Document
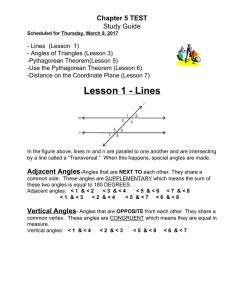
... -Use the Pythagorean Theorem (Lesson 6) -Distance on the Coordinate Plane (Lesson 7) ...
... -Use the Pythagorean Theorem (Lesson 6) -Distance on the Coordinate Plane (Lesson 7) ...
3 The Fundamental Postulate - Princeton University Press
... consider, e.g., a system composed of identical particles of mass m. In this case, the momentum p of a particle is simply proportional to its velocity v, and it is a matter of taste to describe the system in the phase space, i.e., by the collection (r,p) of the position and momentum vectors of the pa ...
... consider, e.g., a system composed of identical particles of mass m. In this case, the momentum p of a particle is simply proportional to its velocity v, and it is a matter of taste to describe the system in the phase space, i.e., by the collection (r,p) of the position and momentum vectors of the pa ...
Chapter 2
... There is a generalization of this theorem that applies to ALL triangles not just right a 2 b 2 c 2 2bc cos A triangles. It is called the Law of Cosines: It has one more term than the Pythagorean Theorem equation and this term adjusts the length of the side opposite A for exactly how “not a ri ...
... There is a generalization of this theorem that applies to ALL triangles not just right a 2 b 2 c 2 2bc cos A triangles. It is called the Law of Cosines: It has one more term than the Pythagorean Theorem equation and this term adjusts the length of the side opposite A for exactly how “not a ri ...
Section 2: Electrostatics
... In some cases it is also possible to use the method of images when the boundary S is a curved surface. However, just as curved mirrors produced distorted images, curved surfaces make the image of a point charge more complicated. The simplest problem of this kind is a point charge in a spherical cavi ...
... In some cases it is also possible to use the method of images when the boundary S is a curved surface. However, just as curved mirrors produced distorted images, curved surfaces make the image of a point charge more complicated. The simplest problem of this kind is a point charge in a spherical cavi ...
(EOC) Practice Test - Answer Key: Geometry
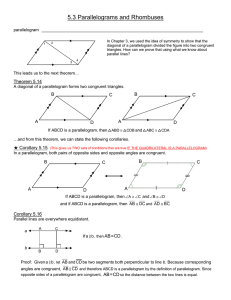
... Conditional: If the table top is rectangular, then its diagonals are congruent. The inverse of the conditional statement is: Inverse: If the diagonals of a table top are congruent, then it is rectangular. Identify by writing yes or no on the first line below if the statement above has correctly iden ...
... Conditional: If the table top is rectangular, then its diagonals are congruent. The inverse of the conditional statement is: Inverse: If the diagonals of a table top are congruent, then it is rectangular. Identify by writing yes or no on the first line below if the statement above has correctly iden ...
Backup of MajorFileds070805jrv.wbk
... associated with pairs of things (at least) while a kinetic energy can be owned by a single entity. The potential energy can be shifted by an additive constant. For SHM, it is often set to zero for a particle positioned at equilibrium. ...
... associated with pairs of things (at least) while a kinetic energy can be owned by a single entity. The potential energy can be shifted by an additive constant. For SHM, it is often set to zero for a particle positioned at equilibrium. ...
Kinetic Energy Estimates for the Accuracy of the Time
... Hartree-Fock approximation is justified up to times of order (λ KN 1/6 )−1 , where K is the kinetic energy (which, for repulsive systems, is bounded by the total energy of the system, uniformly in time) and λ the coupling constant. Hence, our assumption on the initial state is given in terms of energ ...
... Hartree-Fock approximation is justified up to times of order (λ KN 1/6 )−1 , where K is the kinetic energy (which, for repulsive systems, is bounded by the total energy of the system, uniformly in time) and λ the coupling constant. Hence, our assumption on the initial state is given in terms of energ ...
Noether's theorem

Noether's (first) theorem states that every differentiable symmetry of the action of a physical system has a corresponding conservation law. The theorem was proven by German mathematician Emmy Noether in 1915 and published in 1918. The action of a physical system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function (which may or may not be an integral over space of a Lagrangian density function), from which the system's behavior can be determined by the principle of least action.Noether's theorem has become a fundamental tool of modern theoretical physics and the calculus of variations. A generalization of the seminal formulations on constants of motion in Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics (developed in 1788 and 1833, respectively), it does not apply to systems that cannot be modeled with a Lagrangian alone (e.g. systems with a Rayleigh dissipation function). In particular, dissipative systems with continuous symmetries need not have a corresponding conservation law.