Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
... The yo-yo is slowed by the tension force T from the string on the axle. ...
... The yo-yo is slowed by the tension force T from the string on the axle. ...
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
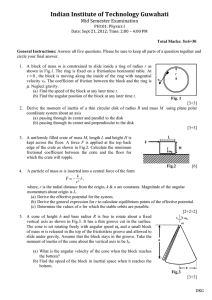
... 5. A cone of height h and base radius R is free to rotate about a fixed vertical axis as shown in Fig.3. It has a thin groove cut in the surface. The cone is set rotating freely with angular speed ω0 and a small block of mass m is released in the top of the frictionless groove and allowed to slide u ...
... 5. A cone of height h and base radius R is free to rotate about a fixed vertical axis as shown in Fig.3. It has a thin groove cut in the surface. The cone is set rotating freely with angular speed ω0 and a small block of mass m is released in the top of the frictionless groove and allowed to slide u ...
rotational kinetic energy
... platform begin to rotate if the man moves from the edge to the centre? (a) 22 rpm ...
... platform begin to rotate if the man moves from the edge to the centre? (a) 22 rpm ...
mechanics 4, m4
... To find that go back to the previous page and click on the connection to OCR. ...
... To find that go back to the previous page and click on the connection to OCR. ...
Document
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object is made up of. The units of mass are kilograms, and because body ‘weight’ is often given in kilograms the two terms are often used to mean the same thing. However, weight is a force that is exerted on the body by gravity. Weight is directly proport ...
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter an object is made up of. The units of mass are kilograms, and because body ‘weight’ is often given in kilograms the two terms are often used to mean the same thing. However, weight is a force that is exerted on the body by gravity. Weight is directly proport ...
Unit 4 - BIOMECHANICS
... vertical force and a forward force, resulting in a vector force somewhere in between. ...
... vertical force and a forward force, resulting in a vector force somewhere in between. ...
Precession

Precession is a change in the orientation of the rotational axis of a rotating body. In an appropriate reference frame it can be defined as a change in the first Euler angle, whereas the third Euler angle defines the rotation itself. In other words, the axis of rotation of a precessing body itself rotates around another axis. A motion in which the second Euler angle changes is called nutation. In physics, there are two types of precession: torque-free and torque-induced.In astronomy, ""precession"" refers to any of several slow changes in an astronomical body's rotational or orbital parameters, and especially to Earth's precession of the equinoxes. (See section Astronomy below.)