White Dwarfs - University of Maryland Astronomy
... No escape means there is no more contact with something that falls in. It increases the hole’s mass, changes its spin or charge, but otherwise loses its ...
... No escape means there is no more contact with something that falls in. It increases the hole’s mass, changes its spin or charge, but otherwise loses its ...
Newton's Third Law - Fulton County Schools
... If an object weighs 397 N, what is its mass? 0.02 kg ...
... If an object weighs 397 N, what is its mass? 0.02 kg ...
Lecture 26
... • Very likely started as a stellar-mass black hole and then grew via acretion of other material (stars, gas, and other black holes!) • Some objects just pass directly into the event horizon and disappear • Others (especially clouds of gas) will be broken up by tidal gravitational forces and because ...
... • Very likely started as a stellar-mass black hole and then grew via acretion of other material (stars, gas, and other black holes!) • Some objects just pass directly into the event horizon and disappear • Others (especially clouds of gas) will be broken up by tidal gravitational forces and because ...
PHYSICS 111 HOMEWORK SOLUTION #10 April 8, 2013
... A solid sphere is released from height h from the top of an incline making an angle θ with the horizontal. • a)Calculate the speed of the sphere when it reaches the bottom of the incline in the case that it rolls without slipping. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as ...
... A solid sphere is released from height h from the top of an incline making an angle θ with the horizontal. • a)Calculate the speed of the sphere when it reaches the bottom of the incline in the case that it rolls without slipping. (Use any variable or symbol stated above along with the following as ...
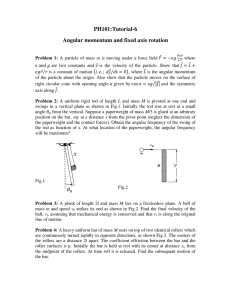
Angular momentum and PH101:Tutorial
... angle from the vertical. Suppose a paperweight of mass M/3 /3 is glued at an arbitrary position on the bar, say at a distance x from the pivot point (neglect the dimension of the paperweight and the contact forces). Obtain the angular frequency of the swing of the rod as function of x. At what lo ...
... angle from the vertical. Suppose a paperweight of mass M/3 /3 is glued at an arbitrary position on the bar, say at a distance x from the pivot point (neglect the dimension of the paperweight and the contact forces). Obtain the angular frequency of the swing of the rod as function of x. At what lo ...
Conservation of Linear Momentum
... that acts between the objects (i.e. internal forces) will not affect momentum conservation, since, by Newton’s third law, this force must affect both equally in magnitude but in opposite directions. The gravitational attraction between the ...
... that acts between the objects (i.e. internal forces) will not affect momentum conservation, since, by Newton’s third law, this force must affect both equally in magnitude but in opposite directions. The gravitational attraction between the ...
Quiz on Chapter 11
... black holes lose mass by emitting photons from their interiors c) black holes lose mass by creating particles outside themselves X d) black holes lose mass by accreting matter from binary companions and then exploding that matter off their surfaces 11-26. A friend takes a ride on a spaceship to a di ...
... black holes lose mass by emitting photons from their interiors c) black holes lose mass by creating particles outside themselves X d) black holes lose mass by accreting matter from binary companions and then exploding that matter off their surfaces 11-26. A friend takes a ride on a spaceship to a di ...
4.3.2 The multipole expansion
... ~j = σ E where σ is the conductivity. ~ = ~0 and σ = 0 is a (perfect) insulator σ = ∞ is a (perfect) conductor where E (for example a vacuum). We shall usually consider good conductors, such as copper ...
... ~j = σ E where σ is the conductivity. ~ = ~0 and σ = 0 is a (perfect) insulator σ = ∞ is a (perfect) conductor where E (for example a vacuum). We shall usually consider good conductors, such as copper ...
Concept Questions
... I cm about the center of mass starts from rest and moves down an incline tilted at an angle from the horizontal. The center of mass of the cylinder has dropped a vertical distance h when it reaches the bottom of the incline. Let g denote the gravitational constant. The coefficient of static fricti ...
... I cm about the center of mass starts from rest and moves down an incline tilted at an angle from the horizontal. The center of mass of the cylinder has dropped a vertical distance h when it reaches the bottom of the incline. Let g denote the gravitational constant. The coefficient of static fricti ...