Chapter 5
... Signals are carried across the synaptic cleft between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells by the diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules. Fast direct chemical synapses: the transmitter receptor proteins include the both the binding site for the transmitter and an ion channel. Neurotransmitters ar ...
... Signals are carried across the synaptic cleft between the presynaptic and postsynaptic cells by the diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules. Fast direct chemical synapses: the transmitter receptor proteins include the both the binding site for the transmitter and an ion channel. Neurotransmitters ar ...
Cell Membranes Osmosis and Diffusion
... • The word "HYPER" means more, in this case there are more solute (salt) molecules outside the cell, which causes the water to be sucked in that direction. • In plant cells, the central vacuole loses water and the cells shrink, causing wilting. • In animal cells, the cells also shrink. • In both cas ...
... • The word "HYPER" means more, in this case there are more solute (salt) molecules outside the cell, which causes the water to be sucked in that direction. • In plant cells, the central vacuole loses water and the cells shrink, causing wilting. • In animal cells, the cells also shrink. • In both cas ...
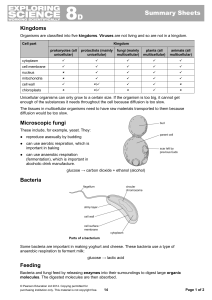
8D Unicellular Organisms
... Unicellular organisms can only grow to a certain size. If the organism is too big, it cannot get enough of the substances it needs throughout the cell because diffusion is too slow. The tissues in multicellular organisms need to have raw materials transported to them because diffusion would be too s ...
... Unicellular organisms can only grow to a certain size. If the organism is too big, it cannot get enough of the substances it needs throughout the cell because diffusion is too slow. The tissues in multicellular organisms need to have raw materials transported to them because diffusion would be too s ...
Cell - Cloudfront.net
... (like a solution) •The proteins take the food molecules in and combine them with Oxygen to release the energy ...
... (like a solution) •The proteins take the food molecules in and combine them with Oxygen to release the energy ...
Chapter 7 Test Review
... 36. hypotonic? _hypotonic______________________ 37. Of the following which structure(s) are/is found in all living organisms? ____*____ DNA and/or RNA _________ Mitochondria _________ Nucleus _________ Cell wall 38. Compared to a skin cell, a muscle cell is likely to have more __Mitochondria________ ...
... 36. hypotonic? _hypotonic______________________ 37. Of the following which structure(s) are/is found in all living organisms? ____*____ DNA and/or RNA _________ Mitochondria _________ Nucleus _________ Cell wall 38. Compared to a skin cell, a muscle cell is likely to have more __Mitochondria________ ...
CELL STRUCTURE_2012
... expelled into the intercellular space (which may be into the bloodstream). ...
... expelled into the intercellular space (which may be into the bloodstream). ...
CELL ENVIRONMENTS REVIEW SHEET
... you open the package and release the molecules, hat would be an example of osmosis. Explain whether this statement is true or false and WHY. THIS IS FALSE BECAUSE IT DOES NOT TALK ABOUT WATER, WHICH IS OSMOSIS. THIS IS AN EXAMPLE OF DIFFUSION. ...
... you open the package and release the molecules, hat would be an example of osmosis. Explain whether this statement is true or false and WHY. THIS IS FALSE BECAUSE IT DOES NOT TALK ABOUT WATER, WHICH IS OSMOSIS. THIS IS AN EXAMPLE OF DIFFUSION. ...
Transport-modified - Brookings School District
... and toes to wrinkle up when water ________ enters your skin cells by osmosis ...
... and toes to wrinkle up when water ________ enters your skin cells by osmosis ...
The Cell - TeacherWeb
... 1. All living things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Some organisms may have as little as 1 cell, like Giardia. Other organisms have millions of cells. ...
... 1. All living things are made up of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from existing cells Some organisms may have as little as 1 cell, like Giardia. Other organisms have millions of cells. ...
Cell Growth & Division Notes
... nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane. The larger a cell becomes, the more demands it puts on its DNA. ...
... nutrients and wastes across the cell membrane. The larger a cell becomes, the more demands it puts on its DNA. ...
sample exam questions
... Is the most common method used by microorganisms to convert glucose to pyruvate Is primarily used by cells that decompose citric acid in the environment as a nutrient Is particularly important in photosynthesis Functions in cells to produce citric acid that is then incorporated into new cellular mat ...
... Is the most common method used by microorganisms to convert glucose to pyruvate Is primarily used by cells that decompose citric acid in the environment as a nutrient Is particularly important in photosynthesis Functions in cells to produce citric acid that is then incorporated into new cellular mat ...
Document
... * During _______________, the centromeres split and the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. D. Telophase: the fourth stage of mitosis. * During ________________, two distinct daughter cells are formed. The cells ...
... * During _______________, the centromeres split and the sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. D. Telophase: the fourth stage of mitosis. * During ________________, two distinct daughter cells are formed. The cells ...
Endoplasmosis and exoplasmosis: the evolutionary principles
... This concept is in line with the fact that there are many similarities between different forms of endoplasmosis or exoplasmosis, meaning trans- and cis-membrane fusion events, respectively. A common feature of endoplasmosis is the requirement for coat proteins at the plasmatic face of the membrane ( ...
... This concept is in line with the fact that there are many similarities between different forms of endoplasmosis or exoplasmosis, meaning trans- and cis-membrane fusion events, respectively. A common feature of endoplasmosis is the requirement for coat proteins at the plasmatic face of the membrane ( ...
Eukaryotic Cellular Organelles
... Different? How are they related? Describe the characteristics they have in common with bacteria. Plant cells contain both mitochondria and chloroplasts. Explain why they must contain both. ...
... Different? How are they related? Describe the characteristics they have in common with bacteria. Plant cells contain both mitochondria and chloroplasts. Explain why they must contain both. ...
Page 1 of 1 DTU Systems Biology Mette Voldby Larsen, CBS
... vacuoles enlarge and provide the pressure needed to stretch the cell wall and provide structural support for the plant. 17. The cytoskeleton within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells provides shape, strength, and movement. It consists of three interacting types of protein fibers: microfilaments, whic ...
... vacuoles enlarge and provide the pressure needed to stretch the cell wall and provide structural support for the plant. 17. The cytoskeleton within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells provides shape, strength, and movement. It consists of three interacting types of protein fibers: microfilaments, whic ...
Plant Cells and Tissues
... Saturated (bad fats) vs. Unsaturated (better) - most abundant in seeds ...
... Saturated (bad fats) vs. Unsaturated (better) - most abundant in seeds ...
Understanding by Design Unit Plan
... 7.3.2a: Explain why organisms need food, water, air, and a living space to survive B.2.2: Compare and contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells 7.3.3: Discuss how form and function are directly related in a cell 7.3.4a: Compare and contrast an animal and plant cell 7.3.4b: State the importance of a ...
... 7.3.2a: Explain why organisms need food, water, air, and a living space to survive B.2.2: Compare and contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells 7.3.3: Discuss how form and function are directly related in a cell 7.3.4a: Compare and contrast an animal and plant cell 7.3.4b: State the importance of a ...
Introduction: plant cell wall proteins
... the plasma membrane and then processed for release to the cell wall and/or as extracellular secretions. The expression of AGP genes is then considered along with the localization patterns of various AGPs; these data highlight the involvement of AGPs in plant development. Whereas AGPs are likely to h ...
... the plasma membrane and then processed for release to the cell wall and/or as extracellular secretions. The expression of AGP genes is then considered along with the localization patterns of various AGPs; these data highlight the involvement of AGPs in plant development. Whereas AGPs are likely to h ...
cell structure &function-2
... • Ribosomes are small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cell (mostly cytoplasm). • Ribosomes produce proteins by following coded instructions that come from the nucleus. ...
... • Ribosomes are small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cell (mostly cytoplasm). • Ribosomes produce proteins by following coded instructions that come from the nucleus. ...
Proteins - Houston ISD
... • Ribosomes are small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cell (mostly cytoplasm). • Ribosomes produce proteins by following coded instructions that come from the nucleus. ...
... • Ribosomes are small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cell (mostly cytoplasm). • Ribosomes produce proteins by following coded instructions that come from the nucleus. ...
Introduction to Cells 1p1 2014
... resource use and waste production. DISCUSS which cube (right) would be ...
... resource use and waste production. DISCUSS which cube (right) would be ...
Cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. The basic function of the cell membrane is to protect the cell from its surroundings. It consists of the phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. Cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, glycocalyx, and intracellular cytoskeleton. Cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.