Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Results from 2 or more polypeptide chains forming 1 macromolecule Collagen – fibrous protein made of 3 polypeptides coiled like a rope Hemoglobin – globular protein made of four polypeptides (2 alpha & 2 beta chains) Sickle-Cell Disease o Inherited blood disorder o Single amino acid change i ...
... Results from 2 or more polypeptide chains forming 1 macromolecule Collagen – fibrous protein made of 3 polypeptides coiled like a rope Hemoglobin – globular protein made of four polypeptides (2 alpha & 2 beta chains) Sickle-Cell Disease o Inherited blood disorder o Single amino acid change i ...
Information- Part 1 Study Guide
... Mutations are the primary source of _________________________________________. Changes in genotype may affect phenotypes that are subject to natural selection. Genetic changes that enhance survival and reproduction can be selected by environmental conditions. Be familiar with these examples: ...
... Mutations are the primary source of _________________________________________. Changes in genotype may affect phenotypes that are subject to natural selection. Genetic changes that enhance survival and reproduction can be selected by environmental conditions. Be familiar with these examples: ...
Ch. 12 Notes
... Mutations in the Hox genes can cause a fruit fly to develop a leg where its antennae should be. ...
... Mutations in the Hox genes can cause a fruit fly to develop a leg where its antennae should be. ...
Evolution
... • The more similar the DNA, the more closely related the species are. • Ex. The DNA of Gorillas and Humans are ~92% similar whereas the DNA of any two humans is 99.9% similar. ...
... • The more similar the DNA, the more closely related the species are. • Ex. The DNA of Gorillas and Humans are ~92% similar whereas the DNA of any two humans is 99.9% similar. ...
Key Concepts - O. Henry Science
... “differences”). For example, some humans have blue eyes while other humans have green, brown, or grey eyes. And, some humans are tall, while others are short. Each trait is controlled by at least one __________________ I’m not sure about you, but all of our genes are coded in our __________________ ...
... “differences”). For example, some humans have blue eyes while other humans have green, brown, or grey eyes. And, some humans are tall, while others are short. Each trait is controlled by at least one __________________ I’m not sure about you, but all of our genes are coded in our __________________ ...
Jeet Guram
... mutants that conferred ampicillin resistance after each successive round of mutagenesis; cells containing mutants not conferring resistance died. The number of cumulative mutations was also measured. Two mathematical models were established to quantify the effects of the mutations on fitness. The fi ...
... mutants that conferred ampicillin resistance after each successive round of mutagenesis; cells containing mutants not conferring resistance died. The number of cumulative mutations was also measured. Two mathematical models were established to quantify the effects of the mutations on fitness. The fi ...
PPT: Mitosis, Meiosis, DNA, PS
... • Gametes = haploid = with only one set of chromosomes • For humans: – haploid number is 23 (n = 23) – Each set of 23 consists of 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome ...
... • Gametes = haploid = with only one set of chromosomes • For humans: – haploid number is 23 (n = 23) – Each set of 23 consists of 22 autosomes and one sex chromosome ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code. Codons are three-nucleotide sequences that specify which amino acids (61 codons) will be added to the growing polypeptide. Codons can also signal when translation terminates (3 codons). The codon for methionine (AUG) acts as a ...
... The flow of information from gene to protein is based on a triplet code. Codons are three-nucleotide sequences that specify which amino acids (61 codons) will be added to the growing polypeptide. Codons can also signal when translation terminates (3 codons). The codon for methionine (AUG) acts as a ...
Topic 3 The Chemistry of Life - wfs
... 2. Helicase is the enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds to allow the unwinding. 3. The exposed bases of each strand are then paired with an available nucleotide by complementary base pairing. The result is two strands where only one was first present. 4. DNA polymerase is an enzyme that allows the ...
... 2. Helicase is the enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds to allow the unwinding. 3. The exposed bases of each strand are then paired with an available nucleotide by complementary base pairing. The result is two strands where only one was first present. 4. DNA polymerase is an enzyme that allows the ...
File
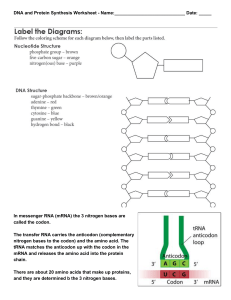
... In messenger RNA (mRNA) the 3 nitrogen bases are called the codon. The transfer RNA carries the anticodon (complementary nitrogen bases to the codon) and the amino acid. The tRNA matches the anticodon up with the codon in the mRNA and releases the amino acid into the protein chain. There are about 2 ...
... In messenger RNA (mRNA) the 3 nitrogen bases are called the codon. The transfer RNA carries the anticodon (complementary nitrogen bases to the codon) and the amino acid. The tRNA matches the anticodon up with the codon in the mRNA and releases the amino acid into the protein chain. There are about 2 ...
BSC 219
... initiation complex that recruits RNA Polymerase to the promoter region. The DNA sequences and some proteins in the complex are variable between promoters. Prokaryotic initiation relies only upon the relative strength of the promoter sequences at recruiting Sigma factor and RNA Polymerase to the prom ...
... initiation complex that recruits RNA Polymerase to the promoter region. The DNA sequences and some proteins in the complex are variable between promoters. Prokaryotic initiation relies only upon the relative strength of the promoter sequences at recruiting Sigma factor and RNA Polymerase to the prom ...
Unit 2 DNA Outline - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... out protein synthesis are separated from one another. Review of Gene Expression Genes are made up of DNA in the nucleus that contains a triplet code. Gene expression involves transcription and translation. 25.4 Control of Gene Expression Differences in gene expression account for the specialization ...
... out protein synthesis are separated from one another. Review of Gene Expression Genes are made up of DNA in the nucleus that contains a triplet code. Gene expression involves transcription and translation. 25.4 Control of Gene Expression Differences in gene expression account for the specialization ...
Genetics BOE approved April 15, 2010 Learner Objective: Cells go
... Learner Objective: Cells go through a natural progression of events to produce new cells. A. Cellular organelles work together to perform a specific function. B. The cell cycle regulates cells during development, growth, and repair. C. Errors in the cell cycle can lead to cancer. D. All cells in the ...
... Learner Objective: Cells go through a natural progression of events to produce new cells. A. Cellular organelles work together to perform a specific function. B. The cell cycle regulates cells during development, growth, and repair. C. Errors in the cell cycle can lead to cancer. D. All cells in the ...
Genes
... heredity. Each gene is a segment of double-stranded DNA that holds the recipe for making a specific molecule, usually a protein. ...
... heredity. Each gene is a segment of double-stranded DNA that holds the recipe for making a specific molecule, usually a protein. ...
8.2: More Evidence for Evolution: Anatomy, Embryology, and DNA
... Analogous Structures: structure of organisms that do not have a common evolutionary origin but perform similar function. Environmental factors pressure for the selection of structures to perform the same functions in different species. ...
... Analogous Structures: structure of organisms that do not have a common evolutionary origin but perform similar function. Environmental factors pressure for the selection of structures to perform the same functions in different species. ...
Document
... • Mutations in same gene usually result in mutant phenotype when present together. • Mutations in different genes complement. • Dominance comes in several types. • Most characters are determined by sets of genes that interact with the environment. • Modified genetic ratios reveal gene interactions, ...
... • Mutations in same gene usually result in mutant phenotype when present together. • Mutations in different genes complement. • Dominance comes in several types. • Most characters are determined by sets of genes that interact with the environment. • Modified genetic ratios reveal gene interactions, ...
Problem Set 3 Solution
... c) The fidelity of transcription is far less compared to replication. Explain why is this so. Also explain why the cell can tolerate the errors in transcription much better than the errors in replication. DNA polymerase has 3’-> 5’ exonuclease activity that proofreads and repairs any mismatched base ...
... c) The fidelity of transcription is far less compared to replication. Explain why is this so. Also explain why the cell can tolerate the errors in transcription much better than the errors in replication. DNA polymerase has 3’-> 5’ exonuclease activity that proofreads and repairs any mismatched base ...
Basic Concepts of Cancer
... surveillance by cytotoxic T cells should remove transformed cells • Tumor associated antigens presented by MHC 1 molecules • Decrease in thymus activity with age means more cancers in older individuals ...
... surveillance by cytotoxic T cells should remove transformed cells • Tumor associated antigens presented by MHC 1 molecules • Decrease in thymus activity with age means more cancers in older individuals ...
Your genes
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic ...
... Date _______________________________ Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic ...
Genetics 314 – Spring 2006
... a) You check one lab and find that several of their chemicals are listed as mutagens, some are listed as causing base change mutations and other chemicals are listed as causing frameshift mutations. What is the difference between the two mutagens and which one would have the greater potential to cau ...
... a) You check one lab and find that several of their chemicals are listed as mutagens, some are listed as causing base change mutations and other chemicals are listed as causing frameshift mutations. What is the difference between the two mutagens and which one would have the greater potential to cau ...
GENETICS
... • If the vital organs of the human body can be cloned, they can serve as backup systems for human beings. Cloning body parts can serve as a lifesaver. When a body organ such as a kidney or heart fails to function, it may be possible to replace it with the cloned body organ. • Cloning in human beings ...
... • If the vital organs of the human body can be cloned, they can serve as backup systems for human beings. Cloning body parts can serve as a lifesaver. When a body organ such as a kidney or heart fails to function, it may be possible to replace it with the cloned body organ. • Cloning in human beings ...
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... Adenine, Thymine, Cytocine, Guanine ...
... Adenine, Thymine, Cytocine, Guanine ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.