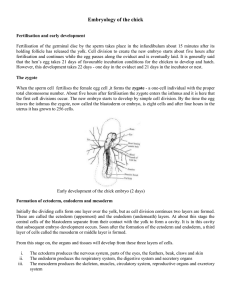
embryology of the chick
... that subsequent embryo development occurs. Soon after the formation of the ectoderm and endoderm, a third layer of cells called the mesoderm or middle layer is formed. From this stage on, the organs and tissues will develop from these three layers of cells. ...
... that subsequent embryo development occurs. Soon after the formation of the ectoderm and endoderm, a third layer of cells called the mesoderm or middle layer is formed. From this stage on, the organs and tissues will develop from these three layers of cells. ...
An Overview of Insect Hormones
... Blastoderm Formation Energid: each nucleus surrounded by a small island of cytoplasm during the meroblastic cleavage of most insects After a series of mitoses, the energids migrate to the egg periphery and continue to divide there. Syncytial blastoderm: lacks any membranes, with all the cleavage nu ...
... Blastoderm Formation Energid: each nucleus surrounded by a small island of cytoplasm during the meroblastic cleavage of most insects After a series of mitoses, the energids migrate to the egg periphery and continue to divide there. Syncytial blastoderm: lacks any membranes, with all the cleavage nu ...
Chapter 21: Reproductive System
... expensive and may not be readily available. Physicians can use several criteria aside from detection of the organism to decide whether to prescribe the proper antibiotics to cure chlamydia. If gonorrhea is present, some physicians also routinely prescribe antibiotics for ...
... expensive and may not be readily available. Physicians can use several criteria aside from detection of the organism to decide whether to prescribe the proper antibiotics to cure chlamydia. If gonorrhea is present, some physicians also routinely prescribe antibiotics for ...
information about pregnancy - University of Michigan School of
... Women who are + for GBS need to have intravenous antibiotic prophylaxis (IAP) during labor in order to reduce the risk to their newborn of acquiring the disease. Babies who are born to mothers with +GBS may require additional assessment after birth. Women’s Hospital Birth Center puts babies on “36 h ...
... Women who are + for GBS need to have intravenous antibiotic prophylaxis (IAP) during labor in order to reduce the risk to their newborn of acquiring the disease. Babies who are born to mothers with +GBS may require additional assessment after birth. Women’s Hospital Birth Center puts babies on “36 h ...
DERIVATIVES OF THE ENDODERMAL GERM LAYER
... exchange Some times called the placental barrier, the placental membrane is not a true barrier, as ...
... exchange Some times called the placental barrier, the placental membrane is not a true barrier, as ...
Animal embryology and development
... Any abnormality that causes the death or disability of a child. They can be caused by chromosomal abnormalities, e.g. . . . Extra copies of chromosome 21 cause Downs syndrome. Genetic defects such as point mutations can cause them too, (remember OMIM at NCBI) e.g. . . . Tay-Sachs, phenylketonuria, a ...
... Any abnormality that causes the death or disability of a child. They can be caused by chromosomal abnormalities, e.g. . . . Extra copies of chromosome 21 cause Downs syndrome. Genetic defects such as point mutations can cause them too, (remember OMIM at NCBI) e.g. . . . Tay-Sachs, phenylketonuria, a ...
OB Unit 4
... Prognosis depends on deformity’s extent Folate(Folic Acid) reduces the risk for neural tube defects ...
... Prognosis depends on deformity’s extent Folate(Folic Acid) reduces the risk for neural tube defects ...
Chapter 6 Growth and Measurement Weight and body composition
... of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor after closure of the epiphyses Abnormalities (Cont.) Cushing Syndrome A disorder associated with a prolonged and excessively high exposure to glucocorticoids Abnormalities (Cont.) Turner syndrome A genetic disorder in which there is partial or complet ...
... of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor after closure of the epiphyses Abnormalities (Cont.) Cushing Syndrome A disorder associated with a prolonged and excessively high exposure to glucocorticoids Abnormalities (Cont.) Turner syndrome A genetic disorder in which there is partial or complet ...
Uterus
... Is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in human reproduction. The female reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty to be able to produce gametes, and to carry a fetus to full term. The internal sex organs are the uterus and Fallopian tubes ...
... Is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in human reproduction. The female reproductive system is immature at birth and develops to maturity at puberty to be able to produce gametes, and to carry a fetus to full term. The internal sex organs are the uterus and Fallopian tubes ...
5 - Pass the FracP
... and the postpartum period are times of increased lupus activity. In severe flares early in gestation, pregnancy termination is often recommended. If pregnancy termination is not an option, then medical therapy to manage the lupus flare should not be influenced by the pregnancy, provided informed con ...
... and the postpartum period are times of increased lupus activity. In severe flares early in gestation, pregnancy termination is often recommended. If pregnancy termination is not an option, then medical therapy to manage the lupus flare should not be influenced by the pregnancy, provided informed con ...
Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum—A Skin
... weeks’ gestation who had vulvovaginal infection due to acyclovirresistant HSV-2 was treated with foscarnet (40 mg/kg intravenously q8h) beginning at week 29 –30 of pregnancy; no further follow-up data are available. Presently, there are no studies of foscarnet use in pregnancy. The toxicity to the f ...
... weeks’ gestation who had vulvovaginal infection due to acyclovirresistant HSV-2 was treated with foscarnet (40 mg/kg intravenously q8h) beginning at week 29 –30 of pregnancy; no further follow-up data are available. Presently, there are no studies of foscarnet use in pregnancy. The toxicity to the f ...
Group Health Prenatal Care Guideline
... Postpartum Visit ......................................................................................................................................... 13 ...
... Postpartum Visit ......................................................................................................................................... 13 ...
PATIENT`S FACT SHEET: Smoking and Infertility
... smoke. Smokeless tobacco also leads to increased miscarriage rates. Women who smoke are more likely to conceive a chromosomally unhealthy pregnancy (such as a pregnancy affected by Down syndrome) ...
... smoke. Smokeless tobacco also leads to increased miscarriage rates. Women who smoke are more likely to conceive a chromosomally unhealthy pregnancy (such as a pregnancy affected by Down syndrome) ...
Genetic Counseling - Michigan Sonographers Society
... – Primary concern: vascular compromise from kinking of the blood vessels coming through the defect which can lead to necrosis – Intestinal atresias and other GI disruptions are found in approximately 5-10% of cases – Extraintestinal abnormalities occur in less than 5% of cases – Usually not associat ...
... – Primary concern: vascular compromise from kinking of the blood vessels coming through the defect which can lead to necrosis – Intestinal atresias and other GI disruptions are found in approximately 5-10% of cases – Extraintestinal abnormalities occur in less than 5% of cases – Usually not associat ...
GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS
... permitted individualized timing of delivery and perinatal survival =85%. TODAY, refinement in management has reduced PM to near that of normal pregnancy, except for cong. abnormality. ...
... permitted individualized timing of delivery and perinatal survival =85%. TODAY, refinement in management has reduced PM to near that of normal pregnancy, except for cong. abnormality. ...
Topic: Reproduction Aim: Describe the stages of embryonic
... Following fertilization, the zygote moves through the oviduct propelled by involuntary smooth muscle contractions and by the cilia lining the oviduct. Around 30 hours after fertilization, the zygote undergoes its first mitosis and cell division. This process, called cleavage, continues, and by the t ...
... Following fertilization, the zygote moves through the oviduct propelled by involuntary smooth muscle contractions and by the cilia lining the oviduct. Around 30 hours after fertilization, the zygote undergoes its first mitosis and cell division. This process, called cleavage, continues, and by the t ...
A Case Study on:
... • Instrumentation of the uterine cavity (D and C for miscarriages or Induced Abortions) ...
... • Instrumentation of the uterine cavity (D and C for miscarriages or Induced Abortions) ...
Release Notes for the v2016B Manual
... Add: Demaerschalk BM, Kleindorfer DO, Adeoye OM, Demchuk AM, et. al., on behalf of the American Heart Association Stroke Council and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. “Scientific Rationale for the Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Statement ...
... Add: Demaerschalk BM, Kleindorfer DO, Adeoye OM, Demchuk AM, et. al., on behalf of the American Heart Association Stroke Council and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. “Scientific Rationale for the Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Statement ...
Physiology of the Newborn The neonatal or newborn period is the
... and needs to adjust insulin dose based on caloric intake. 2. hyperglycemia : Tends to occur in second half of pregnancy. 3. Urinary tract and other infections: - pregnancy predisposes to urinary tract colonization. - Obtain urine cultures at first visit and at 32 weeks or if symptoms develop. 4. Hyp ...
... and needs to adjust insulin dose based on caloric intake. 2. hyperglycemia : Tends to occur in second half of pregnancy. 3. Urinary tract and other infections: - pregnancy predisposes to urinary tract colonization. - Obtain urine cultures at first visit and at 32 weeks or if symptoms develop. 4. Hyp ...
2016-Jul-Coder-Minutes
... baby was born. If thy go to their Office of Vital Statistics for the signing and filing, the form will then be registered, copies will be sent to the Dept. of Health and the Putative (considered or reputed to be) Father registry, and to the parent. There is 60 days post signing rule to withdraw the ...
... baby was born. If thy go to their Office of Vital Statistics for the signing and filing, the form will then be registered, copies will be sent to the Dept. of Health and the Putative (considered or reputed to be) Father registry, and to the parent. There is 60 days post signing rule to withdraw the ...
JCIH Recommendations for Following Children At Risk for Hearing
... You must assign a 7th character to codes in certain ICD-10-CM categories as noted within the Tabular List of codes—primarily Chapter 19 (Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes) and Chapter 15 (Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium). This character must always be in th ...
... You must assign a 7th character to codes in certain ICD-10-CM categories as noted within the Tabular List of codes—primarily Chapter 19 (Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes) and Chapter 15 (Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium). This character must always be in th ...
Cardiac diseases in pregnancy Dr. Batool A. Hashim Physiological
... It is the commonest acquired cardiac lesion, accounting for 90%of rheumatic valvular problem. The stenosis produce left atrial obstruction with consequent elevated left atrial and pulmonary wedge pressures. Eventually, pulmonary oedema and atrial fibrillation may occur. There is a fixed cardiac outp ...
... It is the commonest acquired cardiac lesion, accounting for 90%of rheumatic valvular problem. The stenosis produce left atrial obstruction with consequent elevated left atrial and pulmonary wedge pressures. Eventually, pulmonary oedema and atrial fibrillation may occur. There is a fixed cardiac outp ...
Bariatric Considerations in labor and delivery
... The risk of delivering an infant weighing over 4,000g, or above the 90th percentile (macrosomia) is 1.7-2 times higher for women who are obese or morbidly obese More than a third of infants weighing over 4,500g have shoulder dystocia, whereas normal weight pregnant women have a 0.2-3% occurrence of ...
... The risk of delivering an infant weighing over 4,000g, or above the 90th percentile (macrosomia) is 1.7-2 times higher for women who are obese or morbidly obese More than a third of infants weighing over 4,500g have shoulder dystocia, whereas normal weight pregnant women have a 0.2-3% occurrence of ...
Prenatal development
Prenatal or antenatal development is the process in which a human embryo or fetus (or foetus) gestates during pregnancy, from fertilization until birth. Often, the terms fetal development, foetal development, or embryology are used in a similar sense.After fertilization, the process of embryogenesis, (the early stages of prenatal development) begins. By the end of the tenth week of gestational age the embryo has acquired its basic form and the next period is that of fetal development where the organs become fully developed. This fetal period is described both topically (by organ) and chronologically (by time) with major occurrences being listed by gestational age.