BOWEL CANCER and GENETICS - Queensland Stoma Association
... this disease. This susceptibility is often a single altered gene. It is true to say that all cancer cells contain some genes that have malfunctioned, this allows the cells to behave in an abnormal way and grow as a cancer, yet most of the gene faults (or mutations) within a cell are acquired after b ...
... this disease. This susceptibility is often a single altered gene. It is true to say that all cancer cells contain some genes that have malfunctioned, this allows the cells to behave in an abnormal way and grow as a cancer, yet most of the gene faults (or mutations) within a cell are acquired after b ...
Gene Section MRC1 (mannose receptor, C type 1)
... a type I transmembrane receptor since the protein COOH terminus is located on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. MRC1 is a membrane receptor containing: - a ricin b-type lectin domain (RICIN), that is a cysteinrich (CysR) domain located at the extreme N-terminus and that can bind specific sulphat ...
... a type I transmembrane receptor since the protein COOH terminus is located on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. MRC1 is a membrane receptor containing: - a ricin b-type lectin domain (RICIN), that is a cysteinrich (CysR) domain located at the extreme N-terminus and that can bind specific sulphat ...
Genetic Testing and Japanese Black Cattle
... growth of cattle by controlling energy flow in the body. GH has been shown to have an impact on fat accumulation in certain tissue of Japanese Black cattle. The GH gene resides on chromosome 19 of cattle. The GH gene consists of a DNA strand that has 5 segments (the segment unit is called exon) whic ...
... growth of cattle by controlling energy flow in the body. GH has been shown to have an impact on fat accumulation in certain tissue of Japanese Black cattle. The GH gene resides on chromosome 19 of cattle. The GH gene consists of a DNA strand that has 5 segments (the segment unit is called exon) whic ...
Slides
... vice versa §Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)- point mutations that occur in a population with some frequency §Classification if in coding portion: §Silent mutations have no discernable effect §Missense mutations have an observable effect §Nonsense mutations changes a codon for an amino acid to ...
... vice versa §Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)- point mutations that occur in a population with some frequency §Classification if in coding portion: §Silent mutations have no discernable effect §Missense mutations have an observable effect §Nonsense mutations changes a codon for an amino acid to ...
Presentation
... gene with an inactive gene, and determine results in a living organism. The normal allele of a gene is inserted into a plasmid; restriction enzymes are used to insert a reporter gene in the middle of the normal gene. ...
... gene with an inactive gene, and determine results in a living organism. The normal allele of a gene is inserted into a plasmid; restriction enzymes are used to insert a reporter gene in the middle of the normal gene. ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 8e
... gene with an inactive gene, and determine results in a living organism. The normal allele of a gene is inserted into a plasmid; restriction enzymes are used to insert a reporter gene in the middle of the normal gene. ...
... gene with an inactive gene, and determine results in a living organism. The normal allele of a gene is inserted into a plasmid; restriction enzymes are used to insert a reporter gene in the middle of the normal gene. ...
PROTEIN METABOLISM
... wastes. If nitrogen excretion is greater than the nitrogen content of the diet, the person is said to be in negative nitrogen balance. This is usually interpreted as an indication of tissue destruction. ...
... wastes. If nitrogen excretion is greater than the nitrogen content of the diet, the person is said to be in negative nitrogen balance. This is usually interpreted as an indication of tissue destruction. ...
Modified Mendelian Ratios II
... Assign tall to any plant with both A-B- and dwarf to any plant that is homozygous recessive for either or both the recessive alleles. ...
... Assign tall to any plant with both A-B- and dwarf to any plant that is homozygous recessive for either or both the recessive alleles. ...
Chapter 9
... • Synthesis of protein from amino acids. The linkage between amino acids called peptide bond. Elongation of chain from tripeptide, polypeptide. • All naturally occuring amino acid are in the L-form. which is the biologically active form. (但合成大多為L與D form的混合物). ...
... • Synthesis of protein from amino acids. The linkage between amino acids called peptide bond. Elongation of chain from tripeptide, polypeptide. • All naturally occuring amino acid are in the L-form. which is the biologically active form. (但合成大多為L與D form的混合物). ...
Amino Acid and Nucleobase Synthesis in Meteoritic Parent Bodies
... Implications for general evolution of genetic code? 1. Thermodynamics: provides natural frequency of amino acids for first code. 2. Earliest code used smaller repertoire of amino acids – each with larger no. of codons – stripped down version of ours. - Lowest cost amino acids (eg. G) found in most ...
... Implications for general evolution of genetic code? 1. Thermodynamics: provides natural frequency of amino acids for first code. 2. Earliest code used smaller repertoire of amino acids – each with larger no. of codons – stripped down version of ours. - Lowest cost amino acids (eg. G) found in most ...
Product Datasheets
... This System eliminates restriction enzyme digestion, dephosphorylation, blunting sticky ends, nick ligation, terminal adenylation and intermediate vectors from PCR product cloning. This System takes only 20-30 minutes to fuse DNA fragments to one DNA molecule. This System is recommended for the foll ...
... This System eliminates restriction enzyme digestion, dephosphorylation, blunting sticky ends, nick ligation, terminal adenylation and intermediate vectors from PCR product cloning. This System takes only 20-30 minutes to fuse DNA fragments to one DNA molecule. This System is recommended for the foll ...
Gene Section CDX2 (caudal-related homeobox 2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Abnormal protein Fusion of ETV6 exon 2 to CDX2 exon 2. The predicted protein contains the N-terminal region of ETV6 38 fused to the entire homeobox of CDX2. The single case described that harbours this fusion also expressed normal CDX2, which is not normally expressed in haemopoietic cells. ...
... Abnormal protein Fusion of ETV6 exon 2 to CDX2 exon 2. The predicted protein contains the N-terminal region of ETV6 38 fused to the entire homeobox of CDX2. The single case described that harbours this fusion also expressed normal CDX2, which is not normally expressed in haemopoietic cells. ...
Document
... in a diploid cell, forming a haploid gamete. The phases are as follows: Meiosis I, which is preceded by a replication of chromosomes. Its stages are Prophase I: Each replicated chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome forming a tetrad. During tetrad formation, alleles can be e ...
... in a diploid cell, forming a haploid gamete. The phases are as follows: Meiosis I, which is preceded by a replication of chromosomes. Its stages are Prophase I: Each replicated chromosome pairs with its corresponding homologous chromosome forming a tetrad. During tetrad formation, alleles can be e ...
mini- review - Microbiology
... The separation of sex and reproduction in bacteria and most other microbes makes their evolutionary adaptation primarily dependent on mutation as the ‘ raw material ’. At first sight, producing as many mutations as possible may thus seem a profitable strategy for microbes, because it would allow the ...
... The separation of sex and reproduction in bacteria and most other microbes makes their evolutionary adaptation primarily dependent on mutation as the ‘ raw material ’. At first sight, producing as many mutations as possible may thus seem a profitable strategy for microbes, because it would allow the ...
CHEMCO M M
... proteins were produced. Clones larger than 2.5 kb proved to be unstable.14,15 The same behavior was observed for native silkworm silk genes. An explanation for this phenomenon may lie in the highly repetitive nature of these sequences, which ...
... proteins were produced. Clones larger than 2.5 kb proved to be unstable.14,15 The same behavior was observed for native silkworm silk genes. An explanation for this phenomenon may lie in the highly repetitive nature of these sequences, which ...
Text S4.
... line in Fig. 2C). This prediction appears to be robust to variations of the parameters in the model, including gene length (200 to 600 codons), baseline elongation rate (15 to 30 codons per second), degradation rate (5104 to 1.5105 amino acids per 60 seconds), mean protein molecules produced per m ...
... line in Fig. 2C). This prediction appears to be robust to variations of the parameters in the model, including gene length (200 to 600 codons), baseline elongation rate (15 to 30 codons per second), degradation rate (5104 to 1.5105 amino acids per 60 seconds), mean protein molecules produced per m ...
Evolution
... access via the Internet. Why is this information important? Being able to identify the precise location and sequence of human genes will allow us to better understand genetic diseases. In addition, learning about the sequence of genes in other species helps us understand evolutionary relationships a ...
... access via the Internet. Why is this information important? Being able to identify the precise location and sequence of human genes will allow us to better understand genetic diseases. In addition, learning about the sequence of genes in other species helps us understand evolutionary relationships a ...
Analysis of mutant strains
... Gene names that begin with capital letters refer to dominant alleles, while gene names beginning with lower case letters refer to recessive alleles. (One oddity about budding yeast: S. cerevisiae gene names are unique in that dominant alleles are described with three capital letters. In many other e ...
... Gene names that begin with capital letters refer to dominant alleles, while gene names beginning with lower case letters refer to recessive alleles. (One oddity about budding yeast: S. cerevisiae gene names are unique in that dominant alleles are described with three capital letters. In many other e ...
doc Dr. Pause Notes
... warm, glucose-filled grape juice yeast will rapidly divide and make ethanol o In yeast and bacteria cell cycle progresses rapidly (new cell every 20min) Cell cycle is highly conserved: ALL cells go through it (same basic principle) Once development is over, cell cycle is arrested and cells sit in ...
... warm, glucose-filled grape juice yeast will rapidly divide and make ethanol o In yeast and bacteria cell cycle progresses rapidly (new cell every 20min) Cell cycle is highly conserved: ALL cells go through it (same basic principle) Once development is over, cell cycle is arrested and cells sit in ...
Homologous Recombination (Introductory Concepts
... organism. Bacteria are in general haploid, containing one copy of the chromosome (for practical ...
... organism. Bacteria are in general haploid, containing one copy of the chromosome (for practical ...
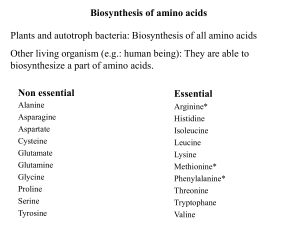
Biosynthesis of amino acids
... Nucleosides are derivatives of purines and pyrimidines that have a sugar linked to a ring nitrogen. Numerals with a prime (eg, 2′ or 3′) distinguish atoms of the sugar from those of the heterocyclic base. ...
... Nucleosides are derivatives of purines and pyrimidines that have a sugar linked to a ring nitrogen. Numerals with a prime (eg, 2′ or 3′) distinguish atoms of the sugar from those of the heterocyclic base. ...
Unit Number- 7611846
... evidence that they have met all the performance criteria for each outcome within the range specified. Details of these requirements are given for each outcome. The assessment instruments used should follow the general guidance offered by the SQA assessment model and an integrative approach to assess ...
... evidence that they have met all the performance criteria for each outcome within the range specified. Details of these requirements are given for each outcome. The assessment instruments used should follow the general guidance offered by the SQA assessment model and an integrative approach to assess ...
Central Dogma at the Single-Molecule Level in Living Cells
... limit theorem. Bacterial cell-cycle time, when limited by chromosome replication, is not stochastic for this reason13. The experiments in Fig. 1b, c were conducted under non-equilibrium steady-state conditions, in which the substrate concentration (thermodynamic driving force) does not change while ...
... limit theorem. Bacterial cell-cycle time, when limited by chromosome replication, is not stochastic for this reason13. The experiments in Fig. 1b, c were conducted under non-equilibrium steady-state conditions, in which the substrate concentration (thermodynamic driving force) does not change while ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.