Lower Extremity Trauma: An Atlas of Radiologic Findings of ACL Injury
... Post-surgical rehab is critical, and usually last 6+ months ...
... Post-surgical rehab is critical, and usually last 6+ months ...
Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
... an isotope that can be injected routinely, it is desirable to have the most sensitive device available to form the clinical images. 2.5. Count Rate Limitations At very high photon detection rates, the camera electronics can have difficulty analyzing every photon. The missed counts, often referred as ...
... an isotope that can be injected routinely, it is desirable to have the most sensitive device available to form the clinical images. 2.5. Count Rate Limitations At very high photon detection rates, the camera electronics can have difficulty analyzing every photon. The missed counts, often referred as ...
Full PDF - Emergency Medicine Cases
... complications.11 Despite being a non–life-threatening illness, the burden of disease of renal colic is significant. The adverse outcomes affect patients and the health care system beyond what may be seen with an isolated ED visit. Patients with renal colic are likely to undergo multiple imaging inve ...
... complications.11 Despite being a non–life-threatening illness, the burden of disease of renal colic is significant. The adverse outcomes affect patients and the health care system beyond what may be seen with an isolated ED visit. Patients with renal colic are likely to undergo multiple imaging inve ...
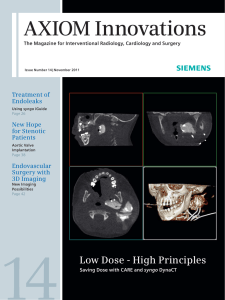
AXIOM Innovations
... Exposure) and CLEAR (an imaging technology to enhance visualization with X-ray) not only reduces radiation dose for patients and staff, but also boosts image quality to an outstanding level. A growing trend in the market for interventional cardiology and hybrid surgery is the minimally invasive repl ...
... Exposure) and CLEAR (an imaging technology to enhance visualization with X-ray) not only reduces radiation dose for patients and staff, but also boosts image quality to an outstanding level. A growing trend in the market for interventional cardiology and hybrid surgery is the minimally invasive repl ...
Verification and correction of geometrical uncertainties in
... Geometrical errors are presented as deviation between intended geometry of radiotherapy plan and real geometry of radiotherapy treatment. Total geometrical error is build up of smaller errors, which can be generally classified as set-up, organ motion, organ delineation, and technical condition relat ...
... Geometrical errors are presented as deviation between intended geometry of radiotherapy plan and real geometry of radiotherapy treatment. Total geometrical error is build up of smaller errors, which can be generally classified as set-up, organ motion, organ delineation, and technical condition relat ...
Technical aspects and utility of fMRI using BOLD and ASL
... coupling (AFC). Changes in blood flow and metabolism occur with excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmission, both of which are energy consuming processes (Nudo and Masterson, 1986). Since regional CBF changes are used as a surrogate marker for changes in regional brain metabolism which in turn reflec ...
... coupling (AFC). Changes in blood flow and metabolism occur with excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmission, both of which are energy consuming processes (Nudo and Masterson, 1986). Since regional CBF changes are used as a surrogate marker for changes in regional brain metabolism which in turn reflec ...
X-ray Technician Refresher Training
... electrons and focusing cup to direct them • Anode – target of high atomic number struck by electrons to produce X-rays • Voltage supply – high voltage supply to accelerate electrons from cathode to anode • Envelope – glass or metal vacuum tube containing anode and cathode • Tube housing – shielding ...
... electrons and focusing cup to direct them • Anode – target of high atomic number struck by electrons to produce X-rays • Voltage supply – high voltage supply to accelerate electrons from cathode to anode • Envelope – glass or metal vacuum tube containing anode and cathode • Tube housing – shielding ...
Refresher Training for X-Ray Equipment Operators
... electrons and focusing cup to direct them • Anode – target of high atomic number struck by electrons to produce X-rays • Voltage supply – high voltage supply to accelerate electrons from cathode to anode • Envelope – glass or metal vacuum tube containing anode and cathode • Tube housing – shielding ...
... electrons and focusing cup to direct them • Anode – target of high atomic number struck by electrons to produce X-rays • Voltage supply – high voltage supply to accelerate electrons from cathode to anode • Envelope – glass or metal vacuum tube containing anode and cathode • Tube housing – shielding ...
Cone Beam Computed Tomography
... Health, Göteborg, Sweden (Fig.1). It was equipped with an image intensifier connected to a CCD-camera as detector. The X-ray field size was 3 cm x 4 cm in the rotation centre and the reproduced volume thus corresponded to a cylinder ...
... Health, Göteborg, Sweden (Fig.1). It was equipped with an image intensifier connected to a CCD-camera as detector. The X-ray field size was 3 cm x 4 cm in the rotation centre and the reproduced volume thus corresponded to a cylinder ...
The Evolution of Stereotactic Radiosurgery
... High dose of “ablative” radiation delivered to a target localized in 3-dimensions with overall end to end precision on the order of 1-2 mm delivered over 1-5 treatments ...
... High dose of “ablative” radiation delivered to a target localized in 3-dimensions with overall end to end precision on the order of 1-2 mm delivered over 1-5 treatments ...
Imaging doses from the Elekta Synergy X
... importantly, the image sequence from rotation fluoroscopy can be used in filtered backprojection to reconstruct an X-ray volumetric image [1] . This form of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) propels IGRT forward into a genuinely three dimensional (3D) technique and consequently has the potential ...
... importantly, the image sequence from rotation fluoroscopy can be used in filtered backprojection to reconstruct an X-ray volumetric image [1] . This form of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) propels IGRT forward into a genuinely three dimensional (3D) technique and consequently has the potential ...
RADIOLOGÍA
... velocity of flow, and may, ocasionally, contribute to the characterization of focal lesions. 2 However, its usefulness in detection of slow flow or flow in deep vascular structures is limited, and it cannot be used to adequately detect tumor or parenchymal microvasculature. 1,3 When ultrasound does ...
... velocity of flow, and may, ocasionally, contribute to the characterization of focal lesions. 2 However, its usefulness in detection of slow flow or flow in deep vascular structures is limited, and it cannot be used to adequately detect tumor or parenchymal microvasculature. 1,3 When ultrasound does ...
(FSD)-prepared balanced - Questions and Answers in MRI
... of life in a large portion of western populations and also involved with increased risk of severe cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke (1). While catheter angiography remains the gold standard for the evaluation of vascular disorders (2), MRI has become a routine diagnostic tool in ...
... of life in a large portion of western populations and also involved with increased risk of severe cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke (1). While catheter angiography remains the gold standard for the evaluation of vascular disorders (2), MRI has become a routine diagnostic tool in ...
University of Arkansas for Medical Science
... structures and extremely high local recurrence rate has led to most of the patients dying from the primary intracranial disease. Recent advances in skull base surgery and radiation therapy provides an opportunity for cure. This can be achieved with precise knowledge of tumor extent and its relations ...
... structures and extremely high local recurrence rate has led to most of the patients dying from the primary intracranial disease. Recent advances in skull base surgery and radiation therapy provides an opportunity for cure. This can be achieved with precise knowledge of tumor extent and its relations ...
ACR Practice Guideline for the Performance and Interpretation of
... indication and with the minimum radiation exposure that provides diagnostic image quality. While important abnormalities of the heart and associated structures can be detected on chest CT performed for other reasons, these guidelines are written specifically for dedicated examinations designed to de ...
... indication and with the minimum radiation exposure that provides diagnostic image quality. While important abnormalities of the heart and associated structures can be detected on chest CT performed for other reasons, these guidelines are written specifically for dedicated examinations designed to de ...
Evaluation of Palpable Breast Masses
... Palpable breast masses are common and usually benign, but efficient evaluation and prompt diagnosis are necessary to rule out malignancy. A thorough clinical breast examination, imaging, and tissue sampling are needed for a definitive diagnosis. Fine-needle aspiration is fast, inexpensive, and accur ...
... Palpable breast masses are common and usually benign, but efficient evaluation and prompt diagnosis are necessary to rule out malignancy. A thorough clinical breast examination, imaging, and tissue sampling are needed for a definitive diagnosis. Fine-needle aspiration is fast, inexpensive, and accur ...
Breast Ultrasound for the Mammography Technologist
... American Journal of Roentgenology (February 2008, Vol. 190:2, pp. 476-480). ...
... American Journal of Roentgenology (February 2008, Vol. 190:2, pp. 476-480). ...
Bone Marrow Edema
... 9MRI features associated with these conditions should be cautiously interpreted, especially in athletes where some capsular and osseous changes can be asymptomatic. 9MR imaging is valuable in assessing the possible soft tissue and osseous abnormalities implicated in a particular clinical setting of ...
... 9MRI features associated with these conditions should be cautiously interpreted, especially in athletes where some capsular and osseous changes can be asymptomatic. 9MR imaging is valuable in assessing the possible soft tissue and osseous abnormalities implicated in a particular clinical setting of ...
Introducing Biograph mCT.
... of RTP devices such as breast boards and makes scanning of bariatric patients easier. In addition, Biograph mCT’s sturdy, extra-wide 228 kg (500 lb) capacity bed provides comfortable support for both obese and standard patients during scans. The unique bed virtually eliminates CT and PET registratio ...
... of RTP devices such as breast boards and makes scanning of bariatric patients easier. In addition, Biograph mCT’s sturdy, extra-wide 228 kg (500 lb) capacity bed provides comfortable support for both obese and standard patients during scans. The unique bed virtually eliminates CT and PET registratio ...
PDF - Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences
... 1. CBCT examinations must not be carried out unless a history and clinical examination have been performed. 2. CBCT examinations must be justified for each patient to demonstrate that the benefits outweigh the risks. 3. CBCT examinations should potentially add new information to aid the patient’s Ma ...
... 1. CBCT examinations must not be carried out unless a history and clinical examination have been performed. 2. CBCT examinations must be justified for each patient to demonstrate that the benefits outweigh the risks. 3. CBCT examinations should potentially add new information to aid the patient’s Ma ...
Water Excitation as an Alternative to Fat Saturation in MR Imaging
... injection (n ⫽ 24), intermediate-weighted fast SE (n ⫽ 36) imaging, and T2weighted fast SE (n ⫽ 36) imaging. Acquisition times of the sequences and signalto-noise and contrast-to-noise ratios of bone, muscle, fat, and water for the two methods were compared quantitatively. Images were then qualitati ...
... injection (n ⫽ 24), intermediate-weighted fast SE (n ⫽ 36) imaging, and T2weighted fast SE (n ⫽ 36) imaging. Acquisition times of the sequences and signalto-noise and contrast-to-noise ratios of bone, muscle, fat, and water for the two methods were compared quantitatively. Images were then qualitati ...
1 FORM 301 HEALTH PROFESSIONS COUNCIL OF SOUTH
... Radiographic technique Radiation safety and protection Use of equipment and accessories Protocol followed Image quality produced Assessment of images including knowledge of anatomy, pathology, artifacts, ...
... Radiographic technique Radiation safety and protection Use of equipment and accessories Protocol followed Image quality produced Assessment of images including knowledge of anatomy, pathology, artifacts, ...
example from X-ray Diagnostic Radiology
... in X-ray departments to ensure the continual production of optimum quality images with the minimum necessary dose to the patient. These programmes should include checks and test measurements on all parts of the imaging system at appropriate time intervals not exceeding one year.. A record of mainten ...
... in X-ray departments to ensure the continual production of optimum quality images with the minimum necessary dose to the patient. These programmes should include checks and test measurements on all parts of the imaging system at appropriate time intervals not exceeding one year.. A record of mainten ...
chest imaging
... subsequent 8 years from initial imaging at diagnosis through follow-up. Posteroanterior chest radiograph at the time of diagnosis (A) shows a large anterior mediastinal mass which extends bilaterally from the midline. A follow-up posteroanterior chest radiograph obtained 8 years from diagnosis (B) s ...
... subsequent 8 years from initial imaging at diagnosis through follow-up. Posteroanterior chest radiograph at the time of diagnosis (A) shows a large anterior mediastinal mass which extends bilaterally from the midline. A follow-up posteroanterior chest radiograph obtained 8 years from diagnosis (B) s ...
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Focused Impact on MRI
... at several levels. First, proper equipment including transducer selection is required to optimize results. Next, the individual performing ultrasound must understand anatomy to find the structure of interest, adequately evaluate that structure in a standardized imaging plane, recognize artifacts suc ...
... at several levels. First, proper equipment including transducer selection is required to optimize results. Next, the individual performing ultrasound must understand anatomy to find the structure of interest, adequately evaluate that structure in a standardized imaging plane, recognize artifacts suc ...
Medical imaging

Medical imaging is the technique and process of creating visual representations of the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention. Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging.As a discipline and in its widest sense, it is part of biological imaging and incorporates radiology which uses the imaging technologies of X-ray radiography, magnetic resonance imaging, medical ultrasonography or ultrasound, endoscopy, elastography, tactile imaging, thermography, medical photography and nuclear medicine functional imaging techniques as positron emission tomography.Measurement and recording techniques which are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others represent other technologies which produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph vs. time or maps which contain information about the measurement locations. In a limited comparison these technologies can be considered as forms of medical imaging in another discipline.Up until 2010, 5 billion medical imaging studies had been conducted worldwide. Radiation exposure from medical imaging in 2006 made up about 50% of total ionizing radiation exposure in the United States.In the clinical context, ""invisible light"" medical imaging is generally equated to radiology or ""clinical imaging"" and the medical practitioner responsible for interpreting (and sometimes acquiring) the images is a radiologist. ""Visible light"" medical imaging involves digital video or still pictures that can be seen without special equipment. Dermatology and wound care are two modalities that use visible light imagery. Diagnostic radiography designates the technical aspects of medical imaging and in particular the acquisition of medical images. The radiographer or radiologic technologist is usually responsible for acquiring medical images of diagnostic quality, although some radiological interventions are performed by radiologists.As a field of scientific investigation, medical imaging constitutes a sub-discipline of biomedical engineering, medical physics or medicine depending on the context: Research and development in the area of instrumentation, image acquisition (e.g. radiography), modeling and quantification are usually the preserve of biomedical engineering, medical physics, and computer science; Research into the application and interpretation of medical images is usually the preserve of radiology and the medical sub-discipline relevant to medical condition or area of medical science (neuroscience, cardiology, psychiatry, psychology, etc.) under investigation. Many of the techniques developed for medical imaging also have scientific and industrial applications.Medical imaging is often perceived to designate the set of techniques that noninvasively produce images of the internal aspect of the body. In this restricted sense, medical imaging can be seen as the solution of mathematical inverse problems. This means that cause (the properties of living tissue) is inferred from effect (the observed signal). In the case of medical ultrasonography, the probe consists of ultrasonic pressure waves and echoes that go inside the tissue to show the internal structure. In the case of projectional radiography, the probe uses X-ray radiation, which is absorbed at different rates by different tissue types such as bone, muscle and fat.The term noninvasive is used to denote a procedure where no instrument is introduced into a patient's body which is the case for most imaging techniques used.