Slide 1
... Question: Can vitamin B6 relieve the symptoms of pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS)? Answer: Studies have shown vitamin B6 to be effective in alleviating some symptoms of "PMS" in some women, such as breast tenderness, headaches, tension, irritability, and bloating. A general dosage range of 50-100mg/day ...
... Question: Can vitamin B6 relieve the symptoms of pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS)? Answer: Studies have shown vitamin B6 to be effective in alleviating some symptoms of "PMS" in some women, such as breast tenderness, headaches, tension, irritability, and bloating. A general dosage range of 50-100mg/day ...
! Mendel`s Law of Independent Assortment
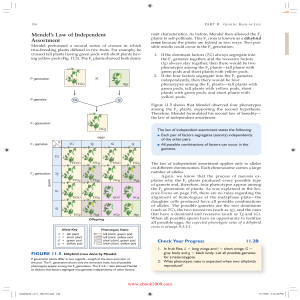
... see that each of these is ¼ of the total number of squares. How do we get the phenotypic results? The sum rule of probability tells us that when the same event can occur in more than one way, we can add the results. Because 1, 2, and 3 all result in unattached earlobes, we add them up to know that t ...
... see that each of these is ¼ of the total number of squares. How do we get the phenotypic results? The sum rule of probability tells us that when the same event can occur in more than one way, we can add the results. Because 1, 2, and 3 all result in unattached earlobes, we add them up to know that t ...
complete
... Question: Can vitamin B6 relieve the symptoms of pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS)? Answer: Studies have shown vitamin B6 to be effective in alleviating some symptoms of "PMS" in some women, such as breast tenderness, headaches, tension, irritability, and bloating. A general dosage range of 50-100mg/day ...
... Question: Can vitamin B6 relieve the symptoms of pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS)? Answer: Studies have shown vitamin B6 to be effective in alleviating some symptoms of "PMS" in some women, such as breast tenderness, headaches, tension, irritability, and bloating. A general dosage range of 50-100mg/day ...
Isolation of All Soluble Tryptic Peptides from the α Polypeptide
... among the species are found in the amino acid sequence. It is considered that these differences were caused by the accumulation of point mutations due to single base changes in genes, DNA, which control the biosynthesis of hemoglobin molecules. This also suggests that present hemoglobins of various ...
... among the species are found in the amino acid sequence. It is considered that these differences were caused by the accumulation of point mutations due to single base changes in genes, DNA, which control the biosynthesis of hemoglobin molecules. This also suggests that present hemoglobins of various ...
A novel approach for protein subcellular location prediction using
... of a protein must be somehow coupled to the physicochemical properties of the environment where the protein performs its function; therefore the differences between environments will be imprinted in the protein amino acid composition [10,11]. This approach has the advantage that it can be applied to ...
... of a protein must be somehow coupled to the physicochemical properties of the environment where the protein performs its function; therefore the differences between environments will be imprinted in the protein amino acid composition [10,11]. This approach has the advantage that it can be applied to ...
1. Nucleic Acids and Chromosomes
... Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases Eukaryotic cells contain three types of RNA polymerases: RNA Polymerase I -Transcribes rRNA genes RNA Polymerase III- Transcribes tRNA and 5S RNA genes RNA Polymerase II - Transcribes genes encoding proteins into mRNA 4. Describe what is meant by a “gene promoter” Th ...
... Eukaryotic RNA Polymerases Eukaryotic cells contain three types of RNA polymerases: RNA Polymerase I -Transcribes rRNA genes RNA Polymerase III- Transcribes tRNA and 5S RNA genes RNA Polymerase II - Transcribes genes encoding proteins into mRNA 4. Describe what is meant by a “gene promoter” Th ...
Assessing Methods of Detecting Osteogenesis Imperfecta.
... Collagen has an unusual amino acid composition and sequence. Glycine (GLY) is found at almost every third residue, and also contains large amounts of proline (PRO), as well as two uncommon post translational amino acids not directly inserted during translation of mRNA: hydroxyproline (HYP) and hydro ...
... Collagen has an unusual amino acid composition and sequence. Glycine (GLY) is found at almost every third residue, and also contains large amounts of proline (PRO), as well as two uncommon post translational amino acids not directly inserted during translation of mRNA: hydroxyproline (HYP) and hydro ...
Crystal structure of a membrane-bound l-amino acid
... LAADs, which are anchored to cytomembrane surface through their N-terminal transmembrane helix (Hossain et al., 2014b). Some bacteria, such as Proteus mirabilis, was found to express two types of LAADs, which share significant sequence similarity but are with distinct substrate preferences: type I p ...
... LAADs, which are anchored to cytomembrane surface through their N-terminal transmembrane helix (Hossain et al., 2014b). Some bacteria, such as Proteus mirabilis, was found to express two types of LAADs, which share significant sequence similarity but are with distinct substrate preferences: type I p ...
Sequence-Specific Resonance Assignments of the `H
... proteins to regulate transcription of DNA to viral RNA and thus replication of the viruses. The best known lentiviral transcriptional regulators are the tar, rev, and nef gene products. The tat gene product activates DNA transcription in trans (tat = trans-activator). It is a key regulatory protein, ...
... proteins to regulate transcription of DNA to viral RNA and thus replication of the viruses. The best known lentiviral transcriptional regulators are the tar, rev, and nef gene products. The tat gene product activates DNA transcription in trans (tat = trans-activator). It is a key regulatory protein, ...
Document
... Mark Distefano Craig Forsyth Jiali Gao John Lipscomb Karin Musier-Forsyth Larry Que ...
... Mark Distefano Craig Forsyth Jiali Gao John Lipscomb Karin Musier-Forsyth Larry Que ...
Dominant Dietary Fatty Acids
... CoA is the carrier o Fatty acid synthesis Acyl group carrier is ACP Contains part of the CoA molecule Homology in acyl carrier group and CoA molecule (?) Acetyl CoA slide… Fig 14.1 o Priming reaction at first Reactions catalyzed by fatty acid synthase (Diagram) o Two business enzymes o Ying- ...
... CoA is the carrier o Fatty acid synthesis Acyl group carrier is ACP Contains part of the CoA molecule Homology in acyl carrier group and CoA molecule (?) Acetyl CoA slide… Fig 14.1 o Priming reaction at first Reactions catalyzed by fatty acid synthase (Diagram) o Two business enzymes o Ying- ...
Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Finding the genes in
... the genome or from average frequencies observed for multiple genomes Probability that an ORF is a protein-coding gene is computed N-terminal (5’) boundary is found by finding a start codon (ATG, GTG, TTG) next to a ribosomal binding site (RBS, Shine-Dalgarno sequence) Different genomes have differen ...
... the genome or from average frequencies observed for multiple genomes Probability that an ORF is a protein-coding gene is computed N-terminal (5’) boundary is found by finding a start codon (ATG, GTG, TTG) next to a ribosomal binding site (RBS, Shine-Dalgarno sequence) Different genomes have differen ...
MOTIFS MOTIFSMARTIFAMORIFSMOOTIFSMICIFC
... where N = Asn, P = Pro, S = Ser, T = Thr; {X} means any amino acid except X; and [XY] means either X or Y. The notation [XY] does not give any indication of the probability of X or Y occurring in the pattern. ...
... where N = Asn, P = Pro, S = Ser, T = Thr; {X} means any amino acid except X; and [XY] means either X or Y. The notation [XY] does not give any indication of the probability of X or Y occurring in the pattern. ...
IvDimitrov_slides
... epitopes and Allergen-Representative Peptides (ARP) - Iterative pairwise sequence similarity encoding scheme with SVM as the discriminating engine ...
... epitopes and Allergen-Representative Peptides (ARP) - Iterative pairwise sequence similarity encoding scheme with SVM as the discriminating engine ...
Identification of the mRNA targets of tRNA
... takes tenths of a second). mRNA-specific translation initiation rates ␣ were derived using an integrated analysis of experimental data using model simulation as described previously (29). The termination rate  was considered not limiting and fixed equal to the fastest rate (i.e. β = γ ) (48). In es ...
... takes tenths of a second). mRNA-specific translation initiation rates ␣ were derived using an integrated analysis of experimental data using model simulation as described previously (29). The termination rate  was considered not limiting and fixed equal to the fastest rate (i.e. β = γ ) (48). In es ...
A Career in Laboratory Genetic Counseling The Not So Non
... appropriateness. This is a key role that not only results in significant cost savings, but enhanced patient care. Genetic counselor review for test appropriateness is helpful as the complexities of genetic testing options increase. Testing for any given genetic condition can often be accomplished in ...
... appropriateness. This is a key role that not only results in significant cost savings, but enhanced patient care. Genetic counselor review for test appropriateness is helpful as the complexities of genetic testing options increase. Testing for any given genetic condition can often be accomplished in ...
Lesson 1.1: Mutation
... Mutations are important for adding variation to the gene pool. A gene pool is the complete set of unique alleles in a population or species. It is all of the alternative forms of a gene in the entire group of an organism. Thinking back to our examples of alleles, the gene pool for a flower species c ...
... Mutations are important for adding variation to the gene pool. A gene pool is the complete set of unique alleles in a population or species. It is all of the alternative forms of a gene in the entire group of an organism. Thinking back to our examples of alleles, the gene pool for a flower species c ...
Document
... A 60-page review of the scientific evidence, some based on stateof-the-art magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain size, has concluded that race differences in average IQ are largely genetic. The lead article in the June 2005 issue of Psychology, Public Policy and Law… examined 10 categories of re ...
... A 60-page review of the scientific evidence, some based on stateof-the-art magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brain size, has concluded that race differences in average IQ are largely genetic. The lead article in the June 2005 issue of Psychology, Public Policy and Law… examined 10 categories of re ...
Genetic Screening
... make a decision about whether they want to be tested and whether they want their unborn child tested. ...
... make a decision about whether they want to be tested and whether they want their unborn child tested. ...
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding proteins related to the short circuit
... the (cHxN),C-binding protein and not from an unlabeled comigrating protein. Fig. 3 shows autoradiographs of [ ''C](cHxN),C-labeled and CNBr-fragmented proteins. The fragments marked with an arrow were used for sequence analysis. From fragmentation of the 22-kDa, 25-kDa, and 27kDa protein, we obtaine ...
... the (cHxN),C-binding protein and not from an unlabeled comigrating protein. Fig. 3 shows autoradiographs of [ ''C](cHxN),C-labeled and CNBr-fragmented proteins. The fragments marked with an arrow were used for sequence analysis. From fragmentation of the 22-kDa, 25-kDa, and 27kDa protein, we obtaine ...
Method for recognizing local descriptors of protein
... characterizing families of proteins [16][21][22]. 1.1.4 Hidden Markov Models Hidden Markov Models are probabilistic models that are used on linear sequences in Bioinformatics [15]. Their uses in bioinformatics are wide, for example prediction of secondary structures from amino acid sequences, lookin ...
... characterizing families of proteins [16][21][22]. 1.1.4 Hidden Markov Models Hidden Markov Models are probabilistic models that are used on linear sequences in Bioinformatics [15]. Their uses in bioinformatics are wide, for example prediction of secondary structures from amino acid sequences, lookin ...
Document
... ester; write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of an ester. Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products from acid and base hydrolysis of esters. Give the common names for amines; draw the condensed structural formulas when given their names. Classify amines as primary, sec ...
... ester; write the balanced chemical equation for the formation of an ester. Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products from acid and base hydrolysis of esters. Give the common names for amines; draw the condensed structural formulas when given their names. Classify amines as primary, sec ...
protein
... higher orders of structure are determined principally by noncovalent forces such as hydrogen bonds and ionic, van der Waals, and hydrophobic interactions. • It is important to emphasize that all the information necessary for a protein molecule to achieve its intricate architecture is contained withi ...
... higher orders of structure are determined principally by noncovalent forces such as hydrogen bonds and ionic, van der Waals, and hydrophobic interactions. • It is important to emphasize that all the information necessary for a protein molecule to achieve its intricate architecture is contained withi ...
Sequence Note vpu and env Sequence V ariability of HIV
... found in two cases (TZ016 and TZ017). Interestingly, the V3 variability of the HIV isolates described here was greater than previously reported for Tanzanian viruses, in which the GPGQ motif was thought to be a consensus sequence. 5 All except two isolates (TZO 16 and TZO 17) had an R instead of a S ...
... found in two cases (TZ016 and TZ017). Interestingly, the V3 variability of the HIV isolates described here was greater than previously reported for Tanzanian viruses, in which the GPGQ motif was thought to be a consensus sequence. 5 All except two isolates (TZO 16 and TZO 17) had an R instead of a S ...
Genetic code

The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA sequences) is translated into proteins by living cells. Biological decoding is accomplished by the ribosome, which links amino acids in an order specified by mRNA, using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries.The code defines how sequences of these nucleotide triplets, called codons, specify which amino acid will be added next during protein synthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. Because the vast majority of genes are encoded with exactly the same code (see the RNA codon table), this particular code is often referred to as the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply the genetic code, though in fact some variant codes have evolved. For example, protein synthesis in human mitochondria relies on a genetic code that differs from the standard genetic code.While the genetic code determines the protein sequence for a given coding region, other genomic regions can influence when and where these proteins are produced.