MIT OpenCourseWare Please use the following citation format: Electromagnetic Fields and .
... is represented by the MQS laws. Space charge waves on an electron beam or spin waves in a saturated magnetizable material are often described by EQS and MQS laws, respectively, even though frequencies of interest are in the GHz range. The parallel developments of EQS (Chaps. 4–7) and MQS systems (Ch ...
... is represented by the MQS laws. Space charge waves on an electron beam or spin waves in a saturated magnetizable material are often described by EQS and MQS laws, respectively, even though frequencies of interest are in the GHz range. The parallel developments of EQS (Chaps. 4–7) and MQS systems (Ch ...
Angle and Circle Characterizations of Tangential Quadrilaterals
... BF + DE. It is obtained by relabeling the vertices according to A → B → C → D → A in comparison to Theorem 4. The direct part of the first circle characterization was a problem proposed and solved at [7]. We will use Theorem 4 to give a very short proof including the converse as well. Theorem 5. In ...
... BF + DE. It is obtained by relabeling the vertices according to A → B → C → D → A in comparison to Theorem 4. The direct part of the first circle characterization was a problem proposed and solved at [7]. We will use Theorem 4 to give a very short proof including the converse as well. Theorem 5. In ...
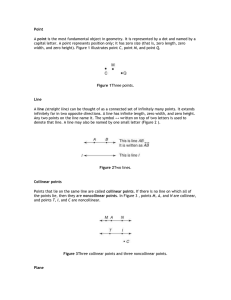
Point - WordPress.com
... extending infinitely far in all directions. A plane has infinite length, infinite width, and zero height (or thickness). It is usually represented in drawings by a four-sided figure. A single capital letter is used to denote a plane. The word plane is written with the letter so as not to be confused ...
... extending infinitely far in all directions. A plane has infinite length, infinite width, and zero height (or thickness). It is usually represented in drawings by a four-sided figure. A single capital letter is used to denote a plane. The word plane is written with the letter so as not to be confused ...
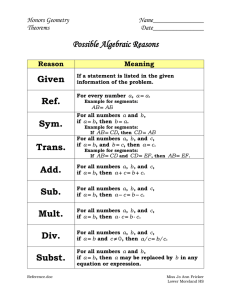
Chapter 4 Flashcards
... When two figures are congruent, there is a correspondence between there is a correspondence their angles and sides such that between their angles and sides corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are such that…? congruent. ...
... When two figures are congruent, there is a correspondence between there is a correspondence their angles and sides such that between their angles and sides corresponding angles are congruent and corresponding sides are such that…? congruent. ...
Meaning - Lower Moreland Township School District
... If the sides of one triangle are congruent to the sides of a second triangle, then the triangles are congruent. If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. If two angles and the included ...
... If the sides of one triangle are congruent to the sides of a second triangle, then the triangles are congruent. If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are congruent to two sides and the included angle of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent. If two angles and the included ...
GEOMETRY, TOPOLOGY AND PHYSICS
... In spite of the extensive use of the concepts of topology, differential geometry and other areas of contemporary mathematics in recent developments in theoretical physics, it is rather difficult to find a self-contained book that is easily accessible to postgraduate students in physics. This book is ...
... In spite of the extensive use of the concepts of topology, differential geometry and other areas of contemporary mathematics in recent developments in theoretical physics, it is rather difficult to find a self-contained book that is easily accessible to postgraduate students in physics. This book is ...
Noether's theorem

Noether's (first) theorem states that every differentiable symmetry of the action of a physical system has a corresponding conservation law. The theorem was proven by German mathematician Emmy Noether in 1915 and published in 1918. The action of a physical system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function (which may or may not be an integral over space of a Lagrangian density function), from which the system's behavior can be determined by the principle of least action.Noether's theorem has become a fundamental tool of modern theoretical physics and the calculus of variations. A generalization of the seminal formulations on constants of motion in Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics (developed in 1788 and 1833, respectively), it does not apply to systems that cannot be modeled with a Lagrangian alone (e.g. systems with a Rayleigh dissipation function). In particular, dissipative systems with continuous symmetries need not have a corresponding conservation law.