Ch. 7-3 and 7-4 Vocabulary
... a process by which the tendency of a fluid, molecules of a solvent usually water, to pass tend to pass through a through a semipermeable semipermeable membrane membrane into a solution from a less concentrated where the solvent solution into a more concentration is higher, ...
... a process by which the tendency of a fluid, molecules of a solvent usually water, to pass tend to pass through a through a semipermeable semipermeable membrane membrane into a solution from a less concentrated where the solvent solution into a more concentration is higher, ...
Chapter 19 - Cloudfront.net
... 2. Conjugation: transfer of genetic information from one cell to another, sexual 3. In unfavorable conditions, many bacteria can form endospores – can remain dormant for months or years (such as anthrax) ...
... 2. Conjugation: transfer of genetic information from one cell to another, sexual 3. In unfavorable conditions, many bacteria can form endospores – can remain dormant for months or years (such as anthrax) ...
Cell Membrane for Biologic Cells
... already broken under the applied electric field to allow the blue dye to diffuse into the cells. ...
... already broken under the applied electric field to allow the blue dye to diffuse into the cells. ...
Cell Transport – Review Sheet
... 27. A cell has 20% salt and 80% water is in a solution that has 10% salt and 90% water. a. In what type of solution is the cell? hypotonic b. Where will water move? Into the cell c. What will happen to the cell? Cytolysis (cell swell and/or burst) 28. A cell has 20% salt and 80% water is in a solut ...
... 27. A cell has 20% salt and 80% water is in a solution that has 10% salt and 90% water. a. In what type of solution is the cell? hypotonic b. Where will water move? Into the cell c. What will happen to the cell? Cytolysis (cell swell and/or burst) 28. A cell has 20% salt and 80% water is in a solut ...
Cell Biology The Cell Theory
... living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. Some organisms are unicellular (made of only one cell) while others are multicellular (made up of several cells). ...
... living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. Some organisms are unicellular (made of only one cell) while others are multicellular (made up of several cells). ...
7.3 ANIMAL and PLANT CELL STRUCTURE HO
... Nucleus: Control center of the cell, that holds the cell’s chromosomes. Chromosomes are made of DNA and hold the cell’s genes (inside is nucleolus that makes ribosomes). Vesicles: storage containers of the cells. Store wastes and other substances temporarily. Mitochondria: power house of the cell. U ...
... Nucleus: Control center of the cell, that holds the cell’s chromosomes. Chromosomes are made of DNA and hold the cell’s genes (inside is nucleolus that makes ribosomes). Vesicles: storage containers of the cells. Store wastes and other substances temporarily. Mitochondria: power house of the cell. U ...
Components of a Cell Membrane
... flowing through CFTR Cl- channels allowing reabsorption of salt in excess of water. This results in the production of dilute sweat, so that we can be cooled by evaporation without losing an undue amount of salt. ...
... flowing through CFTR Cl- channels allowing reabsorption of salt in excess of water. This results in the production of dilute sweat, so that we can be cooled by evaporation without losing an undue amount of salt. ...
L3.b
... animals cannot make their own food? a. Animals do not use water. b. Animals breathe in oxygen. c. Animals need extra energy to survive. d. Animal cells do not contain chloroplasts. Answer: d The nucleus is located in the center of the cell and is known as the cell’s ___________. a. energy source b. ...
... animals cannot make their own food? a. Animals do not use water. b. Animals breathe in oxygen. c. Animals need extra energy to survive. d. Animal cells do not contain chloroplasts. Answer: d The nucleus is located in the center of the cell and is known as the cell’s ___________. a. energy source b. ...
BIOLOGY ONE
... 84. How is facilitated diffusion different from regular diffusion? 85. What is the advantage to facilitated diffusion? 86. For each of the following osmotic solutions, tell where there is more pure water to start, where the pure water moves & what happens to the cell as a result: Isotonic solution, ...
... 84. How is facilitated diffusion different from regular diffusion? 85. What is the advantage to facilitated diffusion? 86. For each of the following osmotic solutions, tell where there is more pure water to start, where the pure water moves & what happens to the cell as a result: Isotonic solution, ...
Everything you wanted to know about organelles
... Everything you wanted to know about organelles Membrane bound structures with particular functions in a eukaryotic cell ...
... Everything you wanted to know about organelles Membrane bound structures with particular functions in a eukaryotic cell ...
Animal Cells
... Cells are extremely small (we need a microscope to see them) Animal cells have some basic properties (although this is a ...
... Cells are extremely small (we need a microscope to see them) Animal cells have some basic properties (although this is a ...
Biomarkers_04-Mechanisms-Membranes
... - Compounds then affect membranes nonspecific disruption of fluidity and/or disruption of membrane proteins - Related to lipophilicity (Kow): tendency of compounds to accumulate in body lipids (incl. membranes) E.g. narcotic toxicity to fish: log (1/LC50) = 0.907 . log Kow - 4.94 ...
... - Compounds then affect membranes nonspecific disruption of fluidity and/or disruption of membrane proteins - Related to lipophilicity (Kow): tendency of compounds to accumulate in body lipids (incl. membranes) E.g. narcotic toxicity to fish: log (1/LC50) = 0.907 . log Kow - 4.94 ...
The amazing plant cell.
... pressure and helps preventing water loss. The plasma membrane controls the cell’s contact with the environment The cytoplasm contains organelles. Many organelles have membranes as boundaries These compartmentalize the interior of the cell This allows the cell to carry out a variety of activities ...
... pressure and helps preventing water loss. The plasma membrane controls the cell’s contact with the environment The cytoplasm contains organelles. Many organelles have membranes as boundaries These compartmentalize the interior of the cell This allows the cell to carry out a variety of activities ...
Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function
... Why must Cells be small? - Cells are small because they must have a large surface area to volume RATIO in order to transport material efficiently - Surface area is the area around the outside of the cell - Volume is amount of space the cell takes up - The higher the surface area AS COMPARED TO the ...
... Why must Cells be small? - Cells are small because they must have a large surface area to volume RATIO in order to transport material efficiently - Surface area is the area around the outside of the cell - Volume is amount of space the cell takes up - The higher the surface area AS COMPARED TO the ...
Solutions
... Applying the Concepts-Hypertonic Solution 2. Hypertonic solution-a solution with a greater concentration of solute compared to the concentration of solute inside the cell ...
... Applying the Concepts-Hypertonic Solution 2. Hypertonic solution-a solution with a greater concentration of solute compared to the concentration of solute inside the cell ...
Cell Organelles
... Apparatus Enzymes in the Golgi Apparatus attach carbohydrates and lipids to proteins. The proteins are then shipped to their final destinations. ...
... Apparatus Enzymes in the Golgi Apparatus attach carbohydrates and lipids to proteins. The proteins are then shipped to their final destinations. ...
Document
... 5. Action potentials are generated by openings and closing of ion channels. 6. Voltage causes electrically charged particles, ions, to move across cell membranes. 7. Major ions in neurons a) Sodium b) Potassium c) Calcium d) Chloride B. Neuron membrane potentials are measured in 1. Ion channels and ...
... 5. Action potentials are generated by openings and closing of ion channels. 6. Voltage causes electrically charged particles, ions, to move across cell membranes. 7. Major ions in neurons a) Sodium b) Potassium c) Calcium d) Chloride B. Neuron membrane potentials are measured in 1. Ion channels and ...
Cell - structural and functional unit of life -
... Begins when chromosome movement stops Two sets of chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin New nuclear membrane forms around each chromatin mass ...
... Begins when chromosome movement stops Two sets of chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin New nuclear membrane forms around each chromatin mass ...
Name and describe five organelles found in the cytoplasm
... _____1. Cell activities, including division, are controlled by information in the cell’s _______. _____2. In plants, sun energy is used to make food by the ______. _____3. Specialized cells organized to perform a certain function are called _______. _____4. A plant cell differs from an animal cell b ...
... _____1. Cell activities, including division, are controlled by information in the cell’s _______. _____2. In plants, sun energy is used to make food by the ______. _____3. Specialized cells organized to perform a certain function are called _______. _____4. A plant cell differs from an animal cell b ...
Cell membrane - Cobb Learning
... chlorophyll, as well as enzymes and other molecules that function in photosynthesis • Chloroplasts are found in leaves and other green organs of plants and in algae ...
... chlorophyll, as well as enzymes and other molecules that function in photosynthesis • Chloroplasts are found in leaves and other green organs of plants and in algae ...
The Cell Theory Notes
... Name__________________________________ period _____ date assigned_____________ date due ______________ date returned _____________ ...
... Name__________________________________ period _____ date assigned_____________ date due ______________ date returned _____________ ...
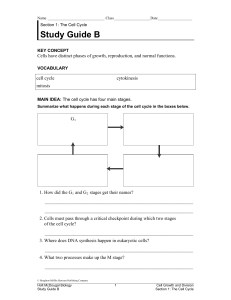
Study Guide B
... 5. Among different types of cells, which stage of the cell cycle varies most in length? _______________________________________________________________ 6. Why does a skin cell divide more often than a liver cell? _______________________________________________________________ 7. What is G 0 ? ______ ...
... 5. Among different types of cells, which stage of the cell cycle varies most in length? _______________________________________________________________ 6. Why does a skin cell divide more often than a liver cell? _______________________________________________________________ 7. What is G 0 ? ______ ...
BIOFE (Biology OFE)
... 1. Gives plant cells firm regular shape. 2. This molecule is combined in a special way to form glycogen. 3. Bodies which pinch off vesicles at end. 4. Site of protein manufacture. 5. Keeps cell contents separate from external environment. 6. Strong substance that makes up cell walls. 7. Spaces betwe ...
... 1. Gives plant cells firm regular shape. 2. This molecule is combined in a special way to form glycogen. 3. Bodies which pinch off vesicles at end. 4. Site of protein manufacture. 5. Keeps cell contents separate from external environment. 6. Strong substance that makes up cell walls. 7. Spaces betwe ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.