A R T I C L E S - Geoscience Research Institute
... present rate of transport of sediment by rivers could fill the oceans 19× in 3500 Ma. Of course, the oceans, which average 3.8 km in depth of water, are not at all full of sediment; and in much of the deep oceanic abyssal plains, sediment thickness averages only a few hundred meters. It would take a ...
... present rate of transport of sediment by rivers could fill the oceans 19× in 3500 Ma. Of course, the oceans, which average 3.8 km in depth of water, are not at all full of sediment; and in much of the deep oceanic abyssal plains, sediment thickness averages only a few hundred meters. It would take a ...
Proterozoic Rocks
... • Deformation and metamorphism ~1.1 Gy • Probably represents the opening and closing of an ocean • Rapikivi granites ~1.4 Gy represent rift ...
... • Deformation and metamorphism ~1.1 Gy • Probably represents the opening and closing of an ocean • Rapikivi granites ~1.4 Gy represent rift ...
The Expanding Pacific
... The Pacific plays an extraordinary role in contemporary geotectonics and this role dates back to Wegener’s theory. Earlier, in the time of the land-bridge theory, the development of all the oceans was considered in the same way, as progressive, and this progressiveness was well-documented by paleont ...
... The Pacific plays an extraordinary role in contemporary geotectonics and this role dates back to Wegener’s theory. Earlier, in the time of the land-bridge theory, the development of all the oceans was considered in the same way, as progressive, and this progressiveness was well-documented by paleont ...
Learning the Age of the Earth. - American Museum of Natural History
... contact between the two rocks, which he found at the now-famous Siccar point. Here in graphic juxtaposition nearly flat-lying beds of the Devonian Old Red Sandstone cover near-vertical beds of Silurian graywacke . These old surfaces of erosion are known as unconformities. This particular one, which ...
... contact between the two rocks, which he found at the now-famous Siccar point. Here in graphic juxtaposition nearly flat-lying beds of the Devonian Old Red Sandstone cover near-vertical beds of Silurian graywacke . These old surfaces of erosion are known as unconformities. This particular one, which ...
049555507X_131304 - ASB
... Laurasia and a southern landmass called Gondwana. As Pangaea broke up, the various continents moved to their present-day locations. The Glossopteris fern, also known as the “Pangaea plant” ...
... Laurasia and a southern landmass called Gondwana. As Pangaea broke up, the various continents moved to their present-day locations. The Glossopteris fern, also known as the “Pangaea plant” ...
Plate tectonics
... Earth’s mantle, then rising hot magma can push up the thin oceanic crust to form a ridge crest. Oceanic crust is typically thinner than continental crust, which is why ridged crests are only formed under water. Mantle rock moves away from the ridge on each side and creates tension, causing the ridge ...
... Earth’s mantle, then rising hot magma can push up the thin oceanic crust to form a ridge crest. Oceanic crust is typically thinner than continental crust, which is why ridged crests are only formed under water. Mantle rock moves away from the ridge on each side and creates tension, causing the ridge ...
Background
... the wind, and eventually deposited. These sediments are usually deposited in water in seas and lakes but they can also accumulate in desert environments. They are often deposited in layers which can be called strata. As the layers accumulate one on top of another they become buried underneath younge ...
... the wind, and eventually deposited. These sediments are usually deposited in water in seas and lakes but they can also accumulate in desert environments. They are often deposited in layers which can be called strata. As the layers accumulate one on top of another they become buried underneath younge ...
Chapter 2
... Positive geoid anomalies of up to 10 – 15 m associated with a number of midocean ridge segments, as well as age-correlated geoid offsets across fracture zones imply that ageing of the ocean lithosphere is accompanied by a decline in potential energy. The geoid anomaly predicted for the cooling half- ...
... Positive geoid anomalies of up to 10 – 15 m associated with a number of midocean ridge segments, as well as age-correlated geoid offsets across fracture zones imply that ageing of the ocean lithosphere is accompanied by a decline in potential energy. The geoid anomaly predicted for the cooling half- ...
Death Valley through time
... and valleys formed as the floors between ranges dropped along normal faults. The big action started in the Death Valley region about 14 million years ago. Be prepared - we're talking big changes! In response to the shifting tectonic plates, strike-slip faults developed in Death Valley. Between two s ...
... and valleys formed as the floors between ranges dropped along normal faults. The big action started in the Death Valley region about 14 million years ago. Be prepared - we're talking big changes! In response to the shifting tectonic plates, strike-slip faults developed in Death Valley. Between two s ...
chapter2
... Laurasia and a southern landmass called Gondwana. As Pangaea broke up, the various continents moved to their present-day locations. The Glossopteris fern, also known as the “Pangaea plant” ...
... Laurasia and a southern landmass called Gondwana. As Pangaea broke up, the various continents moved to their present-day locations. The Glossopteris fern, also known as the “Pangaea plant” ...
chapter9_Proterozoic..
... of granite-gneiss terrains and greenstone belts that were shaped into cratons, Although these same rock associations continued to form during the Proterozoic, they did so at a considerably reduced rate. The change in style of crustal evolution, the Proterozoic was also an important time in the evo ...
... of granite-gneiss terrains and greenstone belts that were shaped into cratons, Although these same rock associations continued to form during the Proterozoic, they did so at a considerably reduced rate. The change in style of crustal evolution, the Proterozoic was also an important time in the evo ...
Earth Geodynamic Hypotheses Updated
... can be detected, and the rotation rate changes in milliseconds per day. This is dependent upon “how the mass distribution of Earth and its atmosphere change from earthquakes and the movement of water and air.” A further explanation of the spin slow down reveals that a day was 18 hours long at 900 Ma ...
... can be detected, and the rotation rate changes in milliseconds per day. This is dependent upon “how the mass distribution of Earth and its atmosphere change from earthquakes and the movement of water and air.” A further explanation of the spin slow down reveals that a day was 18 hours long at 900 Ma ...
global tectonic cycles Temporal relations between mineral deposits
... resultant increase in margin area (Bradley 2008). Smith & McGowan (2007) noted that the Phanerozoic diversity of marine fossils is affected by the supercontinent cycle with marine rocks dominating during rifting phases of supercontinents. Bradley (2011) has recently compiled temporal trends in a num ...
... resultant increase in margin area (Bradley 2008). Smith & McGowan (2007) noted that the Phanerozoic diversity of marine fossils is affected by the supercontinent cycle with marine rocks dominating during rifting phases of supercontinents. Bradley (2011) has recently compiled temporal trends in a num ...
ch13 - earthjay science
... Mesozoic began after the extinction of Paleozoic organisms. Mesozoic rocks contain the remains of organisms that are more advanced than those of Paleozoic, but not as modern as those living today. Two new vertebrate classes appeared: birds and mammals. Mesozoic lasted approximately 186 million years ...
... Mesozoic began after the extinction of Paleozoic organisms. Mesozoic rocks contain the remains of organisms that are more advanced than those of Paleozoic, but not as modern as those living today. Two new vertebrate classes appeared: birds and mammals. Mesozoic lasted approximately 186 million years ...
Geological and Tectonic Background
... denudation, karstification and deposition of bauxites of commercial value. The older Mesozoic formations are unconformably covered by continental and shallow marine Upper Cretaceous formations in the western Transdanubian Range (Bakony). General uplifting took place after the Cretaceous and created t ...
... denudation, karstification and deposition of bauxites of commercial value. The older Mesozoic formations are unconformably covered by continental and shallow marine Upper Cretaceous formations in the western Transdanubian Range (Bakony). General uplifting took place after the Cretaceous and created t ...
Earth`s History Regents Questions
... The 130-million-year-old fossils were found a year ago by farmers in Liaoning Province in northeastern China. After an analysis by Chinese and American researchers, the fossil animal was identified as a dromaeosaur, a small fast-running dinosaur related to velociraptor. The dinosaurs belonged to a g ...
... The 130-million-year-old fossils were found a year ago by farmers in Liaoning Province in northeastern China. After an analysis by Chinese and American researchers, the fossil animal was identified as a dromaeosaur, a small fast-running dinosaur related to velociraptor. The dinosaurs belonged to a g ...
Fields of Science
... The compass direction of a fold or a rock layer exposed at the surface along a fold is called the strike. Synclines are downfolds in rock, whereas anticlines are upfolds in rock. Valley and ridge locations in the Valley and Ridge provinces of the Appalachian Mountains correspond primarily to weather ...
... The compass direction of a fold or a rock layer exposed at the surface along a fold is called the strike. Synclines are downfolds in rock, whereas anticlines are upfolds in rock. Valley and ridge locations in the Valley and Ridge provinces of the Appalachian Mountains correspond primarily to weather ...
Late Mesozoic Geology.
... The "crumpling up" of the west coast, which intensified with the break up of Pangaea, was transmitted from west to east through the Mesozoic. The Sevier Orogeny is notable for low angle thrust faults which formed further inland (e.g. Nevada, Utah, Montana, B.C. and Alberta), as compressional stress ...
... The "crumpling up" of the west coast, which intensified with the break up of Pangaea, was transmitted from west to east through the Mesozoic. The Sevier Orogeny is notable for low angle thrust faults which formed further inland (e.g. Nevada, Utah, Montana, B.C. and Alberta), as compressional stress ...
جمهورية العراق وزارة الصناعة والمعادن ا
... in the Gaَara, Hussainiyat and Amij formations in the Western Desert. They are fluvial deposits associated with sandstones. About 1200 m.t. are proved and mostly used in ceramic industry. Experimental testing proved that these Kaolinitic claystones may be used to produce alumina by the lime- sinter ...
... in the Gaَara, Hussainiyat and Amij formations in the Western Desert. They are fluvial deposits associated with sandstones. About 1200 m.t. are proved and mostly used in ceramic industry. Experimental testing proved that these Kaolinitic claystones may be used to produce alumina by the lime- sinter ...
Chapter 1 – Plate Tectonics
... New magma from deep within the Earth rises along these weak zones and erupts along the crest of the ridge, forming new oceanic crust. ...
... New magma from deep within the Earth rises along these weak zones and erupts along the crest of the ridge, forming new oceanic crust. ...
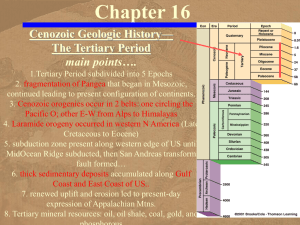
Chapter 16 - Cenozoic - Tertiary
... Roof of the World • During the Early Cretaceous, – India broke away from Gondwana – and began moving north, – and oceanic lithosphere was consumed ...
... Roof of the World • During the Early Cretaceous, – India broke away from Gondwana – and began moving north, – and oceanic lithosphere was consumed ...
Lecture 8
... – Isotopic age dates within continents “cluster” suggesting several periods of “orogeny” – Early continents seem to represent “partial melts” of andesitic volcanics or early sediments. – Most of the present-day volume of continental material had formed by ~2.5 billion yrs. ago. ...
... – Isotopic age dates within continents “cluster” suggesting several periods of “orogeny” – Early continents seem to represent “partial melts” of andesitic volcanics or early sediments. – Most of the present-day volume of continental material had formed by ~2.5 billion yrs. ago. ...
Chapter 1 – Plate Tectonics
... New magma from deep within the Earth rises along these weak zones and erupts along the crest of the ridge, forming new oceanic crust. ...
... New magma from deep within the Earth rises along these weak zones and erupts along the crest of the ridge, forming new oceanic crust. ...
Temporal relations between mineral deposits and global tectonic
... resultant increase in margin area (Bradley 2008). Smith & McGowan (2007) noted that the Phanerozoic diversity of marine fossils is affected by the supercontinent cycle with marine rocks dominating during rifting phases of supercontinents. Bradley (2011) has recently compiled temporal trends in a num ...
... resultant increase in margin area (Bradley 2008). Smith & McGowan (2007) noted that the Phanerozoic diversity of marine fossils is affected by the supercontinent cycle with marine rocks dominating during rifting phases of supercontinents. Bradley (2011) has recently compiled temporal trends in a num ...
Geological history of Earth
The geological history of Earth follows the major events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.Earth was initially molten due to extreme volcanism and frequent collisions with other bodies. Eventually, the outer layer of the planet cooled to form a solid crust when water began accumulating in the atmosphere. The Moon formed soon afterwards, possibly as the result of a Mars-sized object with about 10% of the Earth's mass impacting the planet in a glancing blow. Some of this object's mass merged with the Earth, significantly altering its internal composition, and a portion was ejected into space. Some of the material survived to form an orbiting moon. Outgassing and volcanic activity produced the primordial atmosphere. Condensing water vapor, augmented by ice delivered from comets, produced the oceans.As the surface continually reshaped itself over hundreds of millions of years, continents formed and broke apart. They migrated across the surface, occasionally combining to form a supercontinent. Roughly 750 million years ago, the earliest-known supercontinent Rodinia, began to break apart. The continents later recombined to form Pannotia, 600 to 540 million years ago, then finally Pangaea, which broke apart 180 million years ago.The present pattern of ice ages began about 40 million years ago, then intensified at the end of the Pliocene. The polar regions have since undergone repeated cycles of glaciation and thaw, repeating every 40,000–100,000 years. The last glacial period of the current ice age ended about 10,000 years ago.