Site-directed Mutagenesis of Arginine
... A series of single amino acid substitutions of Arg178 were obtained by cassette mutagenesis of plasmid pSCTS9/Smal (See Fig. 2). Plasmid DNA was digested with Smal and MstII to remove a 36-bp fragment, and vector DNA was purified by electrophoresis using 1% low melting point agarose. The 36-bp Smal/ ...
... A series of single amino acid substitutions of Arg178 were obtained by cassette mutagenesis of plasmid pSCTS9/Smal (See Fig. 2). Plasmid DNA was digested with Smal and MstII to remove a 36-bp fragment, and vector DNA was purified by electrophoresis using 1% low melting point agarose. The 36-bp Smal/ ...
No Slide Title
... Coiled-coil, three separate polypeptides called chains are supertwisted Provide strength (stronger than ??) Connective tissue (tendons, cartilage, organic matrix of bone, cornea) ...
... Coiled-coil, three separate polypeptides called chains are supertwisted Provide strength (stronger than ??) Connective tissue (tendons, cartilage, organic matrix of bone, cornea) ...
What are genetic disorders?
... (2) Multifactorial (also called complex or polygenic) - This type is caused by a combination of environmental factors and mutations in multiple genes. For example, different genes that influence breast cancer susceptibility have been found on chromosomes 6, 11, 13, 14, 15, 17, and 22. Its more compl ...
... (2) Multifactorial (also called complex or polygenic) - This type is caused by a combination of environmental factors and mutations in multiple genes. For example, different genes that influence breast cancer susceptibility have been found on chromosomes 6, 11, 13, 14, 15, 17, and 22. Its more compl ...
Microbiology with Diseases Taxonomy
... The chemistry of the cell would basically be impossible without hydrogen bonds. Water, which is required by all cellular reactions, would not have its unique properties of cohesiveness and polarity without hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds hold the double helix of DNA together and contribute to the ove ...
... The chemistry of the cell would basically be impossible without hydrogen bonds. Water, which is required by all cellular reactions, would not have its unique properties of cohesiveness and polarity without hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds hold the double helix of DNA together and contribute to the ove ...
MacronutIII
... be replaced by dietary cysteine, since there is a pathway for conversion of MET to CYS • Much, but not all, of the phenylalanine requirement can be replaced by dietary tyrosine, since there is a pathway for conversion of PHE to TYR • In this way CYS and TYR serve to “spare” requirements for MET and ...
... be replaced by dietary cysteine, since there is a pathway for conversion of MET to CYS • Much, but not all, of the phenylalanine requirement can be replaced by dietary tyrosine, since there is a pathway for conversion of PHE to TYR • In this way CYS and TYR serve to “spare” requirements for MET and ...
2012-ISB-symposium
... structure elements, structural domains, and protein chains. Spaghetti produces two dimensional and three dimensional views of the relationship between observed peptides and protein structure including visualization of the locations of the peptides. Coverage statistics and analysis are provided. This ...
... structure elements, structural domains, and protein chains. Spaghetti produces two dimensional and three dimensional views of the relationship between observed peptides and protein structure including visualization of the locations of the peptides. Coverage statistics and analysis are provided. This ...
Department of Chemistry IIT Kharagpur Biochemical Techniques
... PyMOL reads .pdb files, which come from the Protein Data Bank (PDB). These files are used to describe the 3D structure of any molecule, not just proteins but also nucleic acids (like RNA and DNA) and even small molecules. Click on Start to go the Programs menu where you will find PyMOL. Start the pr ...
... PyMOL reads .pdb files, which come from the Protein Data Bank (PDB). These files are used to describe the 3D structure of any molecule, not just proteins but also nucleic acids (like RNA and DNA) and even small molecules. Click on Start to go the Programs menu where you will find PyMOL. Start the pr ...
Part ONE - UCL Computer Science
... and answer ALL questions in Part TWO on the multiple-choice question answer sheet. Marks for each part of each question are indicated in square brackets Calculators are permitted ...
... and answer ALL questions in Part TWO on the multiple-choice question answer sheet. Marks for each part of each question are indicated in square brackets Calculators are permitted ...
Idling behind the Yellow Line: Cybercensorship and the Liability of
... Followings are excluded: structures with less than three transmembrane helices. structures unusual very open ...
... Followings are excluded: structures with less than three transmembrane helices. structures unusual very open ...
Lecture 8 RNA Secondary Structure Central Dogma
... RNA • In the central dodgma, we talk about mRNA coding for protein. There are also tRNA and rRNA that are also coded for by the DNA. The MicroRNAs (miRNA) are small (22 nucleotides) non-coding RNA gene products that seem to regulate translation • The RNA has features in it sequence that gives it a ...
... RNA • In the central dodgma, we talk about mRNA coding for protein. There are also tRNA and rRNA that are also coded for by the DNA. The MicroRNAs (miRNA) are small (22 nucleotides) non-coding RNA gene products that seem to regulate translation • The RNA has features in it sequence that gives it a ...
Synthesis of biopolymers: proteins, polyesters
... which in their natural environments, direct the synthesis of proteins and thus determine the characteristics of organisms.In addition to the very specific relations between structure and function, another aspect of biopolymers intriguing to materials scientists is the precision with which they are m ...
... which in their natural environments, direct the synthesis of proteins and thus determine the characteristics of organisms.In addition to the very specific relations between structure and function, another aspect of biopolymers intriguing to materials scientists is the precision with which they are m ...
T - Florida Tech Department of Computer Sciences
... Nucleic Acids encode information necessary to produce proteins They are responsible for passing recipe to subsequent generations. 2 types of nucleic acids present in living organisms, RNA (ribonucleic acid) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). ...
... Nucleic Acids encode information necessary to produce proteins They are responsible for passing recipe to subsequent generations. 2 types of nucleic acids present in living organisms, RNA (ribonucleic acid) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). ...
Mark Scheme
... standardisation events which all examiners participate in and is the scheme which was used by them in this examination. The standardisation process ensures that the mark scheme covers the candidates’ responses to questions and that every examiner understands and applies it in the same correct way. A ...
... standardisation events which all examiners participate in and is the scheme which was used by them in this examination. The standardisation process ensures that the mark scheme covers the candidates’ responses to questions and that every examiner understands and applies it in the same correct way. A ...
Reasons for the occurrence of the twenty coded protein amino acids
... amino acid with an a-hydrogen or by the carboxylation of an amine such as isopropylamine. Replacement of the a-hydrogen by larger substituent, such as a methyl group, would also increase significantly steric hinderance around the amino and carboxyl groups. Steric difficulties have been encountered i ...
... amino acid with an a-hydrogen or by the carboxylation of an amine such as isopropylamine. Replacement of the a-hydrogen by larger substituent, such as a methyl group, would also increase significantly steric hinderance around the amino and carboxyl groups. Steric difficulties have been encountered i ...
Document
... the identification of SNP/InDels at coding sequences or exons of the gene. • Since these variations were expected to affect the encoded protein structure and/or function • However, recent reports indicate that the nucleotide changes in non-coding regions (5’UTR) including promoter, introns and 3’ UT ...
... the identification of SNP/InDels at coding sequences or exons of the gene. • Since these variations were expected to affect the encoded protein structure and/or function • However, recent reports indicate that the nucleotide changes in non-coding regions (5’UTR) including promoter, introns and 3’ UT ...
DNA
... cells that are formed from that sex cell will have that mutation. • Mutations add variety to a species when the organism reproduces. ...
... cells that are formed from that sex cell will have that mutation. • Mutations add variety to a species when the organism reproduces. ...
Seminar_3 - Great Lakes Genomics Center
... Less Commonly found: Hydrophobic interfaces Interchain Disulfides ...
... Less Commonly found: Hydrophobic interfaces Interchain Disulfides ...
STUDY GUIDE for Dr. Mohnen`s part of Exam #3
... Yields lariat and spliced exons Alternative splicing: membrane vs soluble antibody CTD of RNA Pol II recruits enzymes to synthesis 5’ cap, splicing complex, and endonuclease for poly A tail generation RNA editing: apolipoprotein B in liver vs small intestine; post transcription modification of C to ...
... Yields lariat and spliced exons Alternative splicing: membrane vs soluble antibody CTD of RNA Pol II recruits enzymes to synthesis 5’ cap, splicing complex, and endonuclease for poly A tail generation RNA editing: apolipoprotein B in liver vs small intestine; post transcription modification of C to ...
DNA Sequencing of the eta Gene Coding for
... shown below the appropriate amino acid. Three sets of -35 and - 10 regions corresponding to the consensus sequence of the E. colipromoter are indicated with solid lines above the respective sequences. SD, ribosome-binding region (Shine-Dalgarno sequence). Four inverted sequences are underlined with ...
... shown below the appropriate amino acid. Three sets of -35 and - 10 regions corresponding to the consensus sequence of the E. colipromoter are indicated with solid lines above the respective sequences. SD, ribosome-binding region (Shine-Dalgarno sequence). Four inverted sequences are underlined with ...
Rampant Adaptive Evolution in Regions of Proteins with Unknown
... domain codons (0.88 vs. 0.94, FET p = 0.008; Table 1). This suggests that although both classes of sites experience frequent adaptive fixation, non-domain codons may experience more adaptive evolution than domain codons. To investigate the distribution of variation on an individual gene basis, we us ...
... domain codons (0.88 vs. 0.94, FET p = 0.008; Table 1). This suggests that although both classes of sites experience frequent adaptive fixation, non-domain codons may experience more adaptive evolution than domain codons. To investigate the distribution of variation on an individual gene basis, we us ...
Bios 302 FINAL FOR 1999.
... You suggest that she analyze the enzyme for the presence of cobalt. Why do you make this suggestion? f. What one slight modification would you make to one enzyme already present in the glycolytic path so that glucose and mannose could be used equally well as starting points for glycolysis? g. The ge ...
... You suggest that she analyze the enzyme for the presence of cobalt. Why do you make this suggestion? f. What one slight modification would you make to one enzyme already present in the glycolytic path so that glucose and mannose could be used equally well as starting points for glycolysis? g. The ge ...
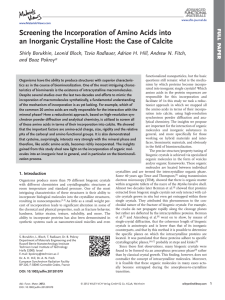
Screening the Incorporation of Amino Acids into an Inorganic
... to a strong peak shift. Not only did the Asp become incorpoGly, Pro). Figure 2 presents a summary of the results for all rated into calcite and cause lattice distortions but this was very the amino acids (induced lattice strain vs. incorporated consimilar to biogenic calcite, in which upon mild isoc ...
... to a strong peak shift. Not only did the Asp become incorpoGly, Pro). Figure 2 presents a summary of the results for all rated into calcite and cause lattice distortions but this was very the amino acids (induced lattice strain vs. incorporated consimilar to biogenic calcite, in which upon mild isoc ...
Haemoglobin.
... Hb as buffer : Hb constitute one of the important buffer of the blood and helps to maintain its acid –base balance. Hb has a strong tendency to combine with carbon monoxide forming a compound called carboxyhaemoglon. CO has almost 250 times stronger affinity for Hb than that of O2 for Hb. CO-Hb once ...
... Hb as buffer : Hb constitute one of the important buffer of the blood and helps to maintain its acid –base balance. Hb has a strong tendency to combine with carbon monoxide forming a compound called carboxyhaemoglon. CO has almost 250 times stronger affinity for Hb than that of O2 for Hb. CO-Hb once ...
CHAPTER 10
... RNA STRUCTURE & FUNCTION DNA and RNA are similar in that they are both made up of nucleotides. DNA and RNA differ in Four Ways: 1. RNA has ribose, DNA has deoxyribose 2. RNA contains a nitrogen base uracil instead of thymine 3. RNA is single stranded* 4. RNA is much shorter than DNA. It contains th ...
... RNA STRUCTURE & FUNCTION DNA and RNA are similar in that they are both made up of nucleotides. DNA and RNA differ in Four Ways: 1. RNA has ribose, DNA has deoxyribose 2. RNA contains a nitrogen base uracil instead of thymine 3. RNA is single stranded* 4. RNA is much shorter than DNA. It contains th ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.