1 and 2, where Mn is t ...
... play in maintaining the health of organisms. The SOD enzymes are a class of oxidoreductases which contain either Cu/Zn, Fe, or Mn at the active site and catalyze this dismutation of the free radical superoxide, the one-electron reduction product of molecular oxygen (eq 1) (eqs 1 and 2, where Mn is t ...
Experiment 2
... The borohydride (or tetrahydroborate) anion, BH4-, is widely used in organic chemistry as a reducing agent. However, it also has many uses in inorganic chemistry, of which two will be explored in this experiment. Controlled oxidation of the borohydride anion results in the formation of borane (BH 3) ...
... The borohydride (or tetrahydroborate) anion, BH4-, is widely used in organic chemistry as a reducing agent. However, it also has many uses in inorganic chemistry, of which two will be explored in this experiment. Controlled oxidation of the borohydride anion results in the formation of borane (BH 3) ...
NUCLEOTIDES METABOLISM Nucleotide
... Humans and other primates excrete uric acid in the urine, but most N goes out as urea Birds, reptiles and insects excrete uric acid and for them it is the major nitrogen excretory compound Gout occurs from accumulation of uric acid crystals in the extremities Allopurinol, which inhibits XO, is a tre ...
... Humans and other primates excrete uric acid in the urine, but most N goes out as urea Birds, reptiles and insects excrete uric acid and for them it is the major nitrogen excretory compound Gout occurs from accumulation of uric acid crystals in the extremities Allopurinol, which inhibits XO, is a tre ...
The Central Role of Acetyl-CoA
... ENERGY PRODUCTION IN THE CELL • Energy is produced by oxidation of molecular fuels small molecules derived from carbohydrates, lipids, proteins • The oxidation uses oxidised forms of coenzymes ultimately producing CO2, H2O and stored energy • Energy is stored directly as ATP or as reduced forms of ...
... ENERGY PRODUCTION IN THE CELL • Energy is produced by oxidation of molecular fuels small molecules derived from carbohydrates, lipids, proteins • The oxidation uses oxidised forms of coenzymes ultimately producing CO2, H2O and stored energy • Energy is stored directly as ATP or as reduced forms of ...
Structure, Mechanism, and Disease Implications of Acetyl CoA
... to form malonyl-CoA, which is the first committed step in fatty acid synthesis.1 ACC is a multifunctional enzyme in that this conversion is accomplished via sequential half-reactions: the ATP-dependent carboxylation of enzyme-bound biotin followed by the transfer of the carboxy group to acetyl-CoA.2 ...
... to form malonyl-CoA, which is the first committed step in fatty acid synthesis.1 ACC is a multifunctional enzyme in that this conversion is accomplished via sequential half-reactions: the ATP-dependent carboxylation of enzyme-bound biotin followed by the transfer of the carboxy group to acetyl-CoA.2 ...
Monodisperse Samarium and Cerium Orthovanadate Nanocrystals
... area, thermal stability, and oxygen storage/release capacity (OSC).1-3 These materials have been used as oxygen ion conductors in solid oxide fuel cells, as three way catalysts (TWCs), and as high-activity catalysts in oxidative dehydrogenation of propane to propene and selective oxidation of hydrog ...
... area, thermal stability, and oxygen storage/release capacity (OSC).1-3 These materials have been used as oxygen ion conductors in solid oxide fuel cells, as three way catalysts (TWCs), and as high-activity catalysts in oxidative dehydrogenation of propane to propene and selective oxidation of hydrog ...
Review Ribosome-independent Peptide Synthesis in Nature and
... reported (44). Obviously, the direct fermentation method is the most cost-effective for dipeptide manufacturing since it dose not need even the substrate amino acids. However, there has been little insight into balancing two metabolic fluxes or the intracellular fate of dipeptides, those of which ar ...
... reported (44). Obviously, the direct fermentation method is the most cost-effective for dipeptide manufacturing since it dose not need even the substrate amino acids. However, there has been little insight into balancing two metabolic fluxes or the intracellular fate of dipeptides, those of which ar ...
Contents and Concepts Learning Objectives
... • The solubility of an insoluble salt can be manipulated by adding a species that reacts with either the cation or the anion. • Effect of pH on Solubility • When a salt contains the conjugate base of a weak acid, the pH will affect the solubility of the salt. ...
... • The solubility of an insoluble salt can be manipulated by adding a species that reacts with either the cation or the anion. • Effect of pH on Solubility • When a salt contains the conjugate base of a weak acid, the pH will affect the solubility of the salt. ...
The maize ID1 flowering time regulator is a zinc finger protein with
... animals, multiple zinc ®nger modules are linked in tandem arrays, with each ®nger separated by a conserved short sequence of seven amino acids known as the H/C link. In these cluster-type zinc ®nger proteins key amino acid residues in the a-helix of each ®nger interact with a triplet of base pairs ( ...
... animals, multiple zinc ®nger modules are linked in tandem arrays, with each ®nger separated by a conserved short sequence of seven amino acids known as the H/C link. In these cluster-type zinc ®nger proteins key amino acid residues in the a-helix of each ®nger interact with a triplet of base pairs ( ...
Preview Sample 1
... 14) At the pH found in cells (about 7.0), what happens to the amino group on an amino acid? A) It acts as a base and gains a proton, giving it a positive charge. B) It acts as an acid and loses a proton, giving it a negative charge. C) It is reduced, and tends to act as an electron donor in redox r ...
... 14) At the pH found in cells (about 7.0), what happens to the amino group on an amino acid? A) It acts as a base and gains a proton, giving it a positive charge. B) It acts as an acid and loses a proton, giving it a negative charge. C) It is reduced, and tends to act as an electron donor in redox r ...
pdf version of ibook - mvhs
... 8. Note the difference between Zn and Zn2+ and Cl2 and 2 Cl-. Zn is an atom while Zn2+ is an ion, which is formed when Zinc atom loses two electrons. Since they are not the same species; they can not be canceled out with each other while writing net ionic equations. Ex. Magnesium turnings are added ...
... 8. Note the difference between Zn and Zn2+ and Cl2 and 2 Cl-. Zn is an atom while Zn2+ is an ion, which is formed when Zinc atom loses two electrons. Since they are not the same species; they can not be canceled out with each other while writing net ionic equations. Ex. Magnesium turnings are added ...
Dominant Dietary Fatty Acids
... Structure of fatty acid synthase (diagram) o Top half is one unit, bottom is the other unit (dimmer) Acyl carrier protein (ACP) o β-oxidation CoA is the carrier o Fatty acid synthesis Acyl group carrier is ACP Contains part of the CoA molecule Homology in acyl carrier group and CoA molecule ...
... Structure of fatty acid synthase (diagram) o Top half is one unit, bottom is the other unit (dimmer) Acyl carrier protein (ACP) o β-oxidation CoA is the carrier o Fatty acid synthesis Acyl group carrier is ACP Contains part of the CoA molecule Homology in acyl carrier group and CoA molecule ...
ELUCIDATION OF A PERIBACTEROID MEMBRANE
... Western blotting demonstrated that GmSAT1 is present as two different size proteins in soybean nodules, with the full length protein present in the insoluble fraction and a truncated protein present in the soluble protein fraction. Biochemical evidence in yeast using a modified two-hybrid reporter s ...
... Western blotting demonstrated that GmSAT1 is present as two different size proteins in soybean nodules, with the full length protein present in the insoluble fraction and a truncated protein present in the soluble protein fraction. Biochemical evidence in yeast using a modified two-hybrid reporter s ...
ch 7.1 - PickIntSci
... How many shoes do you own? Because shoes come in twos, you would most likely count them by the pair rather than individually. The counting units you use depend on what you are counting. For example, you might count eggs by the dozen or paper by the ream. Chemists also need practical units for counti ...
... How many shoes do you own? Because shoes come in twos, you would most likely count them by the pair rather than individually. The counting units you use depend on what you are counting. For example, you might count eggs by the dozen or paper by the ream. Chemists also need practical units for counti ...
Ch.24Pt.5_000
... fatty acid + ATP acyl-adenylate + PPi PPi 2 Pi acyladenylate + HS-CoA acyl-CoA + AMP Thiokinase Overall: fatty acid + ATP + HS-CoA acyl-CoA + AMP + 2 Pi ...
... fatty acid + ATP acyl-adenylate + PPi PPi 2 Pi acyladenylate + HS-CoA acyl-CoA + AMP Thiokinase Overall: fatty acid + ATP + HS-CoA acyl-CoA + AMP + 2 Pi ...
Fyzikální a analytická chemie - Institute of Medical Biochemistry and
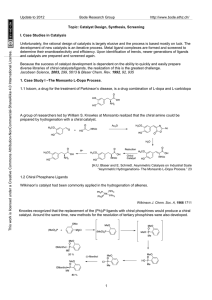
... Precatalysts: For example, Wilkinson's catalyst RhCl(PPh3)3 loses one triphenylphosphine ligand before entering the true catalytic cycle. Precatalysts are easier to store but are easily activated in situ. Because of this preactivation step, many catalytic reactions involve an induction period. ...
... Precatalysts: For example, Wilkinson's catalyst RhCl(PPh3)3 loses one triphenylphosphine ligand before entering the true catalytic cycle. Precatalysts are easier to store but are easily activated in situ. Because of this preactivation step, many catalytic reactions involve an induction period. ...
Preparation and Characterization of Nickel and
... Nickel(II) commonly forms complexes with three different geometries: octahedral, tetrahedral, and square planar. Some five-coordinate complexes are known but are rare. Nickel(II) is a 3d8 system so octahedral and tetrahedral complexes will have 2 unpaired electrons and square planar complexes usuall ...
... Nickel(II) commonly forms complexes with three different geometries: octahedral, tetrahedral, and square planar. Some five-coordinate complexes are known but are rare. Nickel(II) is a 3d8 system so octahedral and tetrahedral complexes will have 2 unpaired electrons and square planar complexes usuall ...
cyt c - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... • Cyanide, azide and CO inhibit Complex IV, binding tightly to the ferric form (Fe3+) of a3 • Oligomycin and DCCD are ATP synthase inhibitors ...
... • Cyanide, azide and CO inhibit Complex IV, binding tightly to the ferric form (Fe3+) of a3 • Oligomycin and DCCD are ATP synthase inhibitors ...
OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION
... • Inner mitochondrial membrane • Is the final common pathway by which electrons from food molecules are used to make ATP and molecular oxygen acts as the final acceptor of the electrons ...
... • Inner mitochondrial membrane • Is the final common pathway by which electrons from food molecules are used to make ATP and molecular oxygen acts as the final acceptor of the electrons ...
chemistry - Canisteo-Greenwood Central School
... The enzyme urease hydrolyzes urea, a constituent of urine, into ammonia and carbon dioxide. ...
... The enzyme urease hydrolyzes urea, a constituent of urine, into ammonia and carbon dioxide. ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.