View Full Text-PDF
... the phenotype. The genetic code stored in DNA is "interpreted" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape and structure or act as enzymes catalyzing ...
... the phenotype. The genetic code stored in DNA is "interpreted" by gene expression, and the properties of the expression give rise to the organism's phenotype. Such phenotypes are often expressed by the synthesis of proteins that control the organism's shape and structure or act as enzymes catalyzing ...
DNA and Protein Synthesis Review Questions
... 13. Name three differences between DNA and RNA 14. The process where the information from DNA is copied to mRNA is __________ 15. Groups of three nitrogen bases on the mRNA are called _________ 16. Codons code for a specific ________ 17. What gets the correct amino acid and brings it to the ribosome ...
... 13. Name three differences between DNA and RNA 14. The process where the information from DNA is copied to mRNA is __________ 15. Groups of three nitrogen bases on the mRNA are called _________ 16. Codons code for a specific ________ 17. What gets the correct amino acid and brings it to the ribosome ...
Table of Contents
... • The neighborhood around the RFLP can be screened for other RFLPs. If one is linked directly, a DNA fragment from the region can be used to identify a cDNA sequence. • The gene in affected and unaffected people is compared to determine the genetic difference responsible for the disease. ...
... • The neighborhood around the RFLP can be screened for other RFLPs. If one is linked directly, a DNA fragment from the region can be used to identify a cDNA sequence. • The gene in affected and unaffected people is compared to determine the genetic difference responsible for the disease. ...
Quantitative genetics
... • G - Genetic factors, E - environmental factors, GxE interactions, A - additive effects, D – dominance (alleles at one locus), E – epistasis (alles at different loci), C common and E - non-shared environment (children in one family are different) • EEE... ...
... • G - Genetic factors, E - environmental factors, GxE interactions, A - additive effects, D – dominance (alleles at one locus), E – epistasis (alles at different loci), C common and E - non-shared environment (children in one family are different) • EEE... ...
2001 AP Biology Scoring Guidelines - AP Central
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service (ETS), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their programs ...
... These materials were produced by Educational Testing Service (ETS), which develops and administers the examinations of the Advanced Placement Program for the College Board. The College Board and Educational Testing Service (ETS) are dedicated to the principle of equal opportunity, and their programs ...
Document
... • DNA helix is opened so complementary base pairing can occur • RNA polymerase joins new RNA nucleotides in a sequence complementary to that on the DNA, in a 5’ to 3’ direction ...
... • DNA helix is opened so complementary base pairing can occur • RNA polymerase joins new RNA nucleotides in a sequence complementary to that on the DNA, in a 5’ to 3’ direction ...
Gesheng - China
... by combination of the phrase “having a percent homology” and the functions of said gene/protein; by possible other features, such as functions, physiochemical properties, origin of said gene/protein, or a process for producing said gene/protein, if it is hard to be defined by any of the above wa ...
... by combination of the phrase “having a percent homology” and the functions of said gene/protein; by possible other features, such as functions, physiochemical properties, origin of said gene/protein, or a process for producing said gene/protein, if it is hard to be defined by any of the above wa ...
Chapter 3 Powerpoint - Trimble County Schools
... Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, have an amino group and a carboxyl group – Both of these are covalently bonded to a central carbon ...
... Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, have an amino group and a carboxyl group – Both of these are covalently bonded to a central carbon ...
Course outline
... Using Iterative Control Structures, An Introduction to the Blocks World Problem Assignment 1, Part 4 due ...
... Using Iterative Control Structures, An Introduction to the Blocks World Problem Assignment 1, Part 4 due ...
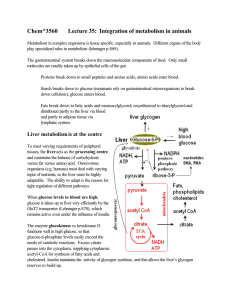
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... very active protein degradation and resynthesis, qamino acids can be withdrawn from the muscle when other nutrients are in short supply. Brain and nervous system: use primarily aerobic glucose metabolism for energy metabolism; ATP is required to maintain the ion gradients of Na+, K+ and Ca2+ generat ...
... very active protein degradation and resynthesis, qamino acids can be withdrawn from the muscle when other nutrients are in short supply. Brain and nervous system: use primarily aerobic glucose metabolism for energy metabolism; ATP is required to maintain the ion gradients of Na+, K+ and Ca2+ generat ...
Genetics PPT
... helix unwinds, just in the segment that contains the nucleic acid sequence (called a GENE) for that protein. The DNA strand that is copied is called the sense strand (or + strand), and the other strand is called the antisense strand (or – strand). The gene is copied in the nucleus and the copy is ...
... helix unwinds, just in the segment that contains the nucleic acid sequence (called a GENE) for that protein. The DNA strand that is copied is called the sense strand (or + strand), and the other strand is called the antisense strand (or – strand). The gene is copied in the nucleus and the copy is ...
Title: Author - Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... If it is necessary, the synthesis of non-essential amino acids can be carried out by aminotransferase catalyzed reactions. In this case an α-keto acid is used as precursor and an amino group is transferred. The transaminase reactions of essential amino acids have only one direction, because the equi ...
... If it is necessary, the synthesis of non-essential amino acids can be carried out by aminotransferase catalyzed reactions. In this case an α-keto acid is used as precursor and an amino group is transferred. The transaminase reactions of essential amino acids have only one direction, because the equi ...
Biology GENETICS Practice Test with Answer Key
... A. The number of chromosomes increases from haploid to diploid. B. The number of chromosomes decreases from diploid to haploid. C. There is a segregation of dominant and recessive genes. D. There is an integration of dominant and recessive genes. 16. Which is true of meiosis? A. Identical cells are ...
... A. The number of chromosomes increases from haploid to diploid. B. The number of chromosomes decreases from diploid to haploid. C. There is a segregation of dominant and recessive genes. D. There is an integration of dominant and recessive genes. 16. Which is true of meiosis? A. Identical cells are ...
Computer Analysis of DNA and Protein Sequences Over the Internet
... Use the NIH bioinformatics program web site, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/. Here you can recover sequences for practically any published experiment involving DNA, RNA or protein. You can also search the results of your own experiments against the database of known sequences. Using BLAST : http://www. ...
... Use the NIH bioinformatics program web site, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/. Here you can recover sequences for practically any published experiment involving DNA, RNA or protein. You can also search the results of your own experiments against the database of known sequences. Using BLAST : http://www. ...
C - bellevuebiology
... 2) Functional – Proteins that have activity Examples-Hormones – used for signaling -Defensive – antibodies that recognize foreign invaders -Transport – Carrier proteins!!! -Enzymes – used for chemical reaction - Hemoglobin – found on RBC and carry oxygen ...
... 2) Functional – Proteins that have activity Examples-Hormones – used for signaling -Defensive – antibodies that recognize foreign invaders -Transport – Carrier proteins!!! -Enzymes – used for chemical reaction - Hemoglobin – found on RBC and carry oxygen ...
AAKG supplement
... body of excess ammonia. This key non-essential amino acid is also important in protein synthesis, as well as for the support of healthy immune function. Alpha-ketoglutarate is another key player in amino acid metabolism, as well as in energy production, and is used as a body building supplement. Tog ...
... body of excess ammonia. This key non-essential amino acid is also important in protein synthesis, as well as for the support of healthy immune function. Alpha-ketoglutarate is another key player in amino acid metabolism, as well as in energy production, and is used as a body building supplement. Tog ...
Unraveling the DNA Myth, The Spurious Foundation of
... have an "impact on human pride" and that "human self-esteem may be in for further blows" from future genome analyses, which had already found that the genes of mice and men are very similar. The project’s scientific reports offered little to explain the shortfall in the gene count. One of the possib ...
... have an "impact on human pride" and that "human self-esteem may be in for further blows" from future genome analyses, which had already found that the genes of mice and men are very similar. The project’s scientific reports offered little to explain the shortfall in the gene count. One of the possib ...
National Exam
... The workstation should have the On-‐Site Model Competition Environment open on the computer. Using the 152cm Mini-‐Toober provided, construct a model of the Cas9 – amino acids 1263-‐1339 of chain B o ...
... The workstation should have the On-‐Site Model Competition Environment open on the computer. Using the 152cm Mini-‐Toober provided, construct a model of the Cas9 – amino acids 1263-‐1339 of chain B o ...
File
... sequence of the DNA by nucleotide position. Letters for each base are stacked on top of each other according to their relative frequency at that position among the aligned sequences, with the most common base as the largest letter at the top of the stack. The height of each letter represents the rel ...
... sequence of the DNA by nucleotide position. Letters for each base are stacked on top of each other according to their relative frequency at that position among the aligned sequences, with the most common base as the largest letter at the top of the stack. The height of each letter represents the rel ...
IJEB 52(1) 73-79
... A common method for analysis of 17 amino acids from various insect species and plant parts was standardized using HPLC-PDA. Prior to hydrolysis, lyophilization of test samples was found indispensible to remove excess moisture, which interferes in hydrolysis and separation of amino acids. After the h ...
... A common method for analysis of 17 amino acids from various insect species and plant parts was standardized using HPLC-PDA. Prior to hydrolysis, lyophilization of test samples was found indispensible to remove excess moisture, which interferes in hydrolysis and separation of amino acids. After the h ...
Variant types of Haemoglobinopathies
... Variant Hbs result from substitution of one or more amino acids in the globin portion of the molecule at selected positions in the two alpha or two beta polypeptide chains. Usually caused by single point mutations. Although more than 100 variants have been described, only hemoglobins S, C, and D are ...
... Variant Hbs result from substitution of one or more amino acids in the globin portion of the molecule at selected positions in the two alpha or two beta polypeptide chains. Usually caused by single point mutations. Although more than 100 variants have been described, only hemoglobins S, C, and D are ...
Analytical challenges in the genetic diagnosis of Lynch
... mutations in one of the mismatch repair (MMR) genes: MLH1, MLH2, MSH6, or PMS21. A genetic diagnosis is essential in families with a suspicion of having LS, as it allows the use of proper and specific surveillance programs for high-risk individuals who carry a pathogenic mutation. Thus, high risk in ...
... mutations in one of the mismatch repair (MMR) genes: MLH1, MLH2, MSH6, or PMS21. A genetic diagnosis is essential in families with a suspicion of having LS, as it allows the use of proper and specific surveillance programs for high-risk individuals who carry a pathogenic mutation. Thus, high risk in ...
Peanut Butter SUPERFOOD Nutritional Facts Protein The human
... The human body is literally a protein factory. Proteins comprise 20% of our total body mass. We are made of protein from our bones to our muscles, arteries and veins, skin, hair, and fingernails. Our heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and lungs are built of tissue made of proteins. To be short of protein ...
... The human body is literally a protein factory. Proteins comprise 20% of our total body mass. We are made of protein from our bones to our muscles, arteries and veins, skin, hair, and fingernails. Our heart, brain, liver, kidneys, and lungs are built of tissue made of proteins. To be short of protein ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.