UNIT 2. Structure and function of proteins.
... gel are separated thanks to the solvent migration (buthanol: water: acetic acid 4:1:1) by capillarity. Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): amino acids are separated on the base of their polarity by the used of a column having a ...
... gel are separated thanks to the solvent migration (buthanol: water: acetic acid 4:1:1) by capillarity. Reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): amino acids are separated on the base of their polarity by the used of a column having a ...
COMMUNICATION Engineering the Amine Transaminase from
... also with pentanal as amine acceptor as this is only accepted if the R415 is mutated.[5d] The screening of 2,240 variants (4.5% coverage of the total library) already resulted in the identification of five hits, which contained up to five mutations in the positions L56, W57, F85, R415 and L417 (Supp ...
... also with pentanal as amine acceptor as this is only accepted if the R415 is mutated.[5d] The screening of 2,240 variants (4.5% coverage of the total library) already resulted in the identification of five hits, which contained up to five mutations in the positions L56, W57, F85, R415 and L417 (Supp ...
Modification of halogen specificity of a vanadium‐dependent
... residue located at the chlorine binding site of various amylases (Machius et al. 1995). In the case of BPO from C. pilulifera, the substituted tryptophan or phenylalanine residues at position 397 could participate in chloride binding. In the native BPO enzyme the active site cavity provides the corr ...
... residue located at the chlorine binding site of various amylases (Machius et al. 1995). In the case of BPO from C. pilulifera, the substituted tryptophan or phenylalanine residues at position 397 could participate in chloride binding. In the native BPO enzyme the active site cavity provides the corr ...
2.3. Three-Dimensional structure and function of proteins.
... the main amino acids. • -helix right handed. • Different grade of hardness on the basis of the % Cys. Disulfide bridges. ...
... the main amino acids. • -helix right handed. • Different grade of hardness on the basis of the % Cys. Disulfide bridges. ...
DNA 2 - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Formation of Initiation Complex mRNA + f-Met + GTP + transcription factors (IF-1, -2, -3) = 30S unit 30S joins 50S and IF’s released and GTP hydrolyzed f-Met binds to P site (A & P are binding sites for tRNA) decides reading frame for rest of coding region Ribosomes recognize Initiation sites on mRN ...
... Formation of Initiation Complex mRNA + f-Met + GTP + transcription factors (IF-1, -2, -3) = 30S unit 30S joins 50S and IF’s released and GTP hydrolyzed f-Met binds to P site (A & P are binding sites for tRNA) decides reading frame for rest of coding region Ribosomes recognize Initiation sites on mRN ...
Respiration
... isolated environment for the mitochondrion. This membrane also adjusts the metabolites entering and leaving the mitochondrion. The inner membrane is folded up a lot to increase the surface area for attachment of ETC. These infolds are called cristae. Attaching to the cristae are many stalked particl ...
... isolated environment for the mitochondrion. This membrane also adjusts the metabolites entering and leaving the mitochondrion. The inner membrane is folded up a lot to increase the surface area for attachment of ETC. These infolds are called cristae. Attaching to the cristae are many stalked particl ...
mcb101 praxexam 2 F`10
... desulfhydrase, which catalyzes the breakdown of cysteine. What product of this reaction reacts with the iron that is in the agar, to produce the black precipitate that is the sign of a positive test? A. ammonia D. various acids ...
... desulfhydrase, which catalyzes the breakdown of cysteine. What product of this reaction reacts with the iron that is in the agar, to produce the black precipitate that is the sign of a positive test? A. ammonia D. various acids ...
Chapter 20 TCA Cycle Bridging Reaction: Pyruvate Ž Acetyl-CoA
... • Mechanism involves two covalent intermediates with the enzyme: • Addition of pyruvate to TPP and loss of CO2 forms hydroxyethyl TPP. • (This same intermediate is formed by pyruvate decarboxylase in yeast alcoholic fermentation). ...
... • Mechanism involves two covalent intermediates with the enzyme: • Addition of pyruvate to TPP and loss of CO2 forms hydroxyethyl TPP. • (This same intermediate is formed by pyruvate decarboxylase in yeast alcoholic fermentation). ...
Chapter 20 TCA Cycle Bridging Reaction: Pyruvate Ž Acetyl-CoA
... • Mechanism involves two covalent intermediates with the enzyme: • Addition of pyruvate to TPP and loss of CO2 forms hydroxyethyl TPP. • (This same intermediate is formed by pyruvate decarboxylase in yeast alcoholic fermentation). ...
... • Mechanism involves two covalent intermediates with the enzyme: • Addition of pyruvate to TPP and loss of CO2 forms hydroxyethyl TPP. • (This same intermediate is formed by pyruvate decarboxylase in yeast alcoholic fermentation). ...
Hepatic encephalopathy
... Hepatic dysfunction Injury of hepatocytes and hepatic dysfunction metabolic dysfunction carbohydrate, protein and electrolyte dysfunction of bile secretion and excretion coagulation system dysfunction ...
... Hepatic dysfunction Injury of hepatocytes and hepatic dysfunction metabolic dysfunction carbohydrate, protein and electrolyte dysfunction of bile secretion and excretion coagulation system dysfunction ...
Amino Acids - Building Blocks of Proteins
... recognized that the structure of a finch’s beak was related to the food it ate. This fundamental structure-function relationship is also true at all levels below the Potassium macro level, including proteins and other structures at the molecular Ion level. For two examples of proteins and their func ...
... recognized that the structure of a finch’s beak was related to the food it ate. This fundamental structure-function relationship is also true at all levels below the Potassium macro level, including proteins and other structures at the molecular Ion level. For two examples of proteins and their func ...
8 Introduction to Metabolism Notes
... In the cell, the energy from the hydrolysis of ATP is directly coupled to endergonic processes by the transfer of the phosphate group to another molecule. The phosphorylated molecule undergoes a change that performs work. E. ATP is regenerated by the addition of a phosphate group to ADP using energy ...
... In the cell, the energy from the hydrolysis of ATP is directly coupled to endergonic processes by the transfer of the phosphate group to another molecule. The phosphorylated molecule undergoes a change that performs work. E. ATP is regenerated by the addition of a phosphate group to ADP using energy ...
Introduction to Metabolism Notes
... In the cell, the energy from the hydrolysis of ATP is directly coupled to endergonic processes by the transfer of the phosphate group to another molecule. The phosphorylated molecule undergoes a change that performs work. E. ATP is regenerated by the addition of a phosphate group to ADP using energy ...
... In the cell, the energy from the hydrolysis of ATP is directly coupled to endergonic processes by the transfer of the phosphate group to another molecule. The phosphorylated molecule undergoes a change that performs work. E. ATP is regenerated by the addition of a phosphate group to ADP using energy ...
1 of 3 Biochemistry Final exam Block 3, 2008 Name Answer all of
... (a) At rest, plenty of O2 is being delivered to the muscle, and pyruvate formed during glycolysis is oxidized to acetyl-CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Acetyl groups then enter the citric acid cycle and are oxidized to CO2. (b) Under the conditions of all-out exertion, skeletal muscle can ...
... (a) At rest, plenty of O2 is being delivered to the muscle, and pyruvate formed during glycolysis is oxidized to acetyl-CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Acetyl groups then enter the citric acid cycle and are oxidized to CO2. (b) Under the conditions of all-out exertion, skeletal muscle can ...
EXAMPLES OF “STEP
... haemorrages in the places of clothes friction. Hypovitaminosis of what vitamin is present at the girl? A С* B В6 C В1 D А E В2 4. There is observed inhibited fibrillation in the patients with bile ducts obstruction, bleeding due to low level of absorbtion of some vitamin. What vitamin is in deficit? ...
... haemorrages in the places of clothes friction. Hypovitaminosis of what vitamin is present at the girl? A С* B В6 C В1 D А E В2 4. There is observed inhibited fibrillation in the patients with bile ducts obstruction, bleeding due to low level of absorbtion of some vitamin. What vitamin is in deficit? ...
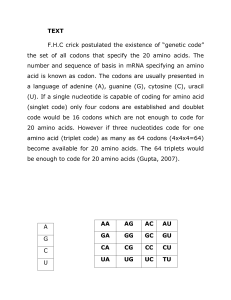
TEXT F.H.C crick postulated the existence of “genetic code” the set
... Similarly consider a repeating sequence of three bases e.g. (ACG)n. Depending upon were the reading is started, three kinds of homopolypeptides are expected. Actual codon assignment i,e. to find out which of three codons codes for which ...
... Similarly consider a repeating sequence of three bases e.g. (ACG)n. Depending upon were the reading is started, three kinds of homopolypeptides are expected. Actual codon assignment i,e. to find out which of three codons codes for which ...
Discrimination of wine age of Chinese rice wine by
... experienced to successfully evaluate the wine age. Instrumental methods have been utilized for wine age or vintage year discrimination to distinguish certain chemical features, such as phenolic compounds[5], amino acids, pigment composition[6], flavonoids[7], acid[8], and volatile compounds[9]. The ...
... experienced to successfully evaluate the wine age. Instrumental methods have been utilized for wine age or vintage year discrimination to distinguish certain chemical features, such as phenolic compounds[5], amino acids, pigment composition[6], flavonoids[7], acid[8], and volatile compounds[9]. The ...
The investigation of enzymes structure, physical
... protein structure and physical-chemical properties. Quantitative definition of protein by a biuretic method. The proof of protein nature of enzymes. Biomedical importance: Thousands of proteins present in the human body perform functions too numerous to list. These include serving as carriers of vit ...
... protein structure and physical-chemical properties. Quantitative definition of protein by a biuretic method. The proof of protein nature of enzymes. Biomedical importance: Thousands of proteins present in the human body perform functions too numerous to list. These include serving as carriers of vit ...
Complementary DNA
... which are absolutely conserved. Some of these regions have been identified to be important for insulin activity. For example, amino acid residues 24 to 28 of the B chain are responsible for the negative cooperativity observed when insulin binds to its cell surface receptor (16). The nucleotide seque ...
... which are absolutely conserved. Some of these regions have been identified to be important for insulin activity. For example, amino acid residues 24 to 28 of the B chain are responsible for the negative cooperativity observed when insulin binds to its cell surface receptor (16). The nucleotide seque ...