Conservation Laws
... Consider the collision of two balls on the billiards table. The collision occurs in an isolated system as long as friction is small enough that its influence upon the momentum of the billiard balls can be neglected. If so, then the only unbalanced forces acting upon the two balls are the contact for ...
... Consider the collision of two balls on the billiards table. The collision occurs in an isolated system as long as friction is small enough that its influence upon the momentum of the billiard balls can be neglected. If so, then the only unbalanced forces acting upon the two balls are the contact for ...
Document
... Recap: 2 magnetic poles, N and S like poles repel, opposite poles attract both poles attract iron (ferromagnetic material) Two poles not separable Compass: a bar magnet Its “north” pole (conventionally defined) points towards the northern direction N ...
... Recap: 2 magnetic poles, N and S like poles repel, opposite poles attract both poles attract iron (ferromagnetic material) Two poles not separable Compass: a bar magnet Its “north” pole (conventionally defined) points towards the northern direction N ...
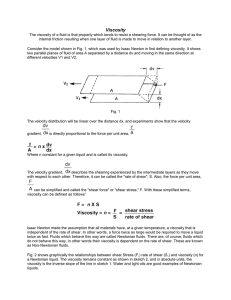
Introduction to Viscosity
... Fig. 3 shows graphically the three most common types of Non--Newtonian liquids. Group A shows a decreasing viscosity with an increasing rate of shear. This is known as a pseudo-plastic material. Examples of this type are grease, molasses, paint, soap, starch, and most emulsions. They present no seri ...
... Fig. 3 shows graphically the three most common types of Non--Newtonian liquids. Group A shows a decreasing viscosity with an increasing rate of shear. This is known as a pseudo-plastic material. Examples of this type are grease, molasses, paint, soap, starch, and most emulsions. They present no seri ...
Magnetic field lines
... A positive ion is released near the center and moves in a semicircular path arrives back at the gap in a time interval T/2, where T is the time interval needed to make one complete trip around the two dees The potential difference is adjusted so that the polarity of the dees is reversed in the same ...
... A positive ion is released near the center and moves in a semicircular path arrives back at the gap in a time interval T/2, where T is the time interval needed to make one complete trip around the two dees The potential difference is adjusted so that the polarity of the dees is reversed in the same ...
CHAPTER 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
... plastic is uniform and has the shape of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure at the right. The axes A and B are two rotation axes that are perpendicular to the plane of the triangle. If the triangle rotates about each axis with the same angular speed ω, the rotational kinetic energy of th ...
... plastic is uniform and has the shape of an equilateral triangle, as shown in the figure at the right. The axes A and B are two rotation axes that are perpendicular to the plane of the triangle. If the triangle rotates about each axis with the same angular speed ω, the rotational kinetic energy of th ...
Why do things move?
... or gas) that is stationary… which causes: - Dust to build up on moving objects such as fan blades, car windows etc! – where least expected! • Viscosity of different fluids varies significantly, e.g. honey, thick oils have much larger viscosities than water. high viscosity ...
... or gas) that is stationary… which causes: - Dust to build up on moving objects such as fan blades, car windows etc! – where least expected! • Viscosity of different fluids varies significantly, e.g. honey, thick oils have much larger viscosities than water. high viscosity ...
Parallelogram law of vector addition : Properties of Scalar Product
... If a body is placed on an inclined plane and if its angle of inclination is gradually increased, then at some angle of inclination θ the body will just on the point to slide down. The angle is called angle of repose (θ). ...
... If a body is placed on an inclined plane and if its angle of inclination is gradually increased, then at some angle of inclination θ the body will just on the point to slide down. The angle is called angle of repose (θ). ...