Astronomy – The Milky Way Galaxy
... If you look at a galaxy that is 7 billion light years away you are seeing that galaxy as it appeared 7 billion years ago. ...
... If you look at a galaxy that is 7 billion light years away you are seeing that galaxy as it appeared 7 billion years ago. ...
b - GPSM
... Focus on potential arc generator region, by using conjugated FAST and CLUSTER data (at 4000km and 100000km altitude, respectively). CLUSTER ESA mission consisting of 4 identical s/c, each of them equipped with 11 identical instruments. Launched in July – August 2000, after a failed start in ...
... Focus on potential arc generator region, by using conjugated FAST and CLUSTER data (at 4000km and 100000km altitude, respectively). CLUSTER ESA mission consisting of 4 identical s/c, each of them equipped with 11 identical instruments. Launched in July – August 2000, after a failed start in ...
Astro 10 Practice Test 1
... c. They would have become much older than the twin who was left behind. d. They had become much smaller than the twin who stayed on Earth. 17. Which of these statements regarding our position in the Universe is most accurate? a. The Milky Way galaxy is within our solar system. b. Our solar system is ...
... c. They would have become much older than the twin who was left behind. d. They had become much smaller than the twin who stayed on Earth. 17. Which of these statements regarding our position in the Universe is most accurate? a. The Milky Way galaxy is within our solar system. b. Our solar system is ...
The Heliocentric Universe
... become complicated. – Based on naked eye observations. – Small inaccuracies in the past had become large ...
... become complicated. – Based on naked eye observations. – Small inaccuracies in the past had become large ...
Lecture 2 - The University Centre in Svalbard
... For thousands of years humans have gazed at the night sky and wondered about the universe. They did not know that the starts were just as our own Sun, that we are part of a large galaxy and that there are billions of other galaxies. With only our own eyes we would not have any possibility to discove ...
... For thousands of years humans have gazed at the night sky and wondered about the universe. They did not know that the starts were just as our own Sun, that we are part of a large galaxy and that there are billions of other galaxies. With only our own eyes we would not have any possibility to discove ...
Lecture 1 – Astronomy
... For thousands of years humans have gazed at the night sky and wondered about the universe. They did not know that the starts were just as our own Sun, that we are part of a large galaxy and that there are billions of other galaxies. With only our own eyes we would not have any possibility to discove ...
... For thousands of years humans have gazed at the night sky and wondered about the universe. They did not know that the starts were just as our own Sun, that we are part of a large galaxy and that there are billions of other galaxies. With only our own eyes we would not have any possibility to discove ...
Astronomy 110G Review Sheet for Exam #3 The
... That all galaxies seem to be moving away from us does NOT mean that we are in any sort of a “special” place or are particularly repulsive. The particular form of the Hubble expansion law indicates that no place in the universe is particularly “special”. Explain. (Hint: What does “linear” mean?) Cosm ...
... That all galaxies seem to be moving away from us does NOT mean that we are in any sort of a “special” place or are particularly repulsive. The particular form of the Hubble expansion law indicates that no place in the universe is particularly “special”. Explain. (Hint: What does “linear” mean?) Cosm ...
Solutions - faculty.ucmerced.edu
... 2. Emission lines of hydrogen, Hβ (n = 4 → 2 and λrest = 4861Å) are observed in the spectrum of a spiral galaxy at redshift z = 0.9. The galaxy disk is inclined by 45◦ to the line of sight (if the inclination was 0◦ then we’d see the galaxy from a top view, while if it was 90◦ , we’d see it edge-o ...
... 2. Emission lines of hydrogen, Hβ (n = 4 → 2 and λrest = 4861Å) are observed in the spectrum of a spiral galaxy at redshift z = 0.9. The galaxy disk is inclined by 45◦ to the line of sight (if the inclination was 0◦ then we’d see the galaxy from a top view, while if it was 90◦ , we’d see it edge-o ...
planetary nebulae
... Reason - big stars are hotter, so burn their fuel quicker. More mass, means more gravity, needing more radiant energy to balance the star.. Solar Masses ...
... Reason - big stars are hotter, so burn their fuel quicker. More mass, means more gravity, needing more radiant energy to balance the star.. Solar Masses ...
Weighing a galaxy
... Stars and gas orbit around the centres of spiral galaxies in much the same way as the Earth orbits around the Sun. The more mass a galaxy contains, the faster the orbits have to be. If the orbit is not fast enough, the orbital radius will decrease in the same way as artificial satellites orbiting th ...
... Stars and gas orbit around the centres of spiral galaxies in much the same way as the Earth orbits around the Sun. The more mass a galaxy contains, the faster the orbits have to be. If the orbit is not fast enough, the orbital radius will decrease in the same way as artificial satellites orbiting th ...
Hifz schooling scienc summer vacation task 5th
... 6. The Earth is not a star but a _____________________________. 7. A planet is ____________________ object that revolves around ______________________. 8. Each planet moves along a certain path known as its _______________________. 9. Different planets take different times to complete one __________ ...
... 6. The Earth is not a star but a _____________________________. 7. A planet is ____________________ object that revolves around ______________________. 8. Each planet moves along a certain path known as its _______________________. 9. Different planets take different times to complete one __________ ...
SpfFin - Academic Program Pages
... the typical sizes of brighter structures in the cosmic microwave background. the ratio of the average density of matter to that of radiation energy in the universe as a whole. the "lensing" or the bending of light from distant galaxies. 26. We can see only a certain distance out into the universe, a ...
... the typical sizes of brighter structures in the cosmic microwave background. the ratio of the average density of matter to that of radiation energy in the universe as a whole. the "lensing" or the bending of light from distant galaxies. 26. We can see only a certain distance out into the universe, a ...
Useful equations - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... is the distance between star and the edge of the habitable zone which corresponds with temperature T – in whatever system of units – and r [AU ] is that distance expressed in astronomical units (AU), the distance between Earth and Sun. ...
... is the distance between star and the edge of the habitable zone which corresponds with temperature T – in whatever system of units – and r [AU ] is that distance expressed in astronomical units (AU), the distance between Earth and Sun. ...
To Quantum Spin, Earth`s Orbit, Unified Field, And Planet 9`s
... gravity's strength). This gives the illusion of the existence of electric and magnetic fields that are not a product of gravitation. * Remember, this is only one example: the so-called weak force’s “strength isn’t constant” and varies with distances [5]. After absorption by atoms, the depleted remna ...
... gravity's strength). This gives the illusion of the existence of electric and magnetic fields that are not a product of gravitation. * Remember, this is only one example: the so-called weak force’s “strength isn’t constant” and varies with distances [5]. After absorption by atoms, the depleted remna ...
Printable PDF version - Laboratoire Leprince
... NASA's Fermi Mission, Namibia's HESS Telescopes Explore a Blazar Collaboration between ground and space An international team of astrophysicists using telescopes on the ground and in space have uncovered surprising changes in radiation emitted by an active galaxy. The picture that emerges from these ...
... NASA's Fermi Mission, Namibia's HESS Telescopes Explore a Blazar Collaboration between ground and space An international team of astrophysicists using telescopes on the ground and in space have uncovered surprising changes in radiation emitted by an active galaxy. The picture that emerges from these ...
Solutions to HW 1-2
... than light!). Inflation solves this problem by assuming that these different parts of the Universe were in thermal equilibrium some time after the Big Bang and then got separated later during the rapid expansion. Monopole problem: the Big Bang theory predicts the existence of a large amount of magne ...
... than light!). Inflation solves this problem by assuming that these different parts of the Universe were in thermal equilibrium some time after the Big Bang and then got separated later during the rapid expansion. Monopole problem: the Big Bang theory predicts the existence of a large amount of magne ...
NEBULAR HYPOTHESIS OF LAPLACE
... (5) The ‘intruding star’ was moving along such a path in such a way that it was destined to come nearer to the primitive sun. (6) There was a great impact of the tidal force of the intruding star on the surface of the primitive sun. ...
... (5) The ‘intruding star’ was moving along such a path in such a way that it was destined to come nearer to the primitive sun. (6) There was a great impact of the tidal force of the intruding star on the surface of the primitive sun. ...
Video: Form and Space in Architecture
... type of spatial experience. Architects may choose organic, flowing shapes or right-angled geometries to create a particular environment. ...
... type of spatial experience. Architects may choose organic, flowing shapes or right-angled geometries to create a particular environment. ...
CosmologyL2
... blue - an open, low density universe, expansion is slowing down, but not as much because the pull of gravity is not as strong. red - a universe with a large fraction of matter in a form of dark energy, causing an accelerated expansion . ...
... blue - an open, low density universe, expansion is slowing down, but not as much because the pull of gravity is not as strong. red - a universe with a large fraction of matter in a form of dark energy, causing an accelerated expansion . ...
Complete the following review packet!
... 1. What landform is found at point X, where the Mississippi River enters the Gulf of Mexico? 2. Notice the Great Lakes are not part of the Mississippi Drainage Basin, what body of water do they drain into? 3. Since the Ohio, Missouri, and Arkansas Rivers all flow into the Mississippi, they are consi ...
... 1. What landform is found at point X, where the Mississippi River enters the Gulf of Mexico? 2. Notice the Great Lakes are not part of the Mississippi Drainage Basin, what body of water do they drain into? 3. Since the Ohio, Missouri, and Arkansas Rivers all flow into the Mississippi, they are consi ...
ASTR 300 Stars and Stellar Systems Fall 2011
... The brightness is given by the flux you see. From slide 8 of Lecture 7, the flux goes as the luminosity over the distance squared. For the earth d = 1AU, while for Mercury d = 0.39AU. The sun’s luminosity is the same for both, so the flux at Mercury’s distance is 1/0.392 = 1/0.1521 = 6.57 times grea ...
... The brightness is given by the flux you see. From slide 8 of Lecture 7, the flux goes as the luminosity over the distance squared. For the earth d = 1AU, while for Mercury d = 0.39AU. The sun’s luminosity is the same for both, so the flux at Mercury’s distance is 1/0.392 = 1/0.1521 = 6.57 times grea ...
4 Viable Transfer of Microorganisms in the Solar System and
... Once rocks have been ejected from the surface of their home planet, microbial passengers have to cope with an entirely new set of problems affecting their survival, namely exposure to the space environment (reviewed in [29-32]). This environment is characterized by a high vacuum, an intense radiatio ...
... Once rocks have been ejected from the surface of their home planet, microbial passengers have to cope with an entirely new set of problems affecting their survival, namely exposure to the space environment (reviewed in [29-32]). This environment is characterized by a high vacuum, an intense radiatio ...
1.1989 x 10 30 kg
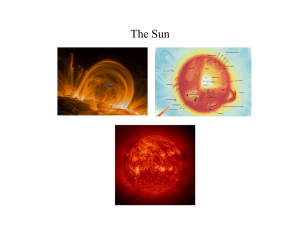
... Solar wind shapes the Earth's magnetosphere and magnetic storms are illustrated here as approaching Earth. These storms, which occur frequently, can disrupt communications and navigational equipment, damage satellites, and even cause blackouts. The white lines represent the solar wind; the purple l ...
... Solar wind shapes the Earth's magnetosphere and magnetic storms are illustrated here as approaching Earth. These storms, which occur frequently, can disrupt communications and navigational equipment, damage satellites, and even cause blackouts. The white lines represent the solar wind; the purple l ...
Outer space
Outer space, or just space, is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles, predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, neutrinos, dust and cosmic rays. The baseline temperature, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvin (K). Plasma with a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a temperature of millions of kelvin in the space between galaxies accounts for most of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in outer space; local concentrations have condensed into stars and galaxies. In most galaxies, observations provide evidence that 90% of the mass is in an unknown form, called dark matter, which interacts with other matter through gravitational but not electromagnetic forces. Data indicates that the majority of the mass-energy in the observable Universe is a poorly understood vacuum energy of space which astronomers label dark energy. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the Universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space.There is no firm boundary where space begins. However the Kármán line, at an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which was passed by the United Nations in 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.Humans began the physical exploration of space during the 20th century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights, followed by manned rocket launches. Earth orbit was first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961 and unmanned spacecraft have since reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Due to the high cost of getting into space, manned spaceflight has been limited to low Earth orbit and the Moon.Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the dual hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity also has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. In addition to these health and environmental issues, the economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is high.