VITAMINS-6
... • Malonyl-CoA is required for the synthesis of fatty acids • Pyruvate carboxylase is a critical enzyme in gluconeogenesis—the formation of glucose from sources other than carbohydrates, for example, amino acids • Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes an essential step in the catabolism of leucine ...
... • Malonyl-CoA is required for the synthesis of fatty acids • Pyruvate carboxylase is a critical enzyme in gluconeogenesis—the formation of glucose from sources other than carbohydrates, for example, amino acids • Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase catalyzes an essential step in the catabolism of leucine ...
BCC-44-4-289-298 - Bulgarian Chemical Communications
... as catalysts in various chemical processes [2, 3], or as models for a better understanding of some biological systems [4-6]. However, the unsymmetric tetradentate Schiff base metal complexes were less studied than the symmetric ones [7]. The investigation of Schiff base metal complexes has been of i ...
... as catalysts in various chemical processes [2, 3], or as models for a better understanding of some biological systems [4-6]. However, the unsymmetric tetradentate Schiff base metal complexes were less studied than the symmetric ones [7]. The investigation of Schiff base metal complexes has been of i ...
Chapter 19 Lipid Metabolism
... Can synthesize fatty acids from sugars, some amino acids, and other fatty acids. →Fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA in the cytosol. The body synthesizes palmitic acid (16:0), and then modifies it to form other fatty acids. Synthesis of Palmitic Acid 8 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP +14NADPH +14H+ → pa ...
... Can synthesize fatty acids from sugars, some amino acids, and other fatty acids. →Fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA in the cytosol. The body synthesizes palmitic acid (16:0), and then modifies it to form other fatty acids. Synthesis of Palmitic Acid 8 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP +14NADPH +14H+ → pa ...
- Wiley Online Library
... this reaction approximately one hundred times more compared with systems with other cations, like Ca2+ (ibid.). The difference in this respect between Mg2+ and Ca2+ is attributed to the difference in ionic radius. The smaller magnesium ion (0.65 Å, coordination number CN = 6) can form a complex wit ...
... this reaction approximately one hundred times more compared with systems with other cations, like Ca2+ (ibid.). The difference in this respect between Mg2+ and Ca2+ is attributed to the difference in ionic radius. The smaller magnesium ion (0.65 Å, coordination number CN = 6) can form a complex wit ...
msb145697-sup-0001-Supp_Info
... To estimate the fraction of total protein mass covered by mass spectrometry, we rely on two pieces of information: 1) the highly non-uniform distribution of individual protein mass as given by the method of spectral counting (shown above); and 2) the absolute protein quantitation results from the 2D ...
... To estimate the fraction of total protein mass covered by mass spectrometry, we rely on two pieces of information: 1) the highly non-uniform distribution of individual protein mass as given by the method of spectral counting (shown above); and 2) the absolute protein quantitation results from the 2D ...
Proceedings of the Nutrition Society Safety and efficacy of high
... limiting ‘intake of red meat to less than 80 g daily’. The UK Reference Nutrient Intake for adult males (19–50 years) is 55.5 g protein and for females 45.0 g (note not meat intake). The upper recommendation is not to eat more than 1.5 g protein kg per d for the general public not engaged in strenuo ...
... limiting ‘intake of red meat to less than 80 g daily’. The UK Reference Nutrient Intake for adult males (19–50 years) is 55.5 g protein and for females 45.0 g (note not meat intake). The upper recommendation is not to eat more than 1.5 g protein kg per d for the general public not engaged in strenuo ...
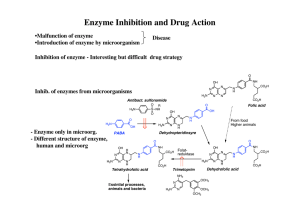
Enzyme Inhibition and Drug Action
... Inhib. and substrate very different structures Difficult to design inhib. ...
... Inhib. and substrate very different structures Difficult to design inhib. ...
Variations in amino acid composition in bacterial single stranded
... proteins involved in all aspects of DNA metabolism. EcoSSB has become one of the standard models for studying ssDNA-SSB interactions, a comprehensive review of which can be found in the work of Shereda and co-authors (5). The crystal structure of EcoSSB proved that the functional protein exists as a ...
... proteins involved in all aspects of DNA metabolism. EcoSSB has become one of the standard models for studying ssDNA-SSB interactions, a comprehensive review of which can be found in the work of Shereda and co-authors (5). The crystal structure of EcoSSB proved that the functional protein exists as a ...
Chapter 6: Cellular Respiration
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
... from organic fuels to oxygen Enzymes are necessary to oxidize glucose and other foods – The enzyme that removes hydrogen from an organic molecule is called dehydrogenase – Dehydrogenase requires a coenzyme called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) to shuttle electrons – NAD+ can become reduc ...
Synthesis and thermal decarbonylation of W(CO)5 complexes
... CO2Prn) groups (see Scheme 1). The reaction of the polymeric ligands 1, 2 and 3 with the corresponding stoichiometric or substoichiometric amounts of [W(MeOH)(CO)5] in a mixture of dichloromethane–methanol gave the complexes (Scheme 2) {[NP(O2C12H8)]0.5[NP(O–C6H4–CO2Prn)(O–C6H4–CN)(W(CO)5)0.4]0.5}n ...
... CO2Prn) groups (see Scheme 1). The reaction of the polymeric ligands 1, 2 and 3 with the corresponding stoichiometric or substoichiometric amounts of [W(MeOH)(CO)5] in a mixture of dichloromethane–methanol gave the complexes (Scheme 2) {[NP(O2C12H8)]0.5[NP(O–C6H4–CO2Prn)(O–C6H4–CN)(W(CO)5)0.4]0.5}n ...
How to deal with oxygen radicals stemming from mitochondrial fatty
... high FADH2/NADH ratios. Clockwise: 1. Development of mechanisms to induce (regulated) mild uncoupling (e.g. uncoupling proteins). 2. Segregation of fatty acid oxidation (completely in neurons, plants and some yeasts, limited to VLCFAs only in most mammalian cells). 3. Evolving specific mitophagy pat ...
... high FADH2/NADH ratios. Clockwise: 1. Development of mechanisms to induce (regulated) mild uncoupling (e.g. uncoupling proteins). 2. Segregation of fatty acid oxidation (completely in neurons, plants and some yeasts, limited to VLCFAs only in most mammalian cells). 3. Evolving specific mitophagy pat ...
1055 BIOTECHNOLOGYDERIVED ARTICLES—PEPTIDE
... Isolation and purification are necessary for analysis of bulk drugs or dosage forms containing interfering excipients and carrier proteins and, when required, will be specified in the monograph. Quantitative recovery of protein from the dosage form should be validated. Selective Cleavage of Peptide ...
... Isolation and purification are necessary for analysis of bulk drugs or dosage forms containing interfering excipients and carrier proteins and, when required, will be specified in the monograph. Quantitative recovery of protein from the dosage form should be validated. Selective Cleavage of Peptide ...
The Natural History of Nitrogen Fixation
... in oxygen-evolving cyanobacteria and organisms carrying out oxidative phosphorylation. Certain cyanobacteria contribute substantial amounts of fixed nitrogen in marine environments and do so because of exquisite controls on temporal and spatial separation of the two processes (Berman-Frank et al. 20 ...
... in oxygen-evolving cyanobacteria and organisms carrying out oxidative phosphorylation. Certain cyanobacteria contribute substantial amounts of fixed nitrogen in marine environments and do so because of exquisite controls on temporal and spatial separation of the two processes (Berman-Frank et al. 20 ...
CH 2
... than the normal peptide-forming carboxyl (attached to the a-carbon). The sulfhydryl group of the cysteine R-group functions as the reducing agent, and recombines with disulfide bonds in a variety of molecules to release as a free sulfhydryl one of those partners in the disulfide. Another molecule of ...
... than the normal peptide-forming carboxyl (attached to the a-carbon). The sulfhydryl group of the cysteine R-group functions as the reducing agent, and recombines with disulfide bonds in a variety of molecules to release as a free sulfhydryl one of those partners in the disulfide. Another molecule of ...
Plasmodium falciparum enolase - Tata Institute of Fundamental
... (Pfen) (EC 4.2.1.11), the dehydrating glycolytic metalloenzyme that catalyzes the inter conversion of 2-phosphoglyceric acid (2-PGA) and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), has not yet been characterized. Enolases are highly conserved across species [9]. In most species, it exists as a symmetric homodimer [1 ...
... (Pfen) (EC 4.2.1.11), the dehydrating glycolytic metalloenzyme that catalyzes the inter conversion of 2-phosphoglyceric acid (2-PGA) and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), has not yet been characterized. Enolases are highly conserved across species [9]. In most species, it exists as a symmetric homodimer [1 ...
Design and Synthesis of a Thermally Stable Organic Electride
... After testing a number of anions, we found that 3-[tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]-1-propanesulfonate (7, abbreviated TAPS-) had the desired properties of solubility and reducibility. This anion is much more flexible than those used previously and probably uses its three hydroxyl groups to form hydr ...
... After testing a number of anions, we found that 3-[tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]-1-propanesulfonate (7, abbreviated TAPS-) had the desired properties of solubility and reducibility. This anion is much more flexible than those used previously and probably uses its three hydroxyl groups to form hydr ...
Introduction to Protein Structure
... • Within protein different domains can be identified – For example: • ligand binding domain • DNA binding domain • Catalytic domain • Domains are built from motifs of secondary structure elements ...
... • Within protein different domains can be identified – For example: • ligand binding domain • DNA binding domain • Catalytic domain • Domains are built from motifs of secondary structure elements ...
Cellular Respiration
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
... respiration and removes CO2 Respiration, as it relates to breathing, and cellular respiration are not the same. – Respiration, in the breathing sense, refers to an exchange of gases. Usually an organism brings in oxygen from the environment and releases waste CO2. – Cellular respiration is the aer ...
Metal Chalcogenide Clusters with Closed Electronic Shells and the
... by CO. Furthermore, the PEt3 and CO derived states always reside either deeper or higher in energy relative to the Fermi level, respectively (Figure 5). Consequently, the progressive shift in the AIE and AEA is associated with the position of HOMO and LUMO states derived from the metal core rather t ...
... by CO. Furthermore, the PEt3 and CO derived states always reside either deeper or higher in energy relative to the Fermi level, respectively (Figure 5). Consequently, the progressive shift in the AIE and AEA is associated with the position of HOMO and LUMO states derived from the metal core rather t ...
CHAPTER 15 ACIDS AND BASES
... At pH 1.00 the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.10 M ([H ] = 10 ). The extra hydrogen ions will tend to suppress the ionization of the weak acid (LeChâtelier's principle, Section 14.5 of the text). The position of equilibrium is shifted in the direction of the un-ionized acid. Let's set up a table ...
... At pH 1.00 the concentration of hydrogen ion is 0.10 M ([H ] = 10 ). The extra hydrogen ions will tend to suppress the ionization of the weak acid (LeChâtelier's principle, Section 14.5 of the text). The position of equilibrium is shifted in the direction of the un-ionized acid. Let's set up a table ...
Metalloprotein

Metalloprotein is a generic term for a protein that contains a metal ion cofactor. A large number of all proteins are part of this category.