Enzyme Hydrolyzed Collagen Protein
... “specific” to collagen and are not regularly found in most amino acid supplements; yet they are very important to collagen regeneration and production. Hence, collagen that has been hydrolyzed with fruit enzymes (not with heat or acids that can destroy the matrix and peptide bonds) will genetically ...
... “specific” to collagen and are not regularly found in most amino acid supplements; yet they are very important to collagen regeneration and production. Hence, collagen that has been hydrolyzed with fruit enzymes (not with heat or acids that can destroy the matrix and peptide bonds) will genetically ...
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... on instructions encoded in the sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA 1. The genetic code is the term for the rules that relate how a sequence of nitrogenous bases in nucleotides corresponds to a particular amino acid. 2. In the code 3 adjacent nucleotides (“letters”) in mRNA specify an amino acid (“wo ...
... on instructions encoded in the sequence of nucleotides in the mRNA 1. The genetic code is the term for the rules that relate how a sequence of nitrogenous bases in nucleotides corresponds to a particular amino acid. 2. In the code 3 adjacent nucleotides (“letters”) in mRNA specify an amino acid (“wo ...
Tree nomenclature
... one amino acid by another, accepted by natural selection. It is the result of two distinct processes: the first is the occurrence of a mutation in the portion of the gene template producing one amino acid of a protein; the second is the acceptance of the mutation by the species as the new predominan ...
... one amino acid by another, accepted by natural selection. It is the result of two distinct processes: the first is the occurrence of a mutation in the portion of the gene template producing one amino acid of a protein; the second is the acceptance of the mutation by the species as the new predominan ...
Synonymous codon bias and functional constraint on GC3
... planation given the taxonomic limitations of this phenomena. Equally puzzling is the recent discovery of many tandem substitution events localized to adjacent synonymous and non-synonymous sites (17) suggesting that evolutionary forces acting on these neighboring sites are not as independent as has ...
... planation given the taxonomic limitations of this phenomena. Equally puzzling is the recent discovery of many tandem substitution events localized to adjacent synonymous and non-synonymous sites (17) suggesting that evolutionary forces acting on these neighboring sites are not as independent as has ...
Genetics Power Point
... • Step 1: mRNA Production – In the nucleus, DNA “unzips” between base pairs, and RNA bases match up along the DNA strands…the genetic info from DNA is transferred to the RNA ...
... • Step 1: mRNA Production – In the nucleus, DNA “unzips” between base pairs, and RNA bases match up along the DNA strands…the genetic info from DNA is transferred to the RNA ...
Preference for and learning of amino acids in larval
... amino acids, unexpectedly, we observed weak to moderate aversion. Thus, there did not appear to be a general upshift in preferences caused by starvation; rather, the data suggest that starvation alters the profile of liked and disliked amino acids. Across the three above-described experiments, the p ...
... amino acids, unexpectedly, we observed weak to moderate aversion. Thus, there did not appear to be a general upshift in preferences caused by starvation; rather, the data suggest that starvation alters the profile of liked and disliked amino acids. Across the three above-described experiments, the p ...
Name: Date: ______ NUID
... are all biological organisms similar? Given this biochemical similarity, how is the structural and functional diversity of living things possible? Ans: Living things are composed primarily of macromolecules, polymers of simple compounds of just a few different types. The properties of these polymers ...
... are all biological organisms similar? Given this biochemical similarity, how is the structural and functional diversity of living things possible? Ans: Living things are composed primarily of macromolecules, polymers of simple compounds of just a few different types. The properties of these polymers ...
Test Info Sheet
... ultrasound in fetuses of families with no family history and mutation detection has identified ITGB4 or ITGA6 mutations,10-13 although this has not been described in EB cases with plectin defects. In one rare case, EB-PA with desquamative enteropathy but without skin disease has been reported.14 Inh ...
... ultrasound in fetuses of families with no family history and mutation detection has identified ITGB4 or ITGA6 mutations,10-13 although this has not been described in EB cases with plectin defects. In one rare case, EB-PA with desquamative enteropathy but without skin disease has been reported.14 Inh ...
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY and GENETICS
... The lecture component of the course is worth 50% of the final assessment and the material is assessed in one 2.5 h exam held in the exam period. Two thirds of the marks in this exam are awarded to questions relating to the lecture material. The practical component contributes 50% to the final mark a ...
... The lecture component of the course is worth 50% of the final assessment and the material is assessed in one 2.5 h exam held in the exam period. Two thirds of the marks in this exam are awarded to questions relating to the lecture material. The practical component contributes 50% to the final mark a ...
Curriculum Vitae - Genomic Sciences Training Program
... available, none are well-suited for use in genetically-uncharacterized organisms. Because of this limitation, I have an equally matched interest in developing and implementing suitable technologies able to acquire genotypes from individuals in natural populations. In my doctoral thesis, I developed ...
... available, none are well-suited for use in genetically-uncharacterized organisms. Because of this limitation, I have an equally matched interest in developing and implementing suitable technologies able to acquire genotypes from individuals in natural populations. In my doctoral thesis, I developed ...
Slides
... • In bugs these sequences are called Proximal Promoter Elements – In eucaryotes, the regulatory sequences can be miles away! • Called enhancer sequences • Remember the hugely coiled nature of eucaryotic DNA ...
... • In bugs these sequences are called Proximal Promoter Elements – In eucaryotes, the regulatory sequences can be miles away! • Called enhancer sequences • Remember the hugely coiled nature of eucaryotic DNA ...
Dynamic Model of the Process of Protein Synthesis in Eukaryotic Cells
... Since eIF4F is a prerequisite for the preinitiation complex to load onto the mRNA, inhibiting its activity will prevent further loading of 40S ribosomes onto the m7 G cap, thus decreasing the ribosome loading rate. Figure 4 shows the pathways and dependencies of the controller while table 3 presents ...
... Since eIF4F is a prerequisite for the preinitiation complex to load onto the mRNA, inhibiting its activity will prevent further loading of 40S ribosomes onto the m7 G cap, thus decreasing the ribosome loading rate. Figure 4 shows the pathways and dependencies of the controller while table 3 presents ...
Protein folding: mechanisms and role in disease - Max
... the tendency of the water-rejecting (hydrophobic) amino acids to interact with one another and form a hydrophobic core while the water-loving (hydrophilic) amino acids remain at the surface. As a result, the expanded protein chain rapidly collapses into a globular structure. This drastically reduces ...
... the tendency of the water-rejecting (hydrophobic) amino acids to interact with one another and form a hydrophobic core while the water-loving (hydrophilic) amino acids remain at the surface. As a result, the expanded protein chain rapidly collapses into a globular structure. This drastically reduces ...
Introduction to molecular population genetics
... especially patterns above the species level, you’ll want to take the courses Paul Lewis and Chris Simon teach. They spend their entire time discussing these problems. ...
... especially patterns above the species level, you’ll want to take the courses Paul Lewis and Chris Simon teach. They spend their entire time discussing these problems. ...
Lecture 1 - Columbus Labs
... introduces the components of biological macromolecules and the principles behind their observed structures. The structure, properties, and functions of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates will be the focus of the course with an additional emphasis on large cellular assemblies such as ...
... introduces the components of biological macromolecules and the principles behind their observed structures. The structure, properties, and functions of nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates will be the focus of the course with an additional emphasis on large cellular assemblies such as ...
Station 1: Carbon Compounds
... Station 1: Carbon Compounds- Close Reading/ Annotate: Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon compounds are also called organic compounds. Many of the molecules in living things are so large that they are known as macromolecules. Macromolecules ...
... Station 1: Carbon Compounds- Close Reading/ Annotate: Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon compounds are also called organic compounds. Many of the molecules in living things are so large that they are known as macromolecules. Macromolecules ...
22: Peptides, Proteins, and
... R group structures, it is helpful for us to group the "standard" amino acids in the three categories shown in Figure (graphic 22.6). R groups of the 5 "charged polar" amino acids are electrically charged (- or +) at physiological pH values (about pH 7), while those of the remaining 15 amino acids ar ...
... R group structures, it is helpful for us to group the "standard" amino acids in the three categories shown in Figure (graphic 22.6). R groups of the 5 "charged polar" amino acids are electrically charged (- or +) at physiological pH values (about pH 7), while those of the remaining 15 amino acids ar ...
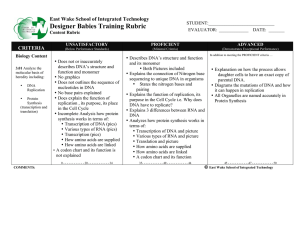
Designer Babies Training Rubric
... • Explains 3 differences between RNA and DNA • Analyzes how protein synthesis works in terms of: • Transcription of DNA and picture • Various types of RNA and picture • Translation and picture • How amino acids are supplied • How amino acids are linked • A codon chart and its function ...
... • Explains 3 differences between RNA and DNA • Analyzes how protein synthesis works in terms of: • Transcription of DNA and picture • Various types of RNA and picture • Translation and picture • How amino acids are supplied • How amino acids are linked • A codon chart and its function ...
DNA
... The Code •Scientists hypothesized that the instructions from protein synthesis were encoded in DNA. •Experiments during the 1960s demonstrated that the DNA code was a three-base code. •The three-base code in DNA or mRNA is called a codon. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education ...
... The Code •Scientists hypothesized that the instructions from protein synthesis were encoded in DNA. •Experiments during the 1960s demonstrated that the DNA code was a three-base code. •The three-base code in DNA or mRNA is called a codon. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education ...
Chapter 11 Vitamins and proteins
... as coenzymes, which enable a particular enzyme to catalyse a reaction. This will be discussed later in the chapter. Vitamins can be divided into two groups: fat soluble and water soluble. Fat-soluble vitamins include vitamins A, D, E and K. They can be absorbed in the intestines and moved via the ly ...
... as coenzymes, which enable a particular enzyme to catalyse a reaction. This will be discussed later in the chapter. Vitamins can be divided into two groups: fat soluble and water soluble. Fat-soluble vitamins include vitamins A, D, E and K. They can be absorbed in the intestines and moved via the ly ...
Structural Location of Disease-associated Single
... pockets or voids – more likely than non-disease associated nsSNPs – binding pockets nsSNPs in shallow depressed or convex regions also cause disease - probably because these can also be binding pockets nsSNPs unlikely to be buried in protein – why? ...
... pockets or voids – more likely than non-disease associated nsSNPs – binding pockets nsSNPs in shallow depressed or convex regions also cause disease - probably because these can also be binding pockets nsSNPs unlikely to be buried in protein – why? ...
Identification of two novel mutations associated
... membranes [20]. Glu67 also appears to be important for protein S secretion from the liver into blood [19]. A second mutation was identified in the 5’ flanking sequence of the PROS1 gene (Figure 1B), and represented a heterozygous CG nucleotide substitution at a position 190 bp upstream of the trans ...
... membranes [20]. Glu67 also appears to be important for protein S secretion from the liver into blood [19]. A second mutation was identified in the 5’ flanking sequence of the PROS1 gene (Figure 1B), and represented a heterozygous CG nucleotide substitution at a position 190 bp upstream of the trans ...
Insights into digestion and absorption of major nutrients in humans
... for the survival of living organisms and has evolved into the complex and specific task of the gastrointestinal (GI) system. While most people simply assume that their GI tract will work properly to use nutrients, provide energy, and release wastes, few nonscientists know the details about how vario ...
... for the survival of living organisms and has evolved into the complex and specific task of the gastrointestinal (GI) system. While most people simply assume that their GI tract will work properly to use nutrients, provide energy, and release wastes, few nonscientists know the details about how vario ...
Metz and Palumbi 1996
... attachment of sperm to an eggsurface receptor during fertilization. Sequences of bindin from closely related urchins show fixed species-specific differences. Within species, highly polymorphic bindin alleles result from point substitution, insertion/deletion, and recombination. Since speciation, pos ...
... attachment of sperm to an eggsurface receptor during fertilization. Sequences of bindin from closely related urchins show fixed species-specific differences. Within species, highly polymorphic bindin alleles result from point substitution, insertion/deletion, and recombination. Since speciation, pos ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.