Momentum
... This is true because the impulse=force • time. Knowing two of these three quantities allows us to compute the third quantity. And finally, observe that knowing any two of the last three columns allows us to compute the remaining column. This is true since momentum change = mass • velocity change. Th ...
... This is true because the impulse=force • time. Knowing two of these three quantities allows us to compute the third quantity. And finally, observe that knowing any two of the last three columns allows us to compute the remaining column. This is true since momentum change = mass • velocity change. Th ...
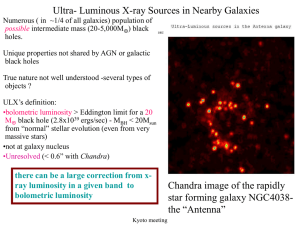
ULXs: General Properties and Variability - X
... •x-ray spectra are often not like AGN or normal galactic black holes • state transitions are often in the opposite sense from galactic objects • luminosities can reach 1000 Ledd for 1 solar mass object •evidence against beaming (QPOs, broad Fe Lines, eclipses) •At least one object has a break in the ...
... •x-ray spectra are often not like AGN or normal galactic black holes • state transitions are often in the opposite sense from galactic objects • luminosities can reach 1000 Ledd for 1 solar mass object •evidence against beaming (QPOs, broad Fe Lines, eclipses) •At least one object has a break in the ...
CHAPTER 7: Linear Momentum Answers to Questions
... The force stopping the wind is exerted by the person, so the force on the person would be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force stopping the wind. Calculate the force from Eq. 7-2, in magnitude only. ...
... The force stopping the wind is exerted by the person, so the force on the person would be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force stopping the wind. Calculate the force from Eq. 7-2, in magnitude only. ...
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights
... 1. Find the magnitude of the torque produced by a 3.0 N force applied to a door at a perpendicular distance of 0.25 m from the hinge. 2. A simple pendulum consists of a 3.0 kg point mass hanging at the end of a 2.0 m long light string that is connected to a pivot point. a. Calculate the magnitude of ...
... 1. Find the magnitude of the torque produced by a 3.0 N force applied to a door at a perpendicular distance of 0.25 m from the hinge. 2. A simple pendulum consists of a 3.0 kg point mass hanging at the end of a 2.0 m long light string that is connected to a pivot point. a. Calculate the magnitude of ...