Introduction to the EarthESci 100Dr. Albanese, Tuesdays and
... 13. Although current technology will allow the construction of much larger optical telescopes, astronomers see no advantage in building these larger instruments. 14. The large size of some of the volcanoes on Mars is due to an earlier period of plate tectonics. 15. Comets are not part of our solar s ...
... 13. Although current technology will allow the construction of much larger optical telescopes, astronomers see no advantage in building these larger instruments. 14. The large size of some of the volcanoes on Mars is due to an earlier period of plate tectonics. 15. Comets are not part of our solar s ...
Transcript - Cheap Astronomy
... became heresy – invoking a standard exit clause to the first commandment, meaning it was punishable by death – and often a fairly grisly death. Presumably to avoid any such complications, Copernicus arranged for the posthumous publication of his book On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres in 15 ...
... became heresy – invoking a standard exit clause to the first commandment, meaning it was punishable by death – and often a fairly grisly death. Presumably to avoid any such complications, Copernicus arranged for the posthumous publication of his book On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres in 15 ...
Cornell Notes Page
... - Elliptical Galaxies are like an sphere_ or _football_ when seen from the side ...
... - Elliptical Galaxies are like an sphere_ or _football_ when seen from the side ...
PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Syllabus: Phys 200 (3 cr
... Our Living Earth Structure of the Earth’s atmosphere (greenhouse effect, ozone layers). Earth’s magnetosphere. Structure of the Earth’s interior. ...
... Our Living Earth Structure of the Earth’s atmosphere (greenhouse effect, ozone layers). Earth’s magnetosphere. Structure of the Earth’s interior. ...
Sir Isaac Newton
... easy enough to map the surface of the Earth, because the Earth has landmarks: rivers, mountains, cities--places of known location, to which other places can be compared. The sky, however, has no landmarks, just the stars themselves. Hipparchus decided to invent "landmarks" of his own. He picked one ...
... easy enough to map the surface of the Earth, because the Earth has landmarks: rivers, mountains, cities--places of known location, to which other places can be compared. The sky, however, has no landmarks, just the stars themselves. Hipparchus decided to invent "landmarks" of his own. He picked one ...
ASTR 1010 – Spring 2016 – Study Notes Dr. Magnani
... word planet in classical Greek means “wanderer” because the planets change their position with respect to the stars continuously. Recall that the stars rise in the east, reach their highest point on ...
... word planet in classical Greek means “wanderer” because the planets change their position with respect to the stars continuously. Recall that the stars rise in the east, reach their highest point on ...
chapter3 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... • Model was only a little more accurate than Ptolemaic model in predicting planetary positions, because it still used perfect circles & stars on a sphere, only a little bigger than Pythagoras claimed. ...
... • Model was only a little more accurate than Ptolemaic model in predicting planetary positions, because it still used perfect circles & stars on a sphere, only a little bigger than Pythagoras claimed. ...
The History of Meteorology
... Birth of Cosmological Models • Greeks – ~A.D. 125 Ptolemy – first astronomy textbook • earth is spherical and at center of cosmos & doesn’t move • predicted planetary motion in a GEOCENTRIC cosmos with accuracy • accepted for 1,400 years ...
... Birth of Cosmological Models • Greeks – ~A.D. 125 Ptolemy – first astronomy textbook • earth is spherical and at center of cosmos & doesn’t move • predicted planetary motion in a GEOCENTRIC cosmos with accuracy • accepted for 1,400 years ...
History of Astronomy
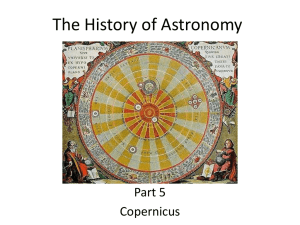
... Copernicus • First Astronomer to theorize that Earth was revolving around the sun = heliocentric • Was not accepted until after his death • First book published on the day of his Death ...
... Copernicus • First Astronomer to theorize that Earth was revolving around the sun = heliocentric • Was not accepted until after his death • First book published on the day of his Death ...
chapter4 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... Sun nor the Moon crashing into the Earth Paths A, B, and C do not have enough horizontal velocity to escape Earth’s surface whereas Paths D, E, and F do. Path E is where the horizontal velocity is exactly what is needed so its orbit matches the circular curve of the Earth ...
... Sun nor the Moon crashing into the Earth Paths A, B, and C do not have enough horizontal velocity to escape Earth’s surface whereas Paths D, E, and F do. Path E is where the horizontal velocity is exactly what is needed so its orbit matches the circular curve of the Earth ...
The History of Astronomy
... Uranus and Neptune). • He even got the relative distances from the sun correct (see chart on page 49). • Moon orbits Earth To avoid religious persecution he published his work “de revolutionibus orbium coelestium” posthumusly. ...
... Uranus and Neptune). • He even got the relative distances from the sun correct (see chart on page 49). • Moon orbits Earth To avoid religious persecution he published his work “de revolutionibus orbium coelestium” posthumusly. ...
Earth and space - Tollgate Teaching Alliance
... Pupils should be taught to: describe the movement of the Earth, and other planets, relative to the Sun in the solar system describe the movement of the Moon relative to the Earth describe the Sun, Earth and Moon as approximately spherical bodies use the idea of the Earth’s rotation to explai ...
... Pupils should be taught to: describe the movement of the Earth, and other planets, relative to the Sun in the solar system describe the movement of the Moon relative to the Earth describe the Sun, Earth and Moon as approximately spherical bodies use the idea of the Earth’s rotation to explai ...
Lecture 4 - Physics and Astronomy
... A planet undergoes retrograde motion as seen from Earth when the Earth and the ...
... A planet undergoes retrograde motion as seen from Earth when the Earth and the ...
Ancient to Modern Astronomy
... The Greeks believed that the planetary orbits were circles and that everything went around the earth, including the sun and planets, and the stars. The stars resided on a crystal sphere through which light shown. Unfortunately for the Greeks, the solar system was not that simple. They had trouble re ...
... The Greeks believed that the planetary orbits were circles and that everything went around the earth, including the sun and planets, and the stars. The stars resided on a crystal sphere through which light shown. Unfortunately for the Greeks, the solar system was not that simple. They had trouble re ...
Early Views of the Solar System • General Greek Principles of
... o What he got wrong Thought earth was a flat, rotating disk. Pythagoras – 530 BC o First to suggest that Earth is a sphere. o One of the earliest advocates of a geocentric solar system Earth at center, surrounded by system of concentric, rotating, transparent spheres. Bodies attached to sphere ...
... o What he got wrong Thought earth was a flat, rotating disk. Pythagoras – 530 BC o First to suggest that Earth is a sphere. o One of the earliest advocates of a geocentric solar system Earth at center, surrounded by system of concentric, rotating, transparent spheres. Bodies attached to sphere ...
Study Guide for Earth/ Space Science Test 1. Rotation – The Earth
... from the sun and the direct angle of sunlight hitting the area. Also caused by revolution. 6. Lunar – Moon – natural satellite – moon cycle is about 28 days long. Moon means month. Be able to identify phases of moon 7. Solar – sun – only average size star in our solar system that gives us light and ...
... from the sun and the direct angle of sunlight hitting the area. Also caused by revolution. 6. Lunar – Moon – natural satellite – moon cycle is about 28 days long. Moon means month. Be able to identify phases of moon 7. Solar – sun – only average size star in our solar system that gives us light and ...
Geocentric Model of the Universe
... • Sometimes, however, the planets appear to Planets usually move west to east, but sometimes east to west (retrograde), relative to stars. ...
... • Sometimes, however, the planets appear to Planets usually move west to east, but sometimes east to west (retrograde), relative to stars. ...
Intro L4 IQ
... “annual” changes that happen once per year. The seasonal (annual) changing of constellations depends upon revolution. Diurnal changes, for example, the transit of stars during the course of the night (or the sun during the day) are caused by the Earth’s rotation. Diurnal changes are far more obvious ...
... “annual” changes that happen once per year. The seasonal (annual) changing of constellations depends upon revolution. Diurnal changes, for example, the transit of stars during the course of the night (or the sun during the day) are caused by the Earth’s rotation. Diurnal changes are far more obvious ...
2b Astronomer space units
... the mysteries of the universe. Sun dials help tell time each day ...
... the mysteries of the universe. Sun dials help tell time each day ...
BABYLON and SUMERIA 3000BC
... Aether, which is the divine substance that makes up the heavenly spheres and heavenly bodies (stars and planets). Each of the four earthly elements has its natural place. All that is earthly tends toward the center of the universe, i.e., the center of the Earth. Water tends toward a sphere surroundi ...
... Aether, which is the divine substance that makes up the heavenly spheres and heavenly bodies (stars and planets). Each of the four earthly elements has its natural place. All that is earthly tends toward the center of the universe, i.e., the center of the Earth. Water tends toward a sphere surroundi ...
Earth ,Moon,and Sun - Laconia School District
... Earth travels on its orbit or its path that leads it around the sun. Earth’s orbit is not quite a circle; it’s more of an oval shape. The ancient Egyptians astronomers counted the number of days between each first appearance of the star Sirius. In this way, they found that there are about 365 days i ...
... Earth travels on its orbit or its path that leads it around the sun. Earth’s orbit is not quite a circle; it’s more of an oval shape. The ancient Egyptians astronomers counted the number of days between each first appearance of the star Sirius. In this way, they found that there are about 365 days i ...
2. Kepler a. They observed the sun, moon, and stars move across
... In the geocentric model of the solar system, _EARTH__ is in the center and the sun and planets orbit around it. Which choice is a reason why people believed in the geocentric model of the solar system? ...
... In the geocentric model of the solar system, _EARTH__ is in the center and the sun and planets orbit around it. Which choice is a reason why people believed in the geocentric model of the solar system? ...
Sept2 - University of Arizona
... by the Congregation of the Index "until corrected." It stayed on this list of prohibited books and teachings until 1822. Martin Luther (1483-1546): [Copernicus] “is a fool who wishes to reverse the entire scheme of astronomy; but sacred scripture tells us that Joshua commanded the Earth to stand sti ...
... by the Congregation of the Index "until corrected." It stayed on this list of prohibited books and teachings until 1822. Martin Luther (1483-1546): [Copernicus] “is a fool who wishes to reverse the entire scheme of astronomy; but sacred scripture tells us that Joshua commanded the Earth to stand sti ...
Geocentric model

In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, or the Ptolemaic system) is a description of the cosmos where Earth is at the orbital center of all celestial bodies. This model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece including the noteworthy systems of Aristotle (see Aristotelian physics) and Ptolemy. As such, they believed that the Sun, Moon, stars, and naked eye planets circled Earth.Two commonly made observations supported the idea that Earth was the center of the Universe. The stars, the sun, and planets appear to revolve around Earth each day, making Earth the center of that system. The stars were thought to be on a celestial sphere, with the earth at its center, that rotated each day, using a line through the north and south pole as an axis. The stars closest to the equator appeared to rise and fall the greatest distance, but each star circled back to its rising point each day. The second observation supporting the geocentric model was that the Earth does not seem to move from the perspective of an Earth-bound observer, and that it is solid, stable, and unmoving.Ancient Roman and medieval philosophers usually combined the geocentric model with a spherical Earth. It is not the same as the older flat Earth model implied in some mythology, as was the case with the biblical and postbiblical Latin cosmology. The ancient Jewish Babylonian uranography pictured a flat Earth with a dome-shaped rigid canopy named firmament placed over it. (רקיע- rāqîa').However, the ancient Greeks believed that the motions of the planets were circular and not elliptical, a view that was not challenged in Western culture until the 17th century through the synthesis of theories by Copernicus and Kepler.The astronomical predictions of Ptolemy's geocentric model were used to prepare astrological and astronomical charts for over 1500 years. The geocentric model held sway into the early modern age, but from the late 16th century onward was gradually superseded by the heliocentric model of Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler. There was much resistance to the transition between these two theories. Christian theologians were reluctant to reject a theory that agreed with Bible passages (e.g. ""Sun, stand you still upon Gibeon"", Joshua 10:12 – King James 2000 Bible). Others felt a new, unknown theory could not subvert an accepted consensus for geocentrism.