Unit 5: Cell Cycles and Genetics Self
... 5) From chapter 8 page 157 titled "CYTOKINESIS", be able to; A) Explain what cytokinesis is and what it accomplishes. 6) From chapter 10 pages 196-199 titled "Structure of DNA" be able to; A) Explain the two basic functions of DNA. B) Explain the two main roles that proteins play in living organisms ...
... 5) From chapter 8 page 157 titled "CYTOKINESIS", be able to; A) Explain what cytokinesis is and what it accomplishes. 6) From chapter 10 pages 196-199 titled "Structure of DNA" be able to; A) Explain the two basic functions of DNA. B) Explain the two main roles that proteins play in living organisms ...
Unit 1 - Personality - St. Agnes Gr 7 Class Wiki
... live in a community with others. First Nations were the first to live in communities on ...
... live in a community with others. First Nations were the first to live in communities on ...
9. Axis Specification in Drosophila
... early in development cell fate depends on interactions among protein gradients specification is flexible; it can alter in response to signals from other cells eventually cells undergo transition from loose commitment to irreversible determination The transition from specification to dete ...
... early in development cell fate depends on interactions among protein gradients specification is flexible; it can alter in response to signals from other cells eventually cells undergo transition from loose commitment to irreversible determination The transition from specification to dete ...
Chapter 11 Power Point
... muscle • Children with muscular dystrophy rarely live past early adulthood • The most common form of MD is caused by a defective version of the gene that codes for a muscle protein known as dystrophin • This gene is located on the X chromosome • Researchers are now using molecular techniques to inse ...
... muscle • Children with muscular dystrophy rarely live past early adulthood • The most common form of MD is caused by a defective version of the gene that codes for a muscle protein known as dystrophin • This gene is located on the X chromosome • Researchers are now using molecular techniques to inse ...
PowerPoint - 埼玉医科大学総合医療センター 内分泌・糖尿病内科
... ChIP-Seq ChIP DNA was prepared using a kit (number 9003; Enzymatic SimpleChIP Magnetic Kit; Cell Signaling) and anti-TCF7L2 antibody (number 2569; Cell Signaling). This antibody was designed against a peptide sequence surrounding Leu330 of the TCF7L2 protein. This residue is at the 3′ end of exon 9 ...
... ChIP-Seq ChIP DNA was prepared using a kit (number 9003; Enzymatic SimpleChIP Magnetic Kit; Cell Signaling) and anti-TCF7L2 antibody (number 2569; Cell Signaling). This antibody was designed against a peptide sequence surrounding Leu330 of the TCF7L2 protein. This residue is at the 3′ end of exon 9 ...
Decode the Mystery of Genes - Genetic Modification Advisory
... For people to consume For animal livestock to consume GM crops can be processed and used as ingredients in other foods. Can these foods be found in Singapore? Singapore buys foods from many countries. Since some of these countries plant GM crops, some foods we buy may contain ingredients from GM p ...
... For people to consume For animal livestock to consume GM crops can be processed and used as ingredients in other foods. Can these foods be found in Singapore? Singapore buys foods from many countries. Since some of these countries plant GM crops, some foods we buy may contain ingredients from GM p ...
ear lobe attachments, tongue rolling, hitchhiker`s thumb, and mid
... 1. Ear lobe attachment: (See Fig. 1) The ear lobes may either hang free or be attached directly to the side of the head. The gene for the free or unattached ear lobe trait is dominant (F), while attached earlobes are caused by having two recessive genes (ff). 2. Tongue rolling: (See Fig. 2) Some peo ...
... 1. Ear lobe attachment: (See Fig. 1) The ear lobes may either hang free or be attached directly to the side of the head. The gene for the free or unattached ear lobe trait is dominant (F), while attached earlobes are caused by having two recessive genes (ff). 2. Tongue rolling: (See Fig. 2) Some peo ...
When Parents Are Relatives—Consanguinity Fact Sheet... Important points
... strengthening family ties and retaining property within the family We all carry several harmful faulty gene copies on our chromosomes but have a working copy on the other partner chromosome to provide the information for our bodies Usually two unrelated people will not carry the same faulty gene cop ...
... strengthening family ties and retaining property within the family We all carry several harmful faulty gene copies on our chromosomes but have a working copy on the other partner chromosome to provide the information for our bodies Usually two unrelated people will not carry the same faulty gene cop ...
Genetically Modified Zoysia Grass (Zoysia japonica Steud
... Control of shoot branching involves auxin, cytokinin and strigolactones (SLs). In pea, most of the high branching ramosus (rms) mutants show high expression of the SL biosynthesis RMS1/CCD8 gene and low xylem-sap cytokinin content. In contrast, the high branching rms2 mutant displays very low expres ...
... Control of shoot branching involves auxin, cytokinin and strigolactones (SLs). In pea, most of the high branching ramosus (rms) mutants show high expression of the SL biosynthesis RMS1/CCD8 gene and low xylem-sap cytokinin content. In contrast, the high branching rms2 mutant displays very low expres ...
Historical review: Deciphering the genetic code – a personal account
... contained in ribosomes because amino acids were known to be incorporated into protein on these organelles. I estimated it would take me two years to set up a cell-free system to determine whether RNA or DNA stimulated protein synthesis, which was a pretty accurate estimate. I knew this was a risky p ...
... contained in ribosomes because amino acids were known to be incorporated into protein on these organelles. I estimated it would take me two years to set up a cell-free system to determine whether RNA or DNA stimulated protein synthesis, which was a pretty accurate estimate. I knew this was a risky p ...
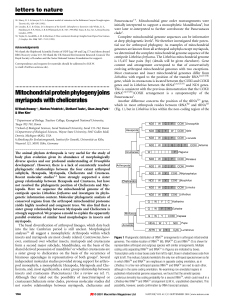
Mitochondrialproteinphylogenyjoins myriapods with chelicerates
... tree included a monophyletic Pancrustacea, branch-support analysis yielded little resolution with regard to the position of the Branchiopoda. The most striking result was a strong support for a sister group relationship between the myriapods and chelicerates with branch-support values equalling thos ...
... tree included a monophyletic Pancrustacea, branch-support analysis yielded little resolution with regard to the position of the Branchiopoda. The most striking result was a strong support for a sister group relationship between the myriapods and chelicerates with branch-support values equalling thos ...
What is a Karyotype?
... Klinefelter’s Syndrome: (XXY Male) When a male has an extra X chromosome in most of their cells. Most common symptom is infertility. Most do not know they have it until puberty. Have less testosterone, so lack some male features. **caused by nondisjunction ...
... Klinefelter’s Syndrome: (XXY Male) When a male has an extra X chromosome in most of their cells. Most common symptom is infertility. Most do not know they have it until puberty. Have less testosterone, so lack some male features. **caused by nondisjunction ...
OncJuly3 6..6
... the genomic region surrounding exon 17 might be a site more prone than others to Alu-mediated rearrangements. The involvement of these types of mutations might have been underestimated to date, because most of the current mutation detection strategies are based on DNA ampli®cation of single exons. O ...
... the genomic region surrounding exon 17 might be a site more prone than others to Alu-mediated rearrangements. The involvement of these types of mutations might have been underestimated to date, because most of the current mutation detection strategies are based on DNA ampli®cation of single exons. O ...
b - AET
... receive a blue eye allele from each parent to have blue eyes. In cattle, the allele that causes horns to grow is recessive. The hornless, or polled, allele is dominant. There are additional genes that affect horn-like growth, called scurs, on an animal's head. Scurs are incompletely developed horns ...
... receive a blue eye allele from each parent to have blue eyes. In cattle, the allele that causes horns to grow is recessive. The hornless, or polled, allele is dominant. There are additional genes that affect horn-like growth, called scurs, on an animal's head. Scurs are incompletely developed horns ...
AP Biology: Chapter 13 - 15
... and round (R) is the dominant allele in seed shape over wrinkled (r). Parents heterozygous for both traits are cross-pollinated. Determine the phenotypic ratios that result in the F2 from this dihybrid cross. ...
... and round (R) is the dominant allele in seed shape over wrinkled (r). Parents heterozygous for both traits are cross-pollinated. Determine the phenotypic ratios that result in the F2 from this dihybrid cross. ...
Characterization of a Negative Thyroid Hormone Response Element
... and dGTP and 50 mCi [32P]dCTP (3000 Ci/mmol) at room temperature for 20 min. Unincorporated [32P]dCTP was removed by chromatography on Sephadex G-25 spin columns. To detect T3R and RXR binding to a3 gene fragments in a 15-ml reaction, each labeled DNA (2.0 –5.0 3 105 cpm, 1.0 ng) was incubated with ...
... and dGTP and 50 mCi [32P]dCTP (3000 Ci/mmol) at room temperature for 20 min. Unincorporated [32P]dCTP was removed by chromatography on Sephadex G-25 spin columns. To detect T3R and RXR binding to a3 gene fragments in a 15-ml reaction, each labeled DNA (2.0 –5.0 3 105 cpm, 1.0 ng) was incubated with ...
CHAPTER 4: CELLULAR METABOLISM OBJECTIVES: 1. Compare
... During electron transport, these molecules alternate between reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons. The final electron acceptor is oxygen. Yield of energy (ATP) from the ETC is: ...
... During electron transport, these molecules alternate between reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons. The final electron acceptor is oxygen. Yield of energy (ATP) from the ETC is: ...
NUCLEIC ACIDS 3115
... RNA has several functions: To copy the DNA of a cell and transfer the DNA’s information to the ribosomes so they can make new protein for use by the cell. Question 1. What are the two types of nucleic acids? Question 2. What is the function of DNA? Question 3. What are the 2 functions of RNA? DNA Ex ...
... RNA has several functions: To copy the DNA of a cell and transfer the DNA’s information to the ribosomes so they can make new protein for use by the cell. Question 1. What are the two types of nucleic acids? Question 2. What is the function of DNA? Question 3. What are the 2 functions of RNA? DNA Ex ...
Mutation - Teacherpage
... • If it happens in a gamete then the mutation is passed on to the offspring. ...
... • If it happens in a gamete then the mutation is passed on to the offspring. ...
1. Which of the following is not a phenotypic description of allele
... Predict the phenotypic ratio of the F2 progeny of a cross between two colorless plants, one homozygous for A and the other homozygous for B. A. 3 colored : 1 colorless B. 9 colored : 7 colorless C. 9 colorless : 7 colored D. 15 colorless : 1 colored E. 15 colored : 1 colorless ...
... Predict the phenotypic ratio of the F2 progeny of a cross between two colorless plants, one homozygous for A and the other homozygous for B. A. 3 colored : 1 colorless B. 9 colored : 7 colorless C. 9 colorless : 7 colored D. 15 colorless : 1 colored E. 15 colored : 1 colorless ...
Chapter 14
... - Stamens (male reproductive organs) could be removed to control mating. (There would be no self-fertilization.) Thus, he could mate male and female gametes as he chose and could control his experiments. ...
... - Stamens (male reproductive organs) could be removed to control mating. (There would be no self-fertilization.) Thus, he could mate male and female gametes as he chose and could control his experiments. ...
Annotating your D - GEP Community Server
... melanogaster ortholog represents an assumption of evolutionary change that underlies your gene model. The best gene models will always minimize these assumptions; as such, you should be able to account for every difference and convince yourself that there is no other acceptable gene model with fewer ...
... melanogaster ortholog represents an assumption of evolutionary change that underlies your gene model. The best gene models will always minimize these assumptions; as such, you should be able to account for every difference and convince yourself that there is no other acceptable gene model with fewer ...