4 Titration Curve of an Amino Acid
... acids can exist as zwitterions, under physiological conditions these amino acids will be charged. If the net charge under physiological conditions is negative, the amino acid is classified as an acidic amino acid because the R group has a proton that dissociates at a pH significantly below pH 7. The ...
... acids can exist as zwitterions, under physiological conditions these amino acids will be charged. If the net charge under physiological conditions is negative, the amino acid is classified as an acidic amino acid because the R group has a proton that dissociates at a pH significantly below pH 7. The ...
Problem Set 8 Key
... results in the inhibition of ACC and decreased synthesis of malonyl-CoA (hence decreased flux through fatty acid synthesis). Insulin activates a phosphatase that will dephosphorylate ACC and reactivate fat synthesis. c. Please comment on how ACC activity influences fatty acid oxidation. The product ...
... results in the inhibition of ACC and decreased synthesis of malonyl-CoA (hence decreased flux through fatty acid synthesis). Insulin activates a phosphatase that will dephosphorylate ACC and reactivate fat synthesis. c. Please comment on how ACC activity influences fatty acid oxidation. The product ...
Week Date Hours Topic Standard IBO Assessment Statement Labs
... the removal of introns to form mature mRNA. Explain that each tRNA molecule is recognized by a tRNA-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the tRNA, using ATP for energy. Outline the structure of ribosomes, including protein and RNA composition, large and small subunits, three tRNA bi ...
... the removal of introns to form mature mRNA. Explain that each tRNA molecule is recognized by a tRNA-activating enzyme that binds a specific amino acid to the tRNA, using ATP for energy. Outline the structure of ribosomes, including protein and RNA composition, large and small subunits, three tRNA bi ...
Mass Spectrometric Studies on Metal
... The anionic products from the reactions of all the studied metal samples with C6F6 were generated under the similar experimental conditions as shown above. The wavelength of the laser(1064 nm or 532 nm) used for the ablation had little effect on the product distribution. The seeding of hexaflurobenz ...
... The anionic products from the reactions of all the studied metal samples with C6F6 were generated under the similar experimental conditions as shown above. The wavelength of the laser(1064 nm or 532 nm) used for the ablation had little effect on the product distribution. The seeding of hexaflurobenz ...
OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES INTRODUCTION
... The scale runs from 0 to 14 with 0 being highest in acidity and 14 lowest. When the pH is in the range of 0 -7, a solution is said to be acidic; if the pH is around 7, the solution is neutral; and if the pH is in the range of 7-14, the solution is basic. Amino acid side chains contain groups, such a ...
... The scale runs from 0 to 14 with 0 being highest in acidity and 14 lowest. When the pH is in the range of 0 -7, a solution is said to be acidic; if the pH is around 7, the solution is neutral; and if the pH is in the range of 7-14, the solution is basic. Amino acid side chains contain groups, such a ...
Polyoxyalkylene cyclic hydrocarbon substituted amines and their
... the‘amine into a cationic ammonium salt. It is to be noted that although long chain alkyl-substi yl and ethyl naphthalene; phenanthrene and the alkyl tuted cyclic‘hydrocarbon amines containing a single long phenanthrenes; the partially hydrogenated polynuclear chain alkyl substituent having from abo ...
... the‘amine into a cationic ammonium salt. It is to be noted that although long chain alkyl-substi yl and ethyl naphthalene; phenanthrene and the alkyl tuted cyclic‘hydrocarbon amines containing a single long phenanthrenes; the partially hydrogenated polynuclear chain alkyl substituent having from abo ...
Weathering and Erosion - Mrs. Brady's Earth Science Website
... • The more exposure to the weathering agents: wind, water, gravity, the faster the rock will weather. • Surface Area: as rocks break into smaller pieces the surface area increases therefore weathering rate increases ...
... • The more exposure to the weathering agents: wind, water, gravity, the faster the rock will weather. • Surface Area: as rocks break into smaller pieces the surface area increases therefore weathering rate increases ...
+ O 2 (g)
... • Oxidation is the loss of electrons from an atom. • Reduction is the gain of electrons by an atom. • Both processes occur together in a single reaction called an oxidation−reduction or redox reaction. • A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one element to another. • A redox react ...
... • Oxidation is the loss of electrons from an atom. • Reduction is the gain of electrons by an atom. • Both processes occur together in a single reaction called an oxidation−reduction or redox reaction. • A redox reaction involves the transfer of electrons from one element to another. • A redox react ...
Chem 2323 Organic Chemistry I Spring 2013 Review Sheet for
... ii. Real structure is a hybrid of all resonance structures. f. Know how to use pKa to tell if a reaction will occur as it is written. Will the acid give up its proton? (quiz #2) i. Lower pKa = stronger acid (more likely to give up H+) g. Know how the resulting resonance structures formed after an ac ...
... ii. Real structure is a hybrid of all resonance structures. f. Know how to use pKa to tell if a reaction will occur as it is written. Will the acid give up its proton? (quiz #2) i. Lower pKa = stronger acid (more likely to give up H+) g. Know how the resulting resonance structures formed after an ac ...
Chapter 2 Geochemical Reactions
... implied in the term geochemistry. These processes include dissolution of air-borne material and gases, weathering at the Earth’s surface, biodegradation and nutrient cycling in the soil, mineral dissolution in the subsurface, and mixing with seawater or deep crustal water. Human activity also plays ...
... implied in the term geochemistry. These processes include dissolution of air-borne material and gases, weathering at the Earth’s surface, biodegradation and nutrient cycling in the soil, mineral dissolution in the subsurface, and mixing with seawater or deep crustal water. Human activity also plays ...
Can correct protein models be identified?
... types of energy function to detect the native, or native-like, protein structure from a large set of decoys. In contrast to earlier studies, we examine here the ability to detect models that only show limited structural similarity to the native structure. These correct models are defined by the exis ...
... types of energy function to detect the native, or native-like, protein structure from a large set of decoys. In contrast to earlier studies, we examine here the ability to detect models that only show limited structural similarity to the native structure. These correct models are defined by the exis ...
An Introduction to Energy, Enzymes, and Metabolism
... To understand why a chemical reaction occurs, we first need to consider energy, which we will define as the ability to promote change or do work. Physicists often consider energy in two forms: kinetic energy and potential energy (Figure 6.1). Kinetic energy is energy associated with movement, such a ...
... To understand why a chemical reaction occurs, we first need to consider energy, which we will define as the ability to promote change or do work. Physicists often consider energy in two forms: kinetic energy and potential energy (Figure 6.1). Kinetic energy is energy associated with movement, such a ...
Formation, photodissociation, and structure studies of group 14(Si
... more favorable when covalent bonding interaction is weakened. These trends could be attributed to many factors, such as valence electrons, ionization energies, electron affinities, atom sizes, etc., whereas the most profound factor is their bonding properties. However, since there is not enough expe ...
... more favorable when covalent bonding interaction is weakened. These trends could be attributed to many factors, such as valence electrons, ionization energies, electron affinities, atom sizes, etc., whereas the most profound factor is their bonding properties. However, since there is not enough expe ...
Unit 7: Reduction, Oxidation and Electrochemistry
... d. In Basic Environment, Add the Same Number of OH− as H+ to BOTH Sides. Combine H+ and OH− that are on the Same Side into H2O. Simplify the H2O on Both Sides. Example: Cl2 (g) → HClO4 (aq) (Cl changes from 0 to +7. Hence, add 7 e− to the product side.) Cl2 (g) → HClO4 (aq) + 7e− (Multiply the HClO4 ...
... d. In Basic Environment, Add the Same Number of OH− as H+ to BOTH Sides. Combine H+ and OH− that are on the Same Side into H2O. Simplify the H2O on Both Sides. Example: Cl2 (g) → HClO4 (aq) (Cl changes from 0 to +7. Hence, add 7 e− to the product side.) Cl2 (g) → HClO4 (aq) + 7e− (Multiply the HClO4 ...
Chapter 4-5
... e.g. 0 for H in H2 2. ON of a monatomic ion = charge on ion e.g. +1 for Na+ , and –2 for sulfur S23. An atom in polyatomic ion or in a molecular compound usually has the same ON it would have if it were a monatomic ion e.g. (OH-) O = -2 and H = +1 4. ON for Hydrogen (H) is +1 in all compounds except ...
... e.g. 0 for H in H2 2. ON of a monatomic ion = charge on ion e.g. +1 for Na+ , and –2 for sulfur S23. An atom in polyatomic ion or in a molecular compound usually has the same ON it would have if it were a monatomic ion e.g. (OH-) O = -2 and H = +1 4. ON for Hydrogen (H) is +1 in all compounds except ...
Chapter 1 – ______
... a. Derived from linoleic acid, an essential fatty acid b. Increases lean body mass in animals c. Few human studies have been performed. 6. Caffeine a. Caffeine can enhance performance by stimulating fatty acid release. b. Adverse effects include stomach upset, nervousness, irritability, headaches, a ...
... a. Derived from linoleic acid, an essential fatty acid b. Increases lean body mass in animals c. Few human studies have been performed. 6. Caffeine a. Caffeine can enhance performance by stimulating fatty acid release. b. Adverse effects include stomach upset, nervousness, irritability, headaches, a ...
INTRODUCTION TO CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
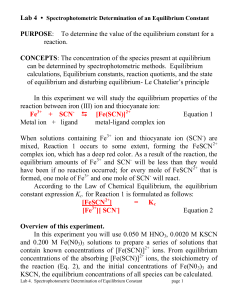
PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a
... Since the Fe3+ concentration is great excess in part A, this error would have no impact on the outcome. The SCN- concentration determines the concentration of FeSCN2+. 8. An error was made in preparing the KSCN solution in Part A. Its concentration was 0.003 molar but was labeled as 0.002 molar. How ...
... Since the Fe3+ concentration is great excess in part A, this error would have no impact on the outcome. The SCN- concentration determines the concentration of FeSCN2+. 8. An error was made in preparing the KSCN solution in Part A. Its concentration was 0.003 molar but was labeled as 0.002 molar. How ...
16-18 Cellular respiration
... Each successive carrier in the chain has a higher electronegativity than the carrier before it, so the electrons are pulled downhill towards oxygen, the final electron acceptor and the molecule with the highest electronegativity. Except for ubiquinone (Q), most of the carrier molecules are proteins ...
... Each successive carrier in the chain has a higher electronegativity than the carrier before it, so the electrons are pulled downhill towards oxygen, the final electron acceptor and the molecule with the highest electronegativity. Except for ubiquinone (Q), most of the carrier molecules are proteins ...
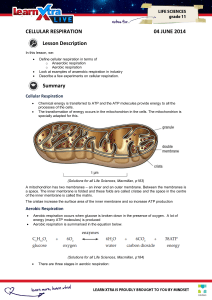
CELLULAR RESPIRATION 04 JUNE 2014 Lesson Description
... carbon dioxide. The hydrogens will be used in oxidative phosphorylation and the carbon dioxide will be breathed out. ...
... carbon dioxide. The hydrogens will be used in oxidative phosphorylation and the carbon dioxide will be breathed out. ...
AAA-Direct Amino Acid Analysis System
... Amino Acids, Amino Sugars, and Carbohydrates Amino sugars are often present in protein hydrolysates and can be determined directly along with amino acids because they are well resolved on the AminoPac PA10 column (Figure 6). In the biotechnology industry, the AAA-Direct Amino Acid Analysis System ha ...
... Amino Acids, Amino Sugars, and Carbohydrates Amino sugars are often present in protein hydrolysates and can be determined directly along with amino acids because they are well resolved on the AminoPac PA10 column (Figure 6). In the biotechnology industry, the AAA-Direct Amino Acid Analysis System ha ...
ICBEnzyEvol
... Nonsynonymous substitutions – Estimation of rate of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions has become an important subject in molecular evolution ...
... Nonsynonymous substitutions – Estimation of rate of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions has become an important subject in molecular evolution ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.