History Of Anatomy - King George`s Medical University
... psychology to the study of human body Noted anatomists of this century – ...
... psychology to the study of human body Noted anatomists of this century – ...
5-9_HypothalamicHormones_SzentgyorgyiR
... The function of the hypothalamic hormones The hypothalamus: The hypothalamus is a small but complex region of the brain located below the thalamus and right above the brain stem. It has links with both the nervous system as well as the endocrine system. Its main role is to maintain the internal bala ...
... The function of the hypothalamic hormones The hypothalamus: The hypothalamus is a small but complex region of the brain located below the thalamus and right above the brain stem. It has links with both the nervous system as well as the endocrine system. Its main role is to maintain the internal bala ...
Our Body Systems!
... Your brain is the boss of your body! It runs the show and controls just about everything you do! The brain is most important part of the nervous system. The parts of the nervous system include the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Your brain can’t do it alone! It ...
... Your brain is the boss of your body! It runs the show and controls just about everything you do! The brain is most important part of the nervous system. The parts of the nervous system include the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem, pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Your brain can’t do it alone! It ...
CHA Laboratory Problem Examples
... thoracodorsal nerve 4) axillary nerve 5) radial nerve. The upper subscapular nerve innervates the subscapularis. the lower subscapular nerve innervates teres major and also subscapularis. The thoracodorsal nerve innervates latisimus dorsi. The axillary nerve innervates deltoid and teres minor. The r ...
... thoracodorsal nerve 4) axillary nerve 5) radial nerve. The upper subscapular nerve innervates the subscapularis. the lower subscapular nerve innervates teres major and also subscapularis. The thoracodorsal nerve innervates latisimus dorsi. The axillary nerve innervates deltoid and teres minor. The r ...
bio 12 8.1 TISSUES
... − Pseudostratified epithelium: appears to be layered, but true layers do not exist because each cell touches the basement membrane ...
... − Pseudostratified epithelium: appears to be layered, but true layers do not exist because each cell touches the basement membrane ...
HBSGlossary - Kenwood Academy High School
... of the brain and spinal cord, to which sensory impulses are transmitted and from which motor impulses pass out, and which supervises and coordinates the activity of the entire nervous system. Cerebellum: A large dorsally projecting part of the brain concerned especially with the coordination of musc ...
... of the brain and spinal cord, to which sensory impulses are transmitted and from which motor impulses pass out, and which supervises and coordinates the activity of the entire nervous system. Cerebellum: A large dorsally projecting part of the brain concerned especially with the coordination of musc ...
Slide 1 - NGHS
... Nervous System and Sense Organs • Double ventral nerve cord runs length of the worm with ganglia in each metamere. • Sense organs include: – Eyes, nuchal organs and statocysts. – Eyes vary from simple eyespots to well-developed image-resolving eyes similar to mollusc eyes. – Nuchal organs are cilia ...
... Nervous System and Sense Organs • Double ventral nerve cord runs length of the worm with ganglia in each metamere. • Sense organs include: – Eyes, nuchal organs and statocysts. – Eyes vary from simple eyespots to well-developed image-resolving eyes similar to mollusc eyes. – Nuchal organs are cilia ...
Document
... Circle ALL that are TRUE. There may be more than one correct answer. Cephalopods are different from other kinds of mollusks because they have ______________________. A. direct development without a trochophore larva B. a closed circulatory system C. chromatophores for camouflage D. the most advanced ...
... Circle ALL that are TRUE. There may be more than one correct answer. Cephalopods are different from other kinds of mollusks because they have ______________________. A. direct development without a trochophore larva B. a closed circulatory system C. chromatophores for camouflage D. the most advanced ...
Cos-Chapter 6 Anatomy and Physiology
... The nervous system is a well-organized body system composed of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves that is responsible for controlling and coordinating all other systems of the body. • Central nervous system (CNS)- consists of brain, spinal cord, spinal nerves and cranial nerves; controls conscious a ...
... The nervous system is a well-organized body system composed of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves that is responsible for controlling and coordinating all other systems of the body. • Central nervous system (CNS)- consists of brain, spinal cord, spinal nerves and cranial nerves; controls conscious a ...
Lecture 21
... to spiracle & alary muscles to anterior body wall to wing to leg to posterior body wall ...
... to spiracle & alary muscles to anterior body wall to wing to leg to posterior body wall ...
EGardner-PN-gradcour.. - Center for Neural Science
... • Sensory transduction occurs in the nerve endings, not in the DRG or trigeminal cell bodies ...
... • Sensory transduction occurs in the nerve endings, not in the DRG or trigeminal cell bodies ...
Circulatory system-things to think about
... What is the difference between bones and cartilage? Discuss the differences between tendons and ligaments. Discuss bone growth, development, and repair How does the skeletal system work with the other body systems? My Question: _____________________________________________ ...
... What is the difference between bones and cartilage? Discuss the differences between tendons and ligaments. Discuss bone growth, development, and repair How does the skeletal system work with the other body systems? My Question: _____________________________________________ ...
exercise - We can offer most test bank and solution manual you need.
... Left Upper Quadrant: left adrenal gland, descending aorta, greater omentum, left kidney, large and small intestine, mesentery, pancreas, spleen, stomach, left ureter ...
... Left Upper Quadrant: left adrenal gland, descending aorta, greater omentum, left kidney, large and small intestine, mesentery, pancreas, spleen, stomach, left ureter ...
FREE Sample Here
... large and small intestine, mesentery, pancreas, spleen, stomach, left ureter Right Lower Quadrant: large and small intestine, mesentery, rectum, right ureter, urinary ...
... large and small intestine, mesentery, pancreas, spleen, stomach, left ureter Right Lower Quadrant: large and small intestine, mesentery, rectum, right ureter, urinary ...
FREE Sample Here - We can offer most test bank and
... Left Upper Quadrant: left adrenal gland, descending aorta, greater omentum, left kidney, large and small intestine, mesentery, pancreas, spleen, stomach, left ureter ...
... Left Upper Quadrant: left adrenal gland, descending aorta, greater omentum, left kidney, large and small intestine, mesentery, pancreas, spleen, stomach, left ureter ...
Airgas template
... Upper Motor Neurons Are in the Brain and Spinal Cord • Upper motor neuron cell bodies are in the motor cortex • They send their axons down through the internal capsule ...
... Upper Motor Neurons Are in the Brain and Spinal Cord • Upper motor neuron cell bodies are in the motor cortex • They send their axons down through the internal capsule ...
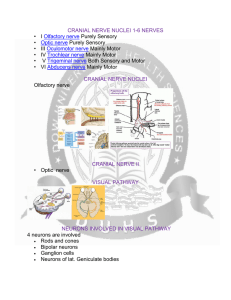
CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI
... The mandibular nerve (V3) carries sensory information from the lower lip, the lower teeth and gums, the chin and jaw (except the angle of the jaw, which is supplied by C2-C3), parts of the external ear, and parts of the meninges. The mandibular nerve carries touch/position and pain/temperature sensa ...
... The mandibular nerve (V3) carries sensory information from the lower lip, the lower teeth and gums, the chin and jaw (except the angle of the jaw, which is supplied by C2-C3), parts of the external ear, and parts of the meninges. The mandibular nerve carries touch/position and pain/temperature sensa ...
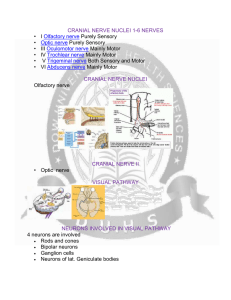
CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI
... II Optic nerve optic canal III Oculomotor nerve superior orbital fissure IV Trochlear nerve superior orbital fissure V Trigeminal nerve superior orbital fissure (ophthalmic nerve - V1), foramen rotundum (maxillary nerve - V2), foramen ovale (mandibular nerve - V3) VI Abducens nerve superior orbital ...
... II Optic nerve optic canal III Oculomotor nerve superior orbital fissure IV Trochlear nerve superior orbital fissure V Trigeminal nerve superior orbital fissure (ophthalmic nerve - V1), foramen rotundum (maxillary nerve - V2), foramen ovale (mandibular nerve - V3) VI Abducens nerve superior orbital ...
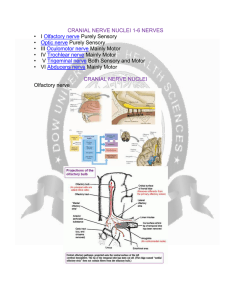
CRANIAL NERVE NUCLEI
... the meninges. The mandibular nerve carries touch/position and pain/temperature sensation from the mouth. It does not carry taste sensation (chorda tympani is responsible for taste), but one of its branches, the lingual nerve, carries multiple types of nerve fibers that do not originate in the mandib ...
... the meninges. The mandibular nerve carries touch/position and pain/temperature sensation from the mouth. It does not carry taste sensation (chorda tympani is responsible for taste), but one of its branches, the lingual nerve, carries multiple types of nerve fibers that do not originate in the mandib ...
2nd nine weeks exam Study guide
... C. The movement of the lungs helps the heart to pump blood. D. The lungs push oxygen into cells that make food for the heart. 41. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide ...
... C. The movement of the lungs helps the heart to pump blood. D. The lungs push oxygen into cells that make food for the heart. 41. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide ...
Lab 1 - Eportfolio@UTM
... 6. Epicardium is another name for ___________________________. 7. The region of the thoracic cavity between the two lungs is called the _______________________. 8. The muscular structure that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities is called the ______________________________. ...
... 6. Epicardium is another name for ___________________________. 7. The region of the thoracic cavity between the two lungs is called the _______________________. 8. The muscular structure that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities is called the ______________________________. ...
Crustaceans
... nerve cells in areas to help speed up responses. • The have eyes to detect light/dark and movement. • They have antennae to detect chemicals and movement in the water. ...
... nerve cells in areas to help speed up responses. • The have eyes to detect light/dark and movement. • They have antennae to detect chemicals and movement in the water. ...
unit 1ppt
... Group Brainstorm • As a group see if you can come up with all the LIFE FUNCTIONS of our body • Write on a piece of white paper • Share with class ...
... Group Brainstorm • As a group see if you can come up with all the LIFE FUNCTIONS of our body • Write on a piece of white paper • Share with class ...
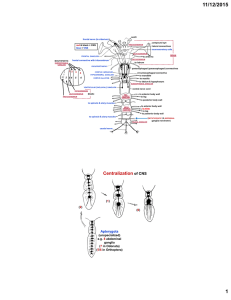
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.