Lecture 7
... Moves from Chromosome 8 to Chromosome 2, 14 or 22. Results in overexpression of normal protein ...
... Moves from Chromosome 8 to Chromosome 2, 14 or 22. Results in overexpression of normal protein ...
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer
... If you have a CDH1 mutation, you have an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer. However, not everyone who has a gene mutation will develop cancer. ...
... If you have a CDH1 mutation, you have an increased risk of developing certain types of cancer. However, not everyone who has a gene mutation will develop cancer. ...
Support for Evolution
... sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves flowering, pollination, and production of fruit that has seeds within. This species is also capable of asexual reproduction. Briefly describe some of the different ways plants can reproduce ...
... sexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves flowering, pollination, and production of fruit that has seeds within. This species is also capable of asexual reproduction. Briefly describe some of the different ways plants can reproduce ...
DNA RNA Proteins - Aurora City Schools
... P site tRNA, moves to the E site and leaves the ribosome. The ribosome then translocates (moves) the tRNA in the A site, with its attached polypeptide, to the P site. Codon and anticodon remain bonded, and the mRNA and tRNA move as a unit Movement brings into the A site the next mRNA codon t ...
... P site tRNA, moves to the E site and leaves the ribosome. The ribosome then translocates (moves) the tRNA in the A site, with its attached polypeptide, to the P site. Codon and anticodon remain bonded, and the mRNA and tRNA move as a unit Movement brings into the A site the next mRNA codon t ...
Chapter 17- Transcription and Translation
... C) What is an activator protein (specific transcription factor)? D) What region of the DNA do the activator proteins bind to? E) How is the binding of transcription factors and activator proteins impacted by the how tightly DNA is bound to histones (level of DNA packing)? ...
... C) What is an activator protein (specific transcription factor)? D) What region of the DNA do the activator proteins bind to? E) How is the binding of transcription factors and activator proteins impacted by the how tightly DNA is bound to histones (level of DNA packing)? ...
Mamm_Genome yTrx1-2 + refs
... imperfect polyA tail is present exactly 3´ after the point at which homology with Trx1 cDNA ceases. Third, the sequence Trx1-2 shows multiple nucleotide changes when compared with Trx1 cDNA. The most striking change affects the conserved active site which is mutated and the translation would then g ...
... imperfect polyA tail is present exactly 3´ after the point at which homology with Trx1 cDNA ceases. Third, the sequence Trx1-2 shows multiple nucleotide changes when compared with Trx1 cDNA. The most striking change affects the conserved active site which is mutated and the translation would then g ...
Notes Genetic Chapter 12 Complete
... - Sickle cell anemia: a genetic disease caused by a point mutation (a single nucleotide change) making codominant alleles that cause red blood cells to be bent and twisted making it hard for them to move through blood vessel, causing pain and even death. - Alleles; HA = normal cells allele, HS = sic ...
... - Sickle cell anemia: a genetic disease caused by a point mutation (a single nucleotide change) making codominant alleles that cause red blood cells to be bent and twisted making it hard for them to move through blood vessel, causing pain and even death. - Alleles; HA = normal cells allele, HS = sic ...
RT-PCR lab
... DNA unwind to allow synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from one strand (the coding strand) • The mRNA moves out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm • mRNA binds to Ribosomes to code for a protein- protein made (translation) • Protein carries out intent of gene (red hair protein = hair gene) ...
... DNA unwind to allow synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) from one strand (the coding strand) • The mRNA moves out of the nucleus to the cytoplasm • mRNA binds to Ribosomes to code for a protein- protein made (translation) • Protein carries out intent of gene (red hair protein = hair gene) ...
Chapter 21 Artificial Selection Artificial selection is the deliberate
... Each gene codes for a specific protein (or polypeptide) and genetic engineering enables a gene that codes for some useful protein in one organism (eg. human) to be transferred to another organism (eg. bacterium). ...
... Each gene codes for a specific protein (or polypeptide) and genetic engineering enables a gene that codes for some useful protein in one organism (eg. human) to be transferred to another organism (eg. bacterium). ...
Achondroplasia - Bellarmine University
... • Appears that the vast majority of FGFR3 mutations arise as new mutations during spermatogenesis before Meiosis I ...
... • Appears that the vast majority of FGFR3 mutations arise as new mutations during spermatogenesis before Meiosis I ...
docx Significance of discoveries in Genetics and DNA
... are called nucleotide bases with the names cytosine(C), thymine (T), guanine (G) and adenine (A). According to genetic scientists, each gene is compared to an instruction manual for making one protein (Calladine, 2004). According to biologists, each protein is a sequence of amino acids. It is throug ...
... are called nucleotide bases with the names cytosine(C), thymine (T), guanine (G) and adenine (A). According to genetic scientists, each gene is compared to an instruction manual for making one protein (Calladine, 2004). According to biologists, each protein is a sequence of amino acids. It is throug ...
mRNA
... • Frameshift: Adding or removing 1 or 2 nucleotides results in changes the reading frame from that point on. • Nonsense: Changing an amino acid codon to a stop codon results in truncated proteins • Missense: Changing an amino acid codon to one encoding a different amino acid - effect depends on type ...
... • Frameshift: Adding or removing 1 or 2 nucleotides results in changes the reading frame from that point on. • Nonsense: Changing an amino acid codon to a stop codon results in truncated proteins • Missense: Changing an amino acid codon to one encoding a different amino acid - effect depends on type ...
CB-Human Genetics
... genes on chromosomes #1-22 where both alleles are recessive for the trait 1. Albinism – lack of pigment in hair, skin, and eyes 2. Cystic fibrosis – mutation on chromosome 7 that causes excess mucus in lungs, digestive tract and liver, and increased infection; patients die by drowning on own mucus. ...
... genes on chromosomes #1-22 where both alleles are recessive for the trait 1. Albinism – lack of pigment in hair, skin, and eyes 2. Cystic fibrosis – mutation on chromosome 7 that causes excess mucus in lungs, digestive tract and liver, and increased infection; patients die by drowning on own mucus. ...
From Genes to Proteins (11
... The _order____ of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the __type amino acids______ in a protein. There are _64___ possible codons but only __20__ Possible Amino Acids Start codon = _AUG (Methionine or Met)___ Stop codons = _UAA UAG UGA_ ...
... The _order____ of the nitrogenous bases in the mRNA determines the type and order of the __type amino acids______ in a protein. There are _64___ possible codons but only __20__ Possible Amino Acids Start codon = _AUG (Methionine or Met)___ Stop codons = _UAA UAG UGA_ ...
Protein Synthesis Poster
... The piece of DNA which codes for a protein is rewritten – transcribed into a new molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This takes places in the nucleus of the cell. DNA uncoils and unzips. The exposed DNA bases are matched up with RNA bases in the nucleus to form mRNA. ...
... The piece of DNA which codes for a protein is rewritten – transcribed into a new molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This takes places in the nucleus of the cell. DNA uncoils and unzips. The exposed DNA bases are matched up with RNA bases in the nucleus to form mRNA. ...
Revision - Mr C Biology
... The piece of DNA which codes for a protein is rewritten – transcribed into a new molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This takes places in the nucleus of the cell. DNA uncoils and unzips. The exposed DNA bases are matched up with RNA bases in the nucleus to form mRNA. ...
... The piece of DNA which codes for a protein is rewritten – transcribed into a new molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This takes places in the nucleus of the cell. DNA uncoils and unzips. The exposed DNA bases are matched up with RNA bases in the nucleus to form mRNA. ...
Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer
... • The agent of such changes can be random spontaneous mutations or environmental influences such as chemical carcinogens or physical mutagens. • Cancer-causing genes, oncogenes, were initially discovered in retroviruses, but close counterparts, proto-oncogenes were found in other organisms. Copyrigh ...
... • The agent of such changes can be random spontaneous mutations or environmental influences such as chemical carcinogens or physical mutagens. • Cancer-causing genes, oncogenes, were initially discovered in retroviruses, but close counterparts, proto-oncogenes were found in other organisms. Copyrigh ...
S1 Genetics
... Why do changes of one amino acid for another destroy the function of a protein? 1. If the protein is an enzyme, the amino acid that carries out the reaction may be changed 2. The altered amino acid may have been involved in pairing with another amino acid to maintain the shape of the protein. ...
... Why do changes of one amino acid for another destroy the function of a protein? 1. If the protein is an enzyme, the amino acid that carries out the reaction may be changed 2. The altered amino acid may have been involved in pairing with another amino acid to maintain the shape of the protein. ...
The Childhood-Onset Epilepsy 40 Genes (3)
... • Mendelian disorders, in which a single major locus can account for segregation of the disease trait • Non-mendelian or 'complex' diseases, in which the pattern of familial clustering can be accounted for by the interaction of the maternal inheritance pattern of mitochondrial DNA • Chromosomal diso ...
... • Mendelian disorders, in which a single major locus can account for segregation of the disease trait • Non-mendelian or 'complex' diseases, in which the pattern of familial clustering can be accounted for by the interaction of the maternal inheritance pattern of mitochondrial DNA • Chromosomal diso ...
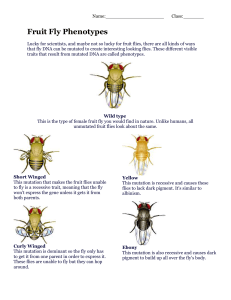
Fruit Fly Phenotypes
... Lucky for scientists, and maybe not so lucky for fruit flies, there are all kinds of ways that fly DNA can be mutated to create interesting looking flies. These different visible traits that result from mutated DNA are called phenotypes. ...
... Lucky for scientists, and maybe not so lucky for fruit flies, there are all kinds of ways that fly DNA can be mutated to create interesting looking flies. These different visible traits that result from mutated DNA are called phenotypes. ...
Hello Ladies, Welcome to AP Biology! I am excited to help guide you la
... of tRNA (transfer RNA) deliver the amino acids needed to make the protein, which the mRNA (messenger RNA) codes for. ...
... of tRNA (transfer RNA) deliver the amino acids needed to make the protein, which the mRNA (messenger RNA) codes for. ...
Cell Transformation
... Quick Review Different enzymes can be used to cut, copy, and move segments of DNA. Characteristics produced by the segments of DNA may be expressed when these segments are inserted into new organisms, such as bacteria. Inserting, deleting, or substituting DNA segments can alter genes. (mutations) A ...
... Quick Review Different enzymes can be used to cut, copy, and move segments of DNA. Characteristics produced by the segments of DNA may be expressed when these segments are inserted into new organisms, such as bacteria. Inserting, deleting, or substituting DNA segments can alter genes. (mutations) A ...
Mitosis, Meiosis, DNA Notes
... Protein synthesis – formation of proteins using genetic code from DNA and carried out by RNA. A. Translation – process of forming proteins from mRNA. 1. mRNA leaves nucleus (nuclear pores) and goes to ribosomes. 2. mRNA is grouped into 3 consecutive bases called codons. a) Each codon corresponds wit ...
... Protein synthesis – formation of proteins using genetic code from DNA and carried out by RNA. A. Translation – process of forming proteins from mRNA. 1. mRNA leaves nucleus (nuclear pores) and goes to ribosomes. 2. mRNA is grouped into 3 consecutive bases called codons. a) Each codon corresponds wit ...
Name: How the Gene for Sickle Cell Hemoglobin Results in Sickle
... Each complete hemoglobin protein has more than 100 amino acids. Sickle cell hemoglobin and normal hemoglobin differ in only a single amino acid. This difference in a single amino acid results in the very different properties of sickle cell hemoglobin, compared to normal hemoglobin. If a person inher ...
... Each complete hemoglobin protein has more than 100 amino acids. Sickle cell hemoglobin and normal hemoglobin differ in only a single amino acid. This difference in a single amino acid results in the very different properties of sickle cell hemoglobin, compared to normal hemoglobin. If a person inher ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.