Amino Acids and Proteins
... protein. The structural formulas of di- and tripeptides are written. The secondary forms of protein structure include the alpha helix, pleated sheet and collagen. The interaction of side groups to form the cross-links of tertiary structure is discussed. The breakdown in the secondary and tertiary st ...
... protein. The structural formulas of di- and tripeptides are written. The secondary forms of protein structure include the alpha helix, pleated sheet and collagen. The interaction of side groups to form the cross-links of tertiary structure is discussed. The breakdown in the secondary and tertiary st ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 9
... Substrate-level phosphorylation Phosphoglycerate kinase creates ATP NADH is produced Pyruvate formation and ATP generation Phosphoenolpyruvate hydrolysis by pyruvate kinase B. Pyruvate oxidation to Acetyl CoA In presence of oxygen Preparation for entry to Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle; tricarboxyli ...
... Substrate-level phosphorylation Phosphoglycerate kinase creates ATP NADH is produced Pyruvate formation and ATP generation Phosphoenolpyruvate hydrolysis by pyruvate kinase B. Pyruvate oxidation to Acetyl CoA In presence of oxygen Preparation for entry to Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle; tricarboxyli ...
Exam 3 Review Sheet Chemistry 1120 Spring 2003 Dr. Doug Harris
... Review the vitamins necessary to create the coenzymes NAD, FAD, and Co-A. Review the oxidized and reduced forms of NAD and FAD. Review the general reaction characteristics that involve NAD and FAD (ie. C-C forms C=C with the help of FAD). Review what is added/removed to/from each of the coenzymes du ...
... Review the vitamins necessary to create the coenzymes NAD, FAD, and Co-A. Review the oxidized and reduced forms of NAD and FAD. Review the general reaction characteristics that involve NAD and FAD (ie. C-C forms C=C with the help of FAD). Review what is added/removed to/from each of the coenzymes du ...
The experiments provide ne~~~den~~~~t the r&rate clewage pathway... of carbon for the synthesis of $tty ack& k‘l...
... Waft, 1965; Leveille atid- Hanson, 19@5a,196&J. On- the basis of these observations, and of the presumed jm~~rmeabil~tyof m~tochon~r~ato palyanions such as citr$tte, it was proposed that e~~rarnito~h~ndria~ citrate is derived from i~trarn~~~~o~l~ia1citrate via the intermediate formation of rr-ketogl ...
... Waft, 1965; Leveille atid- Hanson, 19@5a,196&J. On- the basis of these observations, and of the presumed jm~~rmeabil~tyof m~tochon~r~ato palyanions such as citr$tte, it was proposed that e~~rarnito~h~ndria~ citrate is derived from i~trarn~~~~o~l~ia1citrate via the intermediate formation of rr-ketogl ...
Integration and regulation of fuel metabolism in maintaining
... what was an asset during evolution has become a liability in the current ‘pathoenvironment’ or ‘obesogenic’ environment [1] This hypothesis of the ‘thrifty genotype’ has, however, recently been challenged by Speakman [2] who offers an alternative explanation called the ‘predation release’ hypothesis ...
... what was an asset during evolution has become a liability in the current ‘pathoenvironment’ or ‘obesogenic’ environment [1] This hypothesis of the ‘thrifty genotype’ has, however, recently been challenged by Speakman [2] who offers an alternative explanation called the ‘predation release’ hypothesis ...
CHAPTER 2 The Chemistry of Living Things
... How is ATP produced by electron transport/oxidative phosphorylation? ─ Does glucose go straight into this process? ─ What is the role of reduced coenzyme? ─ What is the role/inter-relationship of/between ...
... How is ATP produced by electron transport/oxidative phosphorylation? ─ Does glucose go straight into this process? ─ What is the role of reduced coenzyme? ─ What is the role/inter-relationship of/between ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... a. A C10 fatty acid requires the formation of 4 malonyl ACP, which uses 4 HCO3 . b. 4 ATP are required to produce 4 malonyl CoA. c. 5 acetyl CoA are needed to make 1 acetyl ACP and 4 malonyl ACP. d. A C10 fatty acid requires 4 malonyl ACP and 1 acetyl ACP. e. A C10 fatty acid chain requires 4 cycles ...
... a. A C10 fatty acid requires the formation of 4 malonyl ACP, which uses 4 HCO3 . b. 4 ATP are required to produce 4 malonyl CoA. c. 5 acetyl CoA are needed to make 1 acetyl ACP and 4 malonyl ACP. d. A C10 fatty acid requires 4 malonyl ACP and 1 acetyl ACP. e. A C10 fatty acid chain requires 4 cycles ...
Chapter 4: Amino Acids General Features of Amino Acids
... Peptide bond formation is a condensation reaction leading to the polymerization of amino acids into peptides and proteins. (Peptide: hormones, neurotransmitters, several antibiotics and antitumor agents) The presence of the carbonyl group in a peptide bond allows electron resonance stabilization to ...
... Peptide bond formation is a condensation reaction leading to the polymerization of amino acids into peptides and proteins. (Peptide: hormones, neurotransmitters, several antibiotics and antitumor agents) The presence of the carbonyl group in a peptide bond allows electron resonance stabilization to ...
Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids
... followed by the breakdown of the resulting carbon skeletons. These pathways converge to form seven intermediate products : oxaloacetate, α-ketoglutarate, pyruvate, fumarate ,succinyl CoA, acetyl CoA, and acetoacetyl CoA. These products directly enter the pathways of intermediary metabolism, result ...
... followed by the breakdown of the resulting carbon skeletons. These pathways converge to form seven intermediate products : oxaloacetate, α-ketoglutarate, pyruvate, fumarate ,succinyl CoA, acetyl CoA, and acetoacetyl CoA. These products directly enter the pathways of intermediary metabolism, result ...
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
... For instance, GLUT-1 is abundant in erythrocytes whereas GLUT-4 is abundant in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Insulin increases the number and promotes the activity of GLUT-4 in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. ...
... For instance, GLUT-1 is abundant in erythrocytes whereas GLUT-4 is abundant in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Insulin increases the number and promotes the activity of GLUT-4 in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. ...
AMP-activated protein kinase regulation of fatty acid oxidation in the
... oxidation in isolated working rat hearts [21,22,39,56]. It has been well established that AMPK is able to phosphorylate both isoforms of ACC [47–49] and we have shown that cardiac ACC co-purifies with the α2 isoform of the catalytic subunit of AMPK [58]. These studies suggest a tight association of ...
... oxidation in isolated working rat hearts [21,22,39,56]. It has been well established that AMPK is able to phosphorylate both isoforms of ACC [47–49] and we have shown that cardiac ACC co-purifies with the α2 isoform of the catalytic subunit of AMPK [58]. These studies suggest a tight association of ...
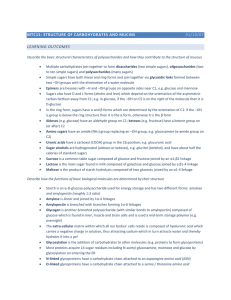
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
... • Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. • Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. Polymer (starch) Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. ...
Slides
... • The amino acid sequence determines the structure which determines the function. • Proteins make up over 50% of the cell by dry weight. • Proteins give the cell its shape, they form receptors, enzymes, hormones and growth factors, toxins, transporters and antibodies. ...
... • The amino acid sequence determines the structure which determines the function. • Proteins make up over 50% of the cell by dry weight. • Proteins give the cell its shape, they form receptors, enzymes, hormones and growth factors, toxins, transporters and antibodies. ...
7 - Anaerobic Respiration
... • The Lactic Acid system is essentially the process of glycolysis. • Occurs in the cell cytoplasm, • Glucose is split into 2 x pyruvate molecules • 2x ATP molecules are produced • In aerobic respiration the pyruvate is then converted into Acetyl Co A by pyruvate dehydrogenase, and this enters Krebs ...
... • The Lactic Acid system is essentially the process of glycolysis. • Occurs in the cell cytoplasm, • Glucose is split into 2 x pyruvate molecules • 2x ATP molecules are produced • In aerobic respiration the pyruvate is then converted into Acetyl Co A by pyruvate dehydrogenase, and this enters Krebs ...
notes - Main
... 1. Since glucose is the body’s preferred source for synthesizing ATP, the fate of absorbed glucose depends on the energy needs of body cells. 2. If the cells require immediate energy, glucose is oxidized by the cells to produce ATP. 3. Glucose can be used to form amino acids, which then can be incor ...
... 1. Since glucose is the body’s preferred source for synthesizing ATP, the fate of absorbed glucose depends on the energy needs of body cells. 2. If the cells require immediate energy, glucose is oxidized by the cells to produce ATP. 3. Glucose can be used to form amino acids, which then can be incor ...
ch25 Metabolism
... 1. Since glucose is the body’s preferred source for synthesizing ATP, the fate of absorbed glucose depends on the energy needs of body cells. 2. If the cells require immediate energy, glucose is oxidized by the cells to produce ATP. 3. Glucose can be used to form amino acids, which then can be incor ...
... 1. Since glucose is the body’s preferred source for synthesizing ATP, the fate of absorbed glucose depends on the energy needs of body cells. 2. If the cells require immediate energy, glucose is oxidized by the cells to produce ATP. 3. Glucose can be used to form amino acids, which then can be incor ...
description - In
... FUNCTION: Natural PEG-free and hydrolyzed protein free Soft and Emollient Emulsifier of vegetal origin DESCRIPTION: A new non-ethoxylated, vegetal derived emulsifier that combines the unique lipidic chains of olive oil with the glutamic acid called Olivoyl Glutamate, a lipo-aminoacid with a fatty am ...
... FUNCTION: Natural PEG-free and hydrolyzed protein free Soft and Emollient Emulsifier of vegetal origin DESCRIPTION: A new non-ethoxylated, vegetal derived emulsifier that combines the unique lipidic chains of olive oil with the glutamic acid called Olivoyl Glutamate, a lipo-aminoacid with a fatty am ...
Human Fatty Acid Transport Protein 2a/Very Long Chain Acyl
... distinct patterns are generated and maintained is poorly understood, but it is reasonable to expect that the source of the fatty acid, either from endogenous or exogenous sources, will lead to different metabolic fates. These processes are likely governed by proteins and enzymes, which function in f ...
... distinct patterns are generated and maintained is poorly understood, but it is reasonable to expect that the source of the fatty acid, either from endogenous or exogenous sources, will lead to different metabolic fates. These processes are likely governed by proteins and enzymes, which function in f ...
B) Contain an alcohol - LSU School of Medicine
... 5) phospholipase C cleavage of protein and inositol phosphate leaves diacylglycerol (which activates protein kinase C) I) Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) – mitochondrial membranes; precursor of cardiolipin; made from CDP-diacylglycerol and glycerol-P (Fig. 17.5) J) Cardiolipin (diphosphatidylglycerol) – d ...
... 5) phospholipase C cleavage of protein and inositol phosphate leaves diacylglycerol (which activates protein kinase C) I) Phosphatidylglycerol (PG) – mitochondrial membranes; precursor of cardiolipin; made from CDP-diacylglycerol and glycerol-P (Fig. 17.5) J) Cardiolipin (diphosphatidylglycerol) – d ...
Identification of Two Mammalian Reductases
... the manufacturer’s instructions. On day 4, the cells were harvested for membrane protein and total RNA as described (1). Blot Hybridization of RNA—The multiple tissue Northern blot (Clontech, catalogue number 7780-1) was used to determine KAR and TER expression in human tissues. The blot was hybridi ...
... the manufacturer’s instructions. On day 4, the cells were harvested for membrane protein and total RNA as described (1). Blot Hybridization of RNA—The multiple tissue Northern blot (Clontech, catalogue number 7780-1) was used to determine KAR and TER expression in human tissues. The blot was hybridi ...
pbl – night starvation - UQMBBS-2013
... including alcohol, glycogen, lactic acid, dextrins. Cellulose is starch we eat but is not digested. Salivary amylase begins hydrolysis of CHO in the mouth. In stomach, the low pH stops digestion. Digestion continues in the small intestine from pancreatic amylase. The amylase breaks down starch to ma ...
... including alcohol, glycogen, lactic acid, dextrins. Cellulose is starch we eat but is not digested. Salivary amylase begins hydrolysis of CHO in the mouth. In stomach, the low pH stops digestion. Digestion continues in the small intestine from pancreatic amylase. The amylase breaks down starch to ma ...
Microbiology Of Fermented Foods and Beverages by momina
... Capable of breaking down sugars to produce lactic acid and other products. Make them very important in fermentations. ...
... Capable of breaking down sugars to produce lactic acid and other products. Make them very important in fermentations. ...
No Slide Title - Suffolk County Community College
... - speed up reactions by lowering activation energy, orient molecules to favor reaction ...
... - speed up reactions by lowering activation energy, orient molecules to favor reaction ...
MTC15 - toddgreen
... Starch is an α-D-glucose polysaccharide used for energy storage and has two different forms: amylose and amylopectin (roughly 1:3 ratio) Amylose is linear and joined by 1α-4 linkages Amylopectin is branched with branches forming 1α-6 linkages Glycogen is another branched polysaccharide (with similar ...
... Starch is an α-D-glucose polysaccharide used for energy storage and has two different forms: amylose and amylopectin (roughly 1:3 ratio) Amylose is linear and joined by 1α-4 linkages Amylopectin is branched with branches forming 1α-6 linkages Glycogen is another branched polysaccharide (with similar ...
Micro Lab Unit 1 Flashcards
... 55) What is formed when oxygen accepts the H+ atoms? 56) Can enzymes be inhibited in many ways? 57) What are three ways that substances can act as an enzyme inhibitor? 58) An enzyme molecule is very large compared to its ______ and may contain several active sites. 59) What is a “false” substrate? 6 ...
... 55) What is formed when oxygen accepts the H+ atoms? 56) Can enzymes be inhibited in many ways? 57) What are three ways that substances can act as an enzyme inhibitor? 58) An enzyme molecule is very large compared to its ______ and may contain several active sites. 59) What is a “false” substrate? 6 ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.