Supplemental Methods
... Intermolecular interactions between protein receptor and ligands were analyzed using Protein Interaction Calculators (PIC) [14]. PIC is a server which, given the coordinate set of 3D structure of a protein or an assembly, computes various interactions such as disulphide bonds, interactions between h ...
... Intermolecular interactions between protein receptor and ligands were analyzed using Protein Interaction Calculators (PIC) [14]. PIC is a server which, given the coordinate set of 3D structure of a protein or an assembly, computes various interactions such as disulphide bonds, interactions between h ...
Chapter 18
... multiple domains on a single polypeptide chain, or a membrane associated complex. • See Figure 18.5 ...
... multiple domains on a single polypeptide chain, or a membrane associated complex. • See Figure 18.5 ...
Lecture 1 – Cell Biology
... G protein coupled receptor Ligand binds to receptor that activates G protein that slides and activates an enzyme that will either produce IP3 or cyclic AMP that activate second messengers Steroid receptors Lipophilic ligand (e.g. steroid hormones) that cross membrane Receptor initially in ...
... G protein coupled receptor Ligand binds to receptor that activates G protein that slides and activates an enzyme that will either produce IP3 or cyclic AMP that activate second messengers Steroid receptors Lipophilic ligand (e.g. steroid hormones) that cross membrane Receptor initially in ...
Recombinant Protein L
... Protein L has the unique ability to bind through kappa light chain interactions without interfering with the antibody’s antigen-binding site. This gives Protein L the ability to bind a wider range of Ig classes and subclasses than other antibody-binding proteins. Protein L can be used to detect, qua ...
... Protein L has the unique ability to bind through kappa light chain interactions without interfering with the antibody’s antigen-binding site. This gives Protein L the ability to bind a wider range of Ig classes and subclasses than other antibody-binding proteins. Protein L can be used to detect, qua ...
The Wnt signaling pathway mechanisms
... tyrosine kinase (Ryk) (figure 1C). In this case Dvl transduces the signal through either Rho or Rac. The Dvl-dependent Rho pathway requires the Dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis-1 (Daam1) to activate Rho-associated kinase 2 (ROCK2) (Marlow et al., 2002). The Dvl-dependent Rac pathway ...
... tyrosine kinase (Ryk) (figure 1C). In this case Dvl transduces the signal through either Rho or Rac. The Dvl-dependent Rho pathway requires the Dishevelled associated activator of morphogenesis-1 (Daam1) to activate Rho-associated kinase 2 (ROCK2) (Marlow et al., 2002). The Dvl-dependent Rac pathway ...
Berry Malynn Berry Dr. Bert Ely Genetics 303 6 November 2009
... cells, the overall cardiovascular health of the mutants, and effects of the knockouts on neointimal formation in the mutants after vascular injury by carotid artery ligation. By comparing vascular smooth muscle cells from mutant and from wild type mice in culture, the researchers determined that the ...
... cells, the overall cardiovascular health of the mutants, and effects of the knockouts on neointimal formation in the mutants after vascular injury by carotid artery ligation. By comparing vascular smooth muscle cells from mutant and from wild type mice in culture, the researchers determined that the ...
Canonical Wnt signaling is required for development of
... integration of their graded actions may be important in regulating spatially appropriate cellular responses (Robb and Tam, 2004). In fact, regionalized cell fates in the epiblast are highly correlated with their position along the combined gradient of Nodal/Wnt/Bmp activity (Lawson et al., 1991; Law ...
... integration of their graded actions may be important in regulating spatially appropriate cellular responses (Robb and Tam, 2004). In fact, regionalized cell fates in the epiblast are highly correlated with their position along the combined gradient of Nodal/Wnt/Bmp activity (Lawson et al., 1991; Law ...
Growth Control: A Saga of Cell Walls, ROS, and
... While extracellular signals are often linked to cell reprogramming involving transcription factor targets, it is at present unclear whether there is a direct, dedicated pathway from FER or other CrRLK1Ls to transcription factors. The transcriptome of plants treated with RALF1 has been analyzed (Haru ...
... While extracellular signals are often linked to cell reprogramming involving transcription factor targets, it is at present unclear whether there is a direct, dedicated pathway from FER or other CrRLK1Ls to transcription factors. The transcriptome of plants treated with RALF1 has been analyzed (Haru ...
CNS NEUROTRANSMITTERS
... AMPA receptor (aminomethyl propionic acid) Kainate receptor - Metabotropic receptors (G-protein coupled ) ...
... AMPA receptor (aminomethyl propionic acid) Kainate receptor - Metabotropic receptors (G-protein coupled ) ...
Plant Wnt: deciphering a novel signalling pathway
... canonical version but without the aid of LRP5/6 co-receptor6,33. However, unlike canonical Wnt signalling cascade, the non-canonical pathway does not bank on catenin to carry out downstream signalling, hence is known as -catenin independent Wnt signalling. PCP signalling is involved mainly in the ...
... canonical version but without the aid of LRP5/6 co-receptor6,33. However, unlike canonical Wnt signalling cascade, the non-canonical pathway does not bank on catenin to carry out downstream signalling, hence is known as -catenin independent Wnt signalling. PCP signalling is involved mainly in the ...
碩命題橫式 - 國立彰化師範大學圖書館
... 9. All of the following enzymes are required in the catabolism of purine nucleotides EXCEPT: (a). xanthine oxidase (b). purine nucleoside phosphorylase (c). 5'-nucleotidase (d). adenosine deaminase (e). ribonucleotide reductase 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Ur ...
... 9. All of the following enzymes are required in the catabolism of purine nucleotides EXCEPT: (a). xanthine oxidase (b). purine nucleoside phosphorylase (c). 5'-nucleotidase (d). adenosine deaminase (e). ribonucleotide reductase 10. The direct sources of nitrogen that are used to make urea via the Ur ...
Kranz Anatomy and the C4 Pathway
... genes that encode enzymes with no photosynthetic function in C3 plants, but which have acquired photosynthetic function in C4 plants (i.e. PEPCase, PPdK, NAD- or NADP-malic enzymes), have had their expression modified in two ways. First, expression has been greatly enhanced, so these enzymes can be p ...
... genes that encode enzymes with no photosynthetic function in C3 plants, but which have acquired photosynthetic function in C4 plants (i.e. PEPCase, PPdK, NAD- or NADP-malic enzymes), have had their expression modified in two ways. First, expression has been greatly enhanced, so these enzymes can be p ...
Gene Section FIGF (c fos induced growth factor (vascular endothelial growth factor D))
... intestine, and is most abundantly expressed in fetal lungs and skin. VEGF-D expression in mouse fibroblasts is induced by cell interaction mediated by cadherin 11 (Orlandini et al., 2006; Avantaggiato et al., 1998). ...
... intestine, and is most abundantly expressed in fetal lungs and skin. VEGF-D expression in mouse fibroblasts is induced by cell interaction mediated by cadherin 11 (Orlandini et al., 2006; Avantaggiato et al., 1998). ...
Protein Modifications and Proteomics
... Figure 1: Complexity to proteome for diverse function with limited number of genes ...
... Figure 1: Complexity to proteome for diverse function with limited number of genes ...
Growth Control: A Saga of Cell Walls, ROS, and Peptide
... While extracellular signals are often linked to cell reprogramming involving transcription factor targets, it is at present unclear whether there is a direct, dedicated pathway from FER or other CrRLK1Ls to transcription factors. The transcriptome of plants treated with RALF1 has been analyzed (Haru ...
... While extracellular signals are often linked to cell reprogramming involving transcription factor targets, it is at present unclear whether there is a direct, dedicated pathway from FER or other CrRLK1Ls to transcription factors. The transcriptome of plants treated with RALF1 has been analyzed (Haru ...
投影片 1
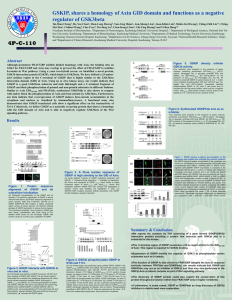
... Although prominent FRAT/GBP exhibits limited homology with Axin, the binding sites on GSK3 for FRAT/GBP and Axin may overlap to prevent the effect of FRAT/GBP to stabilize b-catenin in Wnt pathway. Using a yeast two-hybrid screen, we identified a novel protein, GSK3b interaction protein (GSKIP), whi ...
... Although prominent FRAT/GBP exhibits limited homology with Axin, the binding sites on GSK3 for FRAT/GBP and Axin may overlap to prevent the effect of FRAT/GBP to stabilize b-catenin in Wnt pathway. Using a yeast two-hybrid screen, we identified a novel protein, GSK3b interaction protein (GSKIP), whi ...
Slide 1
... less hormone can bind to the cell and higher concentrations of the hormone remain in the blood plasma Up-regulation—Increase in number of cell receptors; more hormone can bind to the cell and lower concentrations of the hormone remain in the blood plasma ...
... less hormone can bind to the cell and higher concentrations of the hormone remain in the blood plasma Up-regulation—Increase in number of cell receptors; more hormone can bind to the cell and lower concentrations of the hormone remain in the blood plasma ...
Datasheet - Sigma
... recognized as a unique compound. Activins and inhibins are members of the TGF-β superfamily due to amino acid homology with respect to the conservation of 7 of the 9 cysteine residues common to all TGF-β ...
... recognized as a unique compound. Activins and inhibins are members of the TGF-β superfamily due to amino acid homology with respect to the conservation of 7 of the 9 cysteine residues common to all TGF-β ...
Prediction - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... -!- SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=Cell surface protein that rapidly becomes internalized via clathrin-coated pits. During maturation, the immature APP (N-glycosylated in the endoplasmic reticulum) moves to the Golgi complex where complete maturation occurs ...
... -!- SUBCELLULAR LOCATION: Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Note=Cell surface protein that rapidly becomes internalized via clathrin-coated pits. During maturation, the immature APP (N-glycosylated in the endoplasmic reticulum) moves to the Golgi complex where complete maturation occurs ...
NEW EMBO MEMBER`S REVIEW Nuclear and cytosolic events of
... photoreceptors and their undoubted role in controlling the transcription of specific plant genes invited a search for a molecular mechanism that mediates communication between cytosol and nucleus. In animal systems, the communication between cytosolic or membrane-localized receptors and the nucleus ...
... photoreceptors and their undoubted role in controlling the transcription of specific plant genes invited a search for a molecular mechanism that mediates communication between cytosol and nucleus. In animal systems, the communication between cytosolic or membrane-localized receptors and the nucleus ...
BCM 6200 - Purification des proteines membranaires
... Crystallization Methods (Lipidic-cubic phase - LCP): Lipidic cubic phase (LCP) is one of many liquid crystalline phases that form spontaneously upon mixing lipids with water at proper conditions. The protein is mixed with Monoolein and other lipid additives in tightly coupled syringes. Drops are la ...
... Crystallization Methods (Lipidic-cubic phase - LCP): Lipidic cubic phase (LCP) is one of many liquid crystalline phases that form spontaneously upon mixing lipids with water at proper conditions. The protein is mixed with Monoolein and other lipid additives in tightly coupled syringes. Drops are la ...
glutamate - Dental Decks
... - Glutamate, GABA, and glycine. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter. GABA and glycine are inhibitory neurotransmitters. GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter within the CNS. • Amines: - Include the catecholamines ¾ dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine ¾ as well as serotonin, his ...
... - Glutamate, GABA, and glycine. Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter. GABA and glycine are inhibitory neurotransmitters. GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter within the CNS. • Amines: - Include the catecholamines ¾ dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine ¾ as well as serotonin, his ...
PDF
... embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells, and their immediate differentiated progeny PC13END was examined by binding radiolabelled IGF-I to cell monolayers. Both cell types express highaffinity IGF receptors, but the apparent number of unoccupied receptor sites falls by about 60 % upon differentiation. Crossl ...
... embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells, and their immediate differentiated progeny PC13END was examined by binding radiolabelled IGF-I to cell monolayers. Both cell types express highaffinity IGF receptors, but the apparent number of unoccupied receptor sites falls by about 60 % upon differentiation. Crossl ...
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.